| Roman Empire Βασιλεία Ῥωμαίων | |
|---|---|
| 395–1453 | |
|
Imperial banner of the Palaiologos dynasty | |
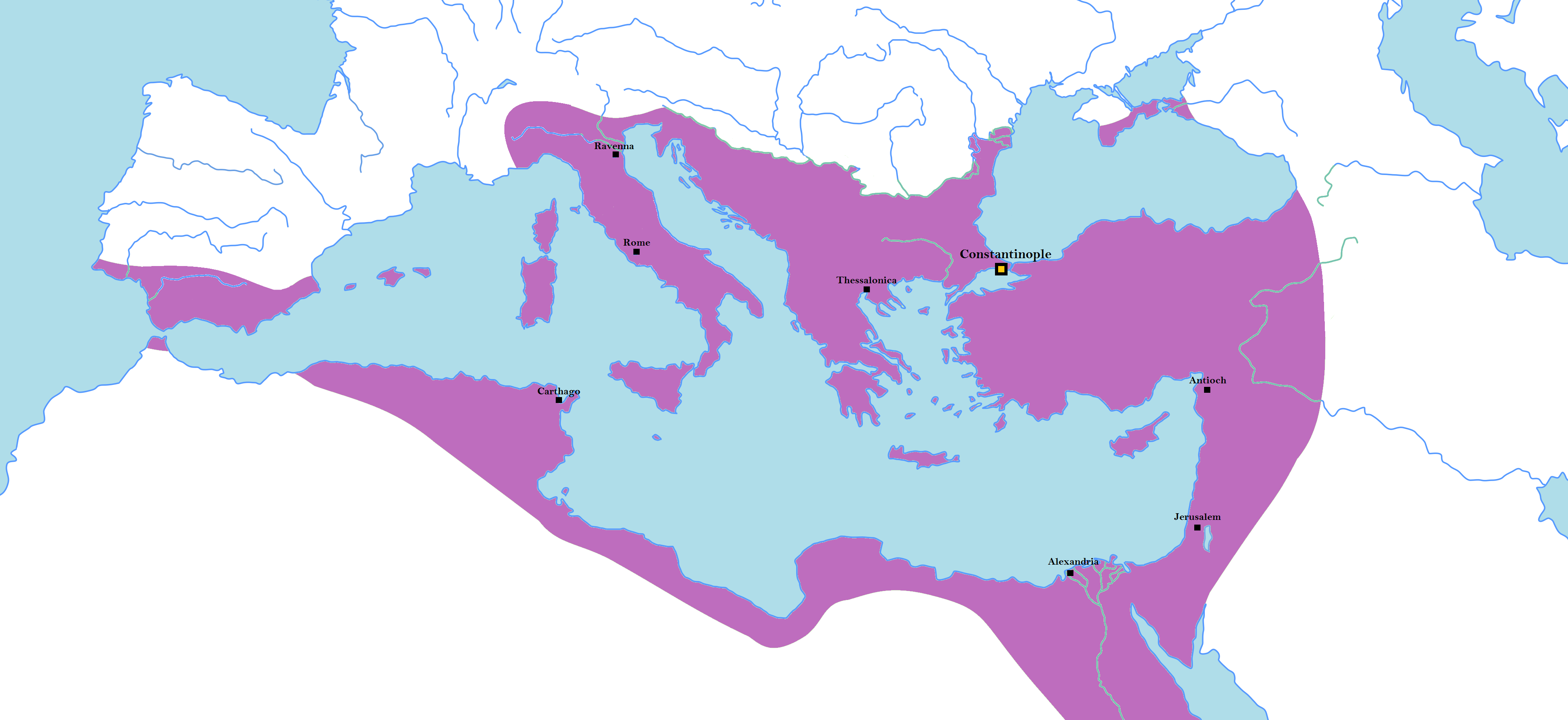 Byzantium in 555CE | |
| Capital | Constantinople |
| Common languages | Greek |
| Dominant mode of production | Feudalism |
| History | |
• Formation of the Roman Empire | 27 BCE |
• Fall of the Western Roman Empire | 395 |
• Constantinople falls; Byzantium ends | 1453 |
| Population | |
• 565 CE estimate | ~26,000,000 |
Byzantium, also called the Byzantine Empire or the Eastern Roman Empire, was an imperial state that lasted from 395 to 1453 CE. It is commonly viewed as a medieval continuation of the Roman Empire. At its foundation, the Byzantine Empire controlled one-third of the Roman army but collected two-thirds of its tax revenue. Its well-equipped, professional armies were able to defeat repeated invasions while the western empire collapsed into a patchwork of warring states.[1]
Byzantium's conservative leadership prevented technological advancement and resorted to knowledge dating to the Roman era in the fields of architecture, metallurgy, and military strategy.[2]
History
Early history
Early Byzantine emperors were able to keep control of the Balkans, Syria, Anatolia, and Egypt. Barely 50 years after Justinian's last attempt to conquer the west, Byzantium lost economic control of its outer territories and reoriented its economy around defense.[2]
Loss of territory
The Arabs took control of Syria in 636 at the Battle of Yarmuk. When the Turks seized eastern Anatolia in 1071, the empire shrank to half its original territory. Crusaders sacked the capital city of Constantinople in 1204, and the remnants of the empire finally fell to the Ottomans in 1453.[1]
Religion
Byzantine authorities persecuted pagans, Jews, and non-Orthodox Christians, who together made up almost half of the total population.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Neil Faulkner (2013). A Marxist History of the World: From Neanderthals to Neoliberals: 'European Feudalism' (p. 79). [PDF] Pluto Press. ISBN 9781849648639 [LG]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Chris Harman (1999). A People's History of the World: 'The ‘Middle Ages’' (pp. 117–120). [PDF] London: Bookmarks Publications Ltd. ISBN 9781898876557 [LG]
