More languages
More actions
| Roman Republic Rēs pūblica Rōmāna | |
|---|---|
| 509 BCE–27 BCE | |
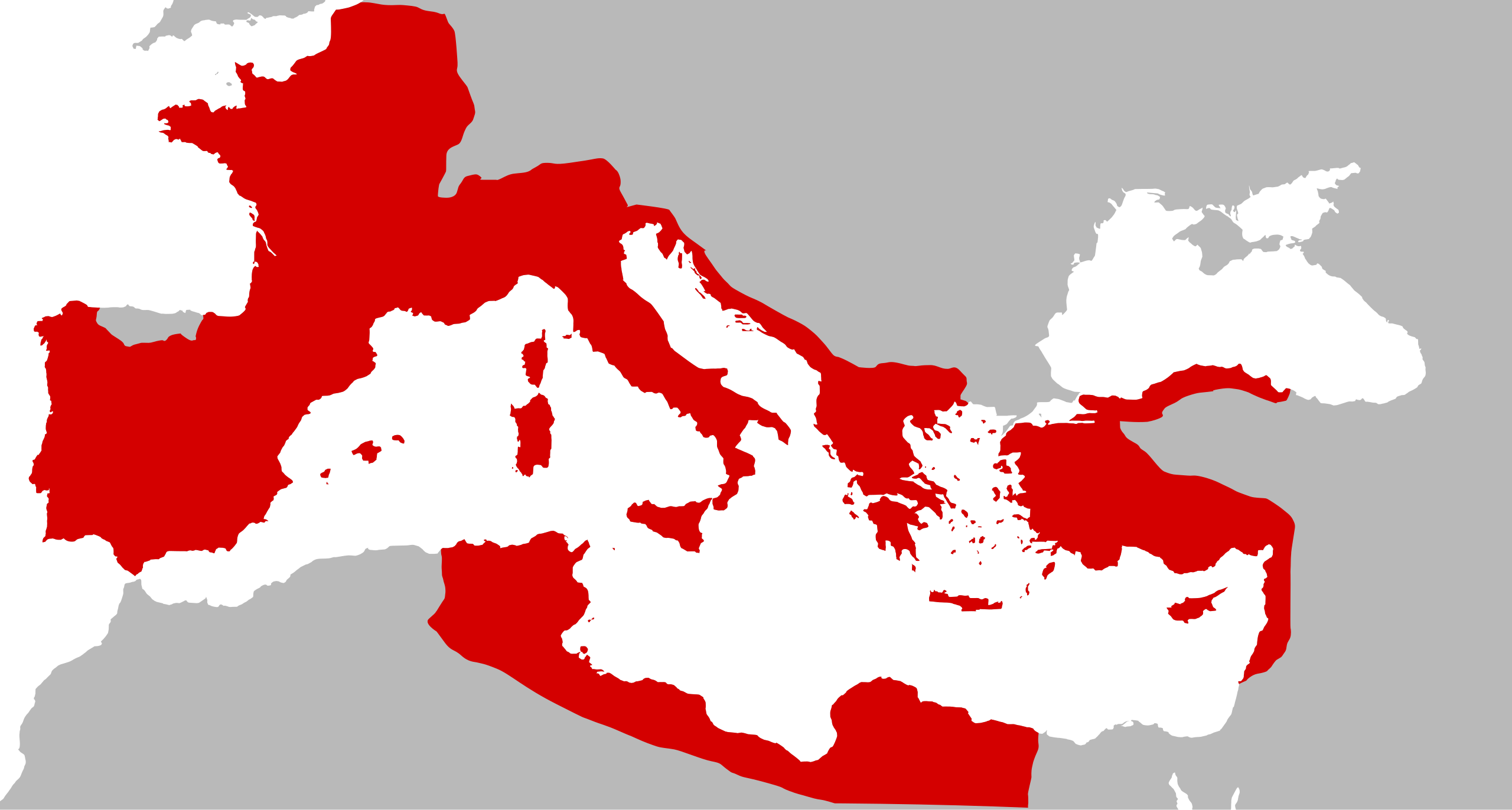 The Roman Republic in 44 BCE | |
| Capital | Rome |
| Official languages | Latin |
| Dominant mode of production | Slavery |
| Government | Aristocratic plutocratic republic |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,950,000 km²(50 BCE) |
The Roman Republic was an ancient country that originated in the Italian peninsula and expanded to include parts of Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia.
History
Foundation
The last king of Rome was overthrown around 509 BCE and a republic was proclaimed.[1]
Expansion
Rome conquered the rest of the Italian peninsula during the third and fourth centuries BCE. After defeating Carthage in the First Punic War, it took control of Sicily, Sardinia, and Corsica in 261 BCE. Carthaginian general Hannibal invaded Italy in the Second Punic War (218–202 BCE) but was eventually defeated, allowing Rome to take control of the Iberian peninsula. Rome conquered Carthage in 146 BCE, beginning its colonization of North Africa. After helping Greek city-states fight against Macedonia, Rome subjugated Greece and made it a Roman province.[1]
Decline and transition to empire
Tiberius Gracchus was elected as a tribune in 133 BCE and planned to revive an old law limiting land ownership to 125 hectares. He would compensate landowners for their land and redistribute it to the poor. He convened the Tribal Assembly of the People to pass the law, but Marcus Octavius, another tribune, vetoed it. Gracchus took the issue to the public forum, which removed Octavius from office and passed the agrarian reform law. After he ran for reelection, the Senate organized his assassination.[2]
In 74 BCE, Spartacus began a slave revolt. It grew to a strength of over 100,000 before being defeated in 71 BCE.[3]
Social classes
One third of the population were slaves who mainly worked on plantations (latifundia) and in mines. Rome enslaved many people through conquests and also used slavery as a punishment for capital crimes or being unable to pay back debt. Above the slaves were a proletarian class who lived in urban slums. There were also landowning middle peasants and a small middle class of merchants and minor officials.
The slave-owning ruling class contained less than 2,000 families. It was divided into a lower equestrian class that included bankers, state contractors, tax collectors, and large landowners. They were similar to knights under feudalism, although by the end of the republic most of them did not actually serve in the military. Above the equestrians were the patricians, who had a similar level of wealth to the equestrians but less political influence.[4]
Politics
Two consuls held executive power and served one-year terms. They were able to veto each other's decisions and presided over the Senate. Only patricians could be members of the Senate.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Michael Parenti (2003). The Assassination of Julius Caesar: A People's History of Ancient Rome: 'A Republic for the Few' (pp. 45–47). [PDF] The New Press. ISBN 9781565847972 [LG]
- ↑ Michael Parenti (2003). The Assassination of Julius Caesar: A People's History of Ancient Rome: '“Demagogues” and Death Squads' (pp. 60–64). [PDF] The New Press. ISBN 9781565847972 [LG]
- ↑ "The War of Spartacus" (2022-10-13). Politsturm. Archived from the original on 2022-10-13. Retrieved 2022-11-05.
- ↑ Michael Parenti (2003). The Assassination of Julius Caesar: A People's History of Ancient Rome: 'Slaves, Proletarians, and Masters' (pp. 27–31). [PDF] The New Press. ISBN 9781565847972 [LG]
