Federative Republic of Brazil: Difference between revisions
(Updated Infobox country template parameter) |
m (History.) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
=== Republic era (1889–present) === | === Republic era (1889–present) === | ||
In 1961, [[Centrism|centrist]] president [[Jânio Quadro]] resigned after seven months in office, leading to his [[Anti-imperialism|anti-imperialist]] vice president, [[João Goulart]], becoming president. Goulart supported agrarian reform and universal suffrage and was supported by Catholic bishops and members of student unions. The United States turned on him after he refused to ban leftists from his cabinet and the [[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]] began funding his opponents in October 1962. In March 1964, he was overthrown in a military coup.<ref>{{Citation|author=Matias Spektor|year=2018|title=The United States and the 1964 Brazilian Military Coup|page=1–3|pdf=https://edisciplinas.usp.br/pluginfile.php/4307854/mod_resource/content/1/Spektor%20US%20Military%20Coup%20in%20Brazil.pdf|publisher=Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Latin American History}}</ref> | In 1961, [[Centrism|centrist]] president [[Jânio Quadro|Jânio Quadros]] resigned after seven months in office, leading to his [[Anti-imperialism|anti-imperialist]] vice president, [[João Goulart]], becoming president. Goulart supported agrarian reform and universal suffrage and was supported by Catholic bishops and members of student [[Trade union|unions]]. The United States turned on him after he refused to ban leftists from his cabinet and the [[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]] began funding his opponents in October 1962. In March 1964, he was overthrown in a military coup.<ref>{{Citation|author=Matias Spektor|year=2018|title=The United States and the 1964 Brazilian Military Coup|page=1–3|pdf=https://edisciplinas.usp.br/pluginfile.php/4307854/mod_resource/content/1/Spektor%20US%20Military%20Coup%20in%20Brazil.pdf|publisher=Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Latin American History}}</ref> | ||
In 1968, Institutional Act No. 5 was passed under military leader [[Artur da Costa e Silva]], removing all limits on the military dictatorship's power. Under the dictatorship, 50,000 people were arrested, 7,000 were exiled, and over 400 were killed. After Costa e Silva's death, [[Emílio Garrastazu Médici]] took power and ruled until 1974. The act was repealed in 1978.<ref>{{News citation|author=Edmilson Costa|newspaper=[[Liberation School]]|title=Remembering the Years of Lead under Brazil’s military rule: AI-5 never again!|date=2019-12-23|url=https://www.liberationschool.org/remembering-the-years-of-lead-under-brazils-military-rule-ai-5-never-again/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20210515161458/https://www.liberationschool.org/remembering-the-years-of-lead-under-brazils-military-rule-ai-5-never-again/|archive-date=2021-05-15|retrieved=2022-05-14}}</ref> | |||
== Economy == | == Economy == | ||
Revision as of 20:13, 14 May 2022
| Federative Republic of Brazil República Federativa do Brasil | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital | Brasília |
| Largest city | São Paulo |
| Government | Federal presidential bourgeois state |
• President | Jair Bolsonaro |
• President of the Chamber of Deputies | Arthur Lira |
• President of the Federal Senate | Rodrigo Pacheco |
• President of the Supreme Federal Court | Luiz Fux |
| History | |
• Proclamation of the Empire of Brazil | 1822 September 7th |
• Proclamation of the Republic of Brazil | 1889 November 15th |
• US-backed right-wing military dictatorship | 1964 April 1st |
• Redemocratization | 1985 March 15th |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 211,755,692[1] |
| Labour | |
• Labour force | 86.621 million[2] |
• Labour force participation | 56.8%[4] |
• Occupation | agriculture: 9.4% industry: 32.1% services: 58.5%[2] |
• Unemployment rate | 14.7%[3] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2019 estimate |
• Total | US$1.84 trillion[5] |
• Per capita | US$8,717.18[6] |
| Exports | 2019 estimate |
• Value | US$263 billion[7] |
• Commodities | soybeans, crude petroleum, iron, corn, wood pulp products[2] |
• Partners | China (28%), United States (13%)[2] |
| Imports | 2019 estimate |
• Value | US$269 billion[8] |
• Commodities | refined petroleum, vehicle parts, crude petroleum, integrated circuits, pesticides[2] |
• Partners | China (21%), United States (18%), Germany (6%) |
| External debt | US$684.6 billion (20th) |
| Gini (2018) | 53.9% (9th) |
| HDI (2019) | 0.765 (84th) |
| Currency | Brazilian real (BRL) |
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is a country in Latin America. It is the most populous country in its continent.
