Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic (1921–1991): Difference between revisions
From ProleWiki, the proletarian encyclopedia
More languages
More actions
(Created) Tag: Visual edit |
(Coup) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
In 1951, [[Joseph Stalin|Stalin]] purged several leaders of the [[Communist Party of Georgia]] for [[corruption]] and connections to [[United States imperialism|U.S. imperialism]]. [[Lavrentiy Beria|Beria]]'s supporters, who made up more than half of the Central Committee, lost their positions. | In 1951, [[Joseph Stalin|Stalin]] purged several leaders of the [[Communist Party of Georgia]] for [[corruption]] and connections to [[United States imperialism|U.S. imperialism]]. [[Lavrentiy Beria|Beria]]'s supporters, who made up more than half of the Central Committee, lost their positions. | ||
In 1953, shortly after Stalin's death, Beria organized a coup in Georgia to restore his supporters to power. [[Vladimir Dekanozov]] replaced [[Rukhadze]] as Georgia's [[MGB|Minister of State Security]].<ref name=":02233232">{{Citation|author=Ludo Martens|year=1996|title=Another View of Stalin|chapter=From Stalin to Khrushchev|isbn=9782872620814|publisher=Editions EPO|pdf=https://gateway.ipfs.io/ipfs/bafykbzaceab64vxtxpqt2cdl4zsrsftmedqidn4foq74gr25qkd35z5nwogdi?filename=Ludo%20Martens%20-%20Another%20View%20of%20Stalin-Editions%20EPO%20%281996%29.pdf|page=261–262}}</ref> | In April 1953, shortly after Stalin's death, Beria organized a coup in Georgia to restore his supporters to power. [[Vladimir Dekanozov]] replaced [[Rukhadze]] as Georgia's [[MGB|Minister of State Security]]. | ||
Generals [[Aleksei Antonov|Antonov]] and [[Sergei Yefimov]] organized another coup on 14 July 1953. They overthrew Beria's supporters installed [[Vasil Mzhavanadze]] as the leader of the CPG.<ref name=":02233232">{{Citation|author=Ludo Martens|year=1996|title=Another View of Stalin|chapter=From Stalin to Khrushchev|isbn=9782872620814|publisher=Editions EPO|pdf=https://gateway.ipfs.io/ipfs/bafykbzaceab64vxtxpqt2cdl4zsrsftmedqidn4foq74gr25qkd35z5nwogdi?filename=Ludo%20Martens%20-%20Another%20View%20of%20Stalin-Editions%20EPO%20%281996%29.pdf|page=261–262}}</ref> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
[[Category:Republics of the Soviet Union]] | [[Category:Republics of the Soviet Union]] | ||
Revision as of 18:13, 9 April 2023
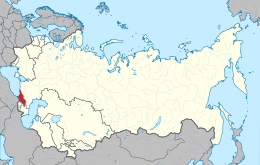
| Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic საქართველოს საბჭოთა სოციალისტური რესპუბლიკა | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Tbilisi |
| Dominant mode of production | Socialism |
| Government | Soviet republic |
The Georgian Soviet Socialist Republic was a republic of the Soviet Union located in the southern Caucasus.
History
In 1951, Stalin purged several leaders of the Communist Party of Georgia for corruption and connections to U.S. imperialism. Beria's supporters, who made up more than half of the Central Committee, lost their positions.
In April 1953, shortly after Stalin's death, Beria organized a coup in Georgia to restore his supporters to power. Vladimir Dekanozov replaced Rukhadze as Georgia's Minister of State Security.
Generals Antonov and Sergei Yefimov organized another coup on 14 July 1953. They overthrew Beria's supporters installed Vasil Mzhavanadze as the leader of the CPG.[1]
References
- ↑ Ludo Martens (1996). Another View of Stalin: 'From Stalin to Khrushchev' (pp. 261–262). [PDF] Editions EPO. ISBN 9782872620814


