More languages
More actions
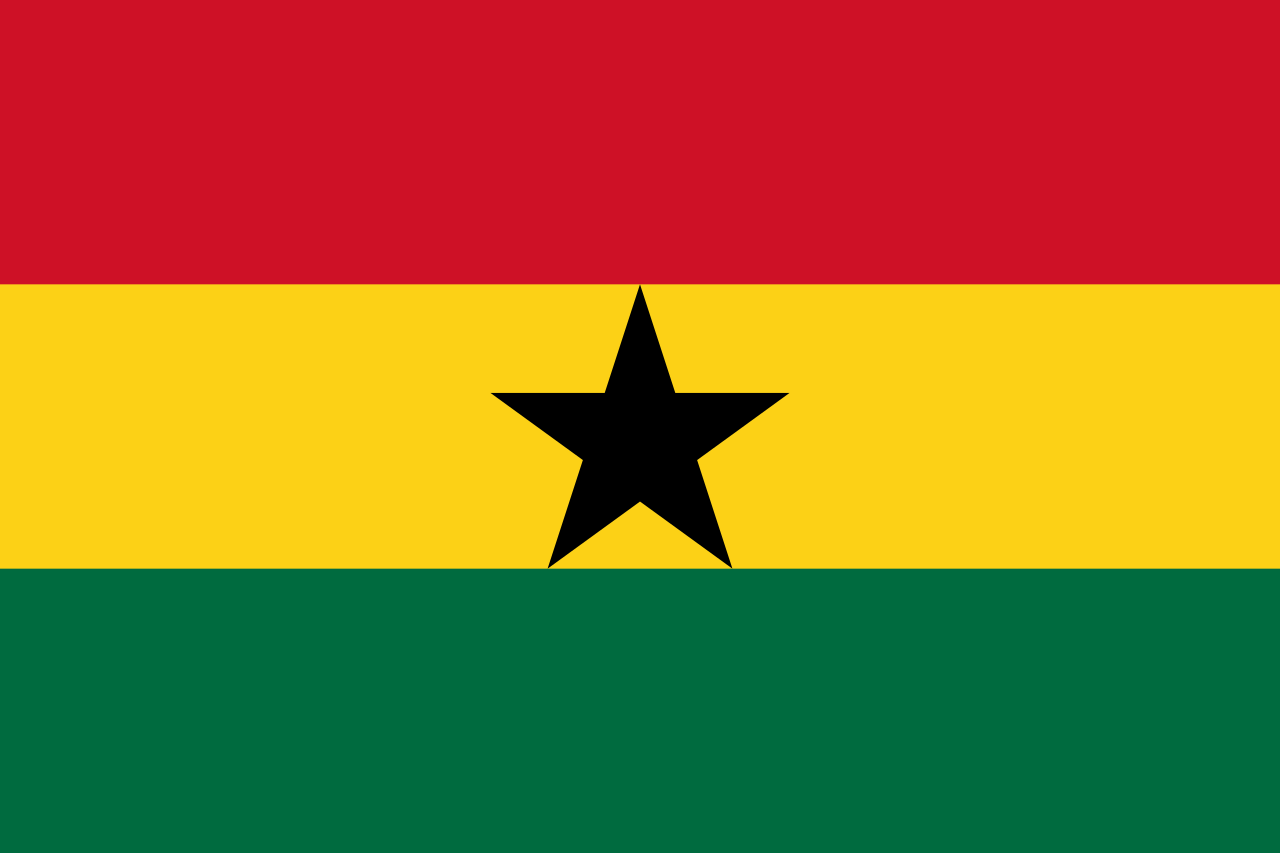
| Republic of Ghana | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1960–1966 | |||||||||
Motto: "Freedom and Justice" | |||||||||
Anthem: "God Bless Our Homeland Ghana" | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Capital and largest city | Accra | ||||||||
| Official languages | English | ||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Ghanaian | ||||||||
| Dominant mode of production | Socialism | ||||||||
| Government | Unitary one-party presidential republic | ||||||||
• President | Kwame Nkrumah | ||||||||
• Speaker of Parliament | Kofi Asante Ofori-Atta | ||||||||
| Legislature | Parliament of Ghana | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• Established | 1960 | ||||||||
• Dissolution | 1966 | ||||||||
| Currency | 1960-1965: Ghanaian pound 1965-1966: Ghanaian Cedi | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The First Republic of Ghana, officially known at the time of its existence as the Republic of Ghana, was a socialist state in West Africa from 1960 to 1966 established via popular referendum after the masses voted to end the Dominion of Ghana by transforming Ghana into a Presidential Republic. In the aftermath of the referendum, former Prime Minister Kwame Nkrumah would become the first President of Ghana. The Republic of Ghana was the first African nation south of the Sahara to obtain independence, and due to the successes of Nkrumah's socialist policies while in power, Ghana became a model-state for African independence movements and a hub for Pan-African philosophy.
History
Government
Houses of Chiefs
For each region of Ghana, leaders of of the country's traditional communities are automatically appointed to a House of Chiefs. Houses of Chiefs are divided into a plethora of Traditional Councils consisting of specific tribes, and act as advisory boards to the government on matters effecting them.[1]
Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of Ghana was the highest court in the republic, and had original jurisdiction on all matters in which the enactment of policy was considered in excess of the powers granted by the National Assembly of Constitution of Ghana. Judges of the court were appointed by the President and were required to retire upon reaching the age of 65 years.[1]
National Assembly
The National Assembly was the unicameral legislature of the of Ghana and was elected following the its dissolution by the President if a new assembly wasn't elected within a period of 5 years. The parliament was responsible for electing the President of Ghana and its speaker, who was the presiding officer of the National Assembly. According to the 1960 constitution of Ghana, the National Assembly could consist of no less than 100 delegates.[1]
President of Ghana
The Presidency of Ghana lacked strict term limits as new presidential elections were only required on the event of the President's resignation, death or dissolution of parliament after its 5 year expiration date. As described in the constitution, the President is the commander-in-chief of the armed forces, has the power to appoint and dismiss cabinet members and can pass/veto legislation.[1]



