More languages
More actions
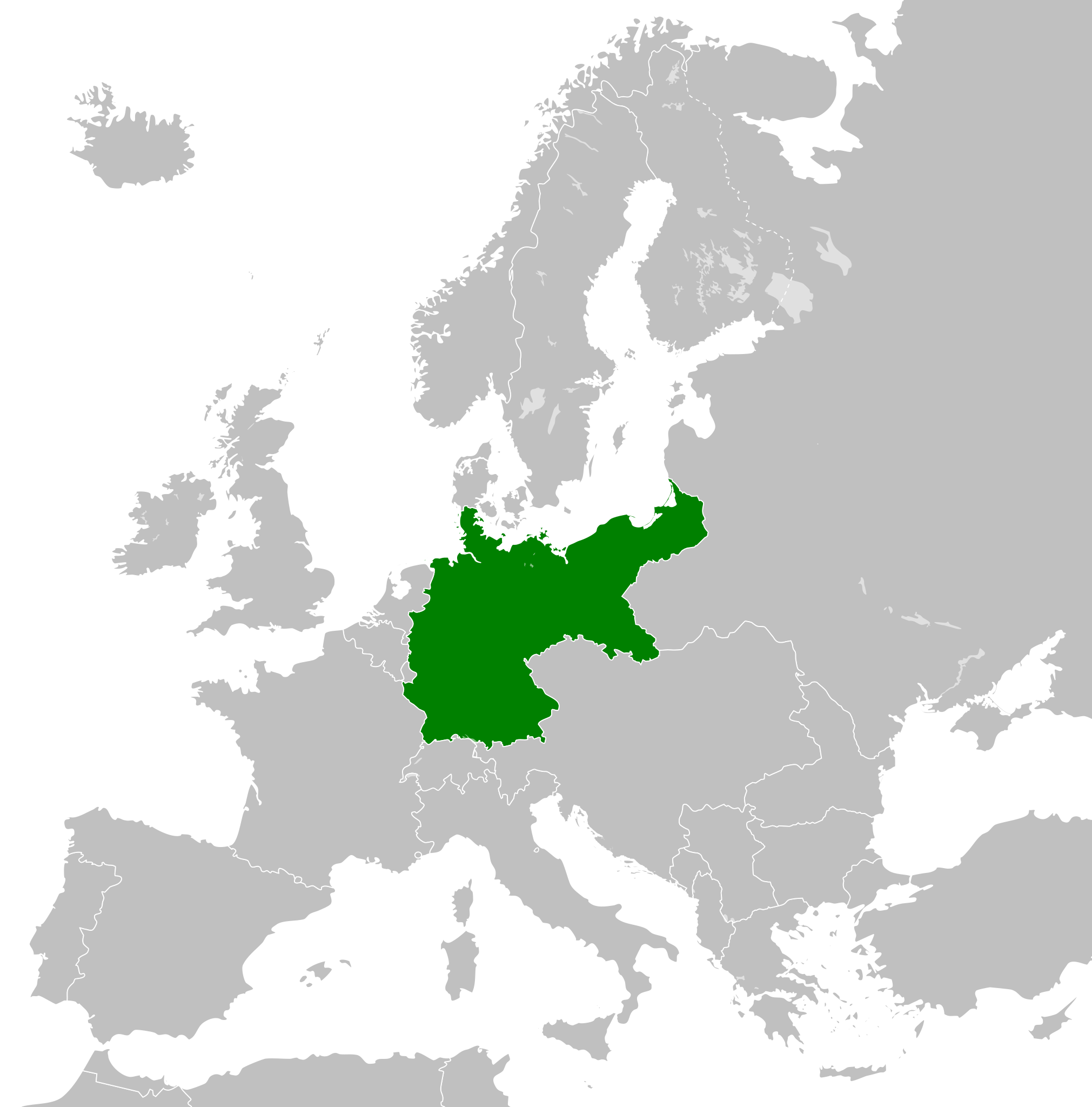
| German Empire Deutsches Reich | |
|---|---|
| 1871-1918 | |
|
Flag | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Berlin |
| Official languages | German |
| Dominant mode of production | Capitalism |
| Government | Federal parliamentary semi-constitutional monarchy[1][2][3][4]
|
| Emperor | |
• 1871–1888 | Wilhelm I |
• 1888 | Friedrich III |
• 1888–1918 | Wilhelm II |
| Chancellor | |
• 1871–1890 | Otto von Bismarck |
• 1890–1894 | Leo von Caprivi |
• 1894–1900 | Chlodwig zu Hohenlohe-Schillingsfürst |
• 1900–1909 | Bernhard von Bülow |
• 1909–1917 | Theobald von Bethmann-Hollweg |
• 1917 | Georg Michaelis |
• 1917–1918 | Georg von Hertling |
• 1918 | Max von Baden |
| Area | |
• Total | 540,858 km² |
| Population | |
• 1910 census | 64,925,993 |
The German Empire (German: Deutsches Kaiserreich), also referred to as Imperial Germany, the Second Reich, as well as simply Germany was a country in Central Europe that existed from the Franco-Prussian War of 1871 until the end of the First World War. In November 1918, the German monarchy was overthrown and the Weimar Republic was established.
Colonialism
The German Empire colonized parts of Africa and Oceania. It committed genocide against the Herero and Nama peoples in what is now Namibia. Germany lost control of its colonies after the First World War.[6]
References
- ↑
- ↑ Nipperdey, Thomas, "Deutsche Geschichte 1866-1918: Zweiter Band: Machtstaat vor der Demokratie" (1995), p. 98–108.
- ↑ Röhl, John C. G. "Kaiser Wilhelm II: A Concise Life" (2014), p. 172–173.
- ↑
- ↑ Wheeler-Bennett, John (1967). The Nemesis of Power The German Army in Politics 1918–1945. London: Macmillan. pp. 13–14. Template:ISBN.
- ↑ "Risen from the Ruins: The Economic History of Socialism in the German Democratic Republic" (2021-04-20). Tricontinental. Archived from the original on 2022-04-26. Retrieved 2022-08-12.