History
Pre-colonization (~60,000 BCE – 1500)
Colonization period (1500–1822)
Empire era (1822–1889)
Republic era (1889–present)
In 1961, centrist president Jânio Quadros resigned after seven months in office, leading to his anti-imperialist vice president, João Goulart, becoming president. Goulart supported agrarian reform and universal suffrage and was supported by Catholic bishops and members of student unions. The United States turned on him after he refused to ban leftists from his cabinet and the CIA began funding his opponents in October 1962. In March 1964, he was overthrown in a military coup.[9]
In 1968, Institutional Act No. 5 was passed under military leader Artur da Costa e Silva, removing all limits on the military dictatorship's power. Under the dictatorship, 50,000 people were arrested, 7,000 were exiled, and over 400 were killed. After Costa e Silva's death, Emílio Garrastazu Médici took power and ruled until 1974. The act was repealed in 1978.[10]
Economy
Brazil exports $28.6B of soybeans (13.36%), $26.5B of iron ore (12.38%), $19.8B of crude petroleum (9.25%), $8.95B of raw sugar (4.18%), $6.69B of bovine meat (3.12%) and $123.5B of other products, totaling $214B in exports. These exports flow mostly towards China ($67.9B), United States ($21.9B), Argentina ($8.57B), Netherlands ($6.7B), and Canada ($4.39B).[11]
Politics
Class struggle in Brazil
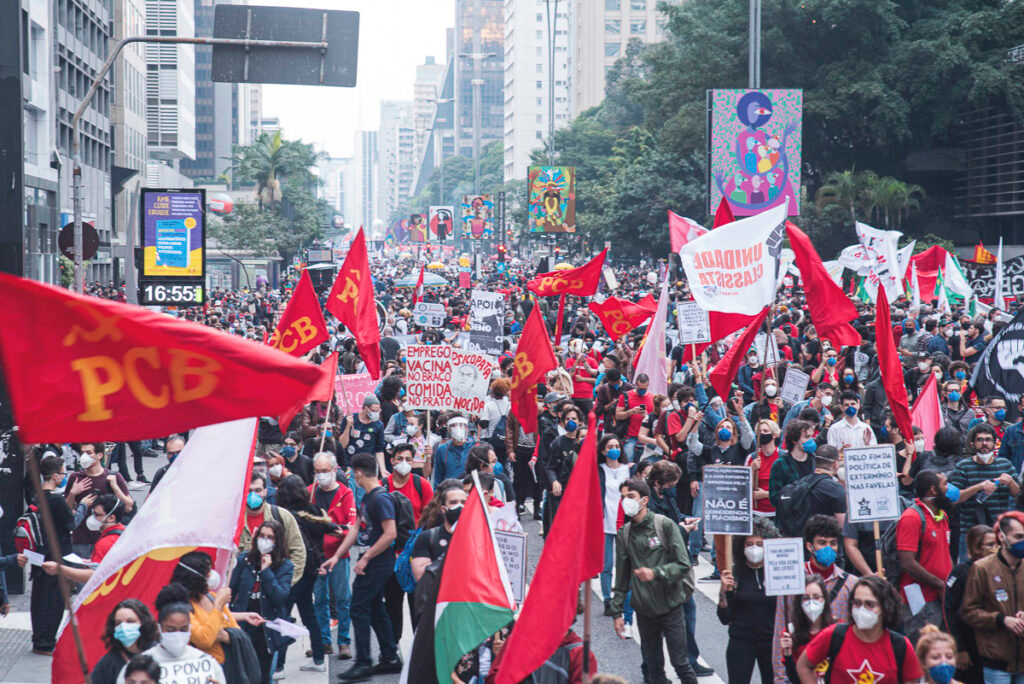

In June 19th, 2021, protesters in over 400 cities in protest of the fascist Jair Bolsonaro government. Militants and activists gathered safely, respecting social isolation guidelines related to the COVID-19 pandemic.[12]
Infrastructure
Demographics
Culture
References
- ↑ Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (2020). Estimates published in official government documents.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 CIA World Factbook (2020). Brazil – The world factbook (economy)
- ↑ Trading economics (2021). Brazil unemployment rate
- ↑ Trading economics (2021). Brazil labor force participation rate
- ↑ World Bank (2019). GDP (current US$) - Brazil
- ↑ World Bank (2019). GDP per capita (current US$) - Brazil
- ↑ World Bank (2019). Exports of goods and services (current US$) - Brazil
- ↑ World Bank (2019). Imports of goods and services (current US$) - Brazil
- ↑ Matias Spektor (2018). The United States and the 1964 Brazilian Military Coup (pp. 1–3). [PDF] Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Latin American History.
- ↑ Edmilson Costa (2019-12-23). "Remembering the Years of Lead under Brazil’s military rule: AI-5 never again!" Liberation School. Archived from the original on 2021-05-15. Retrieved 2022-05-14.
- ↑ "Brazil (BRA) exports, imports, and trade partners" (2020). Observatory of Economic Complexity (OEC).
- ↑ Beatriz Drague Ramos (2021-06-21). For vaccines for all and against Bolsonaro, demonstrators take to the streets this Saturday [Portuguese: Por vacinas para todos e contra Bolsonaro, manifestantes vão às ruas neste sábado]. Ponte Jornalismo.

