More languages
More actions
Jucheguevara (talk | contribs) (again changed up names in intro, most sources use roman numerals) Tag: Visual edit |
Aryan13AKS (talk | contribs) (added a bit of further detail, more work to be done and citations to be added.) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
== Causes == | == Causes == | ||
[[File:World 1914 empires colonies territory.png|link=https://prolewiki.org/wiki/File:World%201914%20empires%20colonies%20territory.png|thumb|Map of colonial empires in the world in 1914. Note the relative size of each. Smaller possessions would form the Triple Alliance, while bigger possessions would form the Triple Entente.]] | [[File:World 1914 empires colonies territory.png|link=https://prolewiki.org/wiki/File:World%201914%20empires%20colonies%20territory.png|thumb|Map of colonial empires in the world in 1914. Note the relative size of each. Smaller possessions would form the Triple Alliance, while bigger possessions would form the Triple Entente.]] | ||
As the Industrial Revolution was winding down and several countries were turning towards imperialism to keep capitalism afloat, others were going to their industrial revolution still, which they had started at a later date (such as Germany). The former countries had already colonised the world and so had enjoyed the benefits of [[imperialism]] for decades. The latter countries on the other hand were barely reaching their imperialist phase, and as such entered the war to redistribute colonial possessions to their advantage. | Although the German 'blank check' for Austro-Hungary to initiate aggression against Serbia was the immediate cause, structural issues of the world capitalist order at the time can be identified. The main branches of bourgeois historiography pin down Imperial Germany as responsible for the war , noting the firebrand nature of Kaiser Wilhelm II (The Fischer thesis), or surmise that the war occurred due to a diplomatic breakdown, with each side 'sleepwalking' into the war. As the Industrial Revolution was winding down and several countries were turning towards imperialism to keep capitalism afloat, others were going to their industrial revolution still, which they had started at a later date (such as Germany). The former countries had already colonised the world and so had enjoyed the benefits of [[imperialism]] for decades. The latter countries on the other hand were barely reaching their imperialist phase, and as such entered the war to redistribute colonial possessions to their advantage. | ||
== Alliances == | == Alliances == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
* Austria-Hungary, | * Austria-Hungary, | ||
* and Italy | * and Italy | ||
== Major Events == | |||
=== The 'July Crisis' === | |||
=== Entry of Italy and the Battles of the Isonzo === | |||
=== The Brest-Litovsk Treaty and withdrawal of Russia === | |||
== Reliance on colonies == | == Reliance on colonies == | ||
Colonies played a primordial role in this conflict, with their masters requiring soldiers and resources be sent to aid in the war effort. | Colonies played a primordial role in this conflict, with their masters requiring soldiers and resources be sent to aid in the war effort. | ||
A major rebellion against the Tsarist colonial government broke out in the Central Asian region in 1916. Another uprising against the British colonists, the Easter uprising also took place in 1916. | |||
In his book ''The Wretched of the Earth'', Franz Fanon recalled a poem by Keita Fodeba, ''African Dawn'', in which a Malian youth is sent to fight for France in World War 1. Picked by the village for his bravery, he leaves in a ship soon after heading for the French front. During his time in the army, his wife receives sparse letters from him and fears for the worst every day. Eventually near the end of the war, she learns that he will be coming back. But on the day his ship arrives back in his home country, he is killed in an undisclosed altercation with two white colonial police officers. | In his book ''The Wretched of the Earth'', Franz Fanon recalled a poem by Keita Fodeba, ''African Dawn'', in which a Malian youth is sent to fight for France in World War 1. Picked by the village for his bravery, he leaves in a ship soon after heading for the French front. During his time in the army, his wife receives sparse letters from him and fears for the worst every day. Eventually near the end of the war, she learns that he will be coming back. But on the day his ship arrives back in his home country, he is killed in an undisclosed altercation with two white colonial police officers. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 36: | ||
== Consequences of World War I == | == Consequences of World War I == | ||
Ultimately, the forces of the Triple Alliance failed to upset the balance like they sought to, instead surrendering in 1918 and losing their meagre colonial possessions. | Ultimately, the forces of the Triple Alliance failed to upset the balance like they sought to, instead surrendering in 1918 and losing their meagre colonial possessions. The infamous Versailles treaty was imposed upon members of the Alliance. | ||
Faced with heavy penalties from the victors and coupled with the fact that they had become unable to enter an imperialist phase and sustain capitalism, fascism was able to take hold in Germany, Italy, and Austria, ultimately leading to [[World War 2]]. It should be noted that fascism was already starting to appear in Italy under an ultranationalist veneer, and as such it wasn't WW1 by itself that was the triggering factor for fascism as an ideology to exist. | Faced with heavy penalties from the victors and coupled with the fact that they had become unable to enter an imperialist phase and sustain capitalism, fascism was able to take hold in Germany, Italy, and Austria, ultimately leading to [[World War 2]]. It should be noted that fascism was already starting to appear in Italy under an ultranationalist veneer, and as such it wasn't WW1 by itself that was the triggering factor for fascism as an ideology to exist. | ||
== Resistance to World War I == | |||
Several European socialist parties confirmed their commitment against the warmongering machinations of their respective ruling classes at the [[Basel Conference]] in 1912. However, most parties turned back on this commitment and joined their ruling classes to wage war against workers from other countries. Russia, after having undergone the Bolshevik Revolution, withdrew from the war in 1917 and appealed to all countries to cease the war. | |||
Revision as of 23:06, 26 November 2020
World War I, also known as the First World War and abbreviated as WW1 or WWI, was a conflict taking place from the years of 1914 to 1918. It is called a world war due to the fact that most countries in the world at the time directly participated in the conflict. Most of these participants were colonies of the main powers, as much of the conflict took place in Europe.
Causes
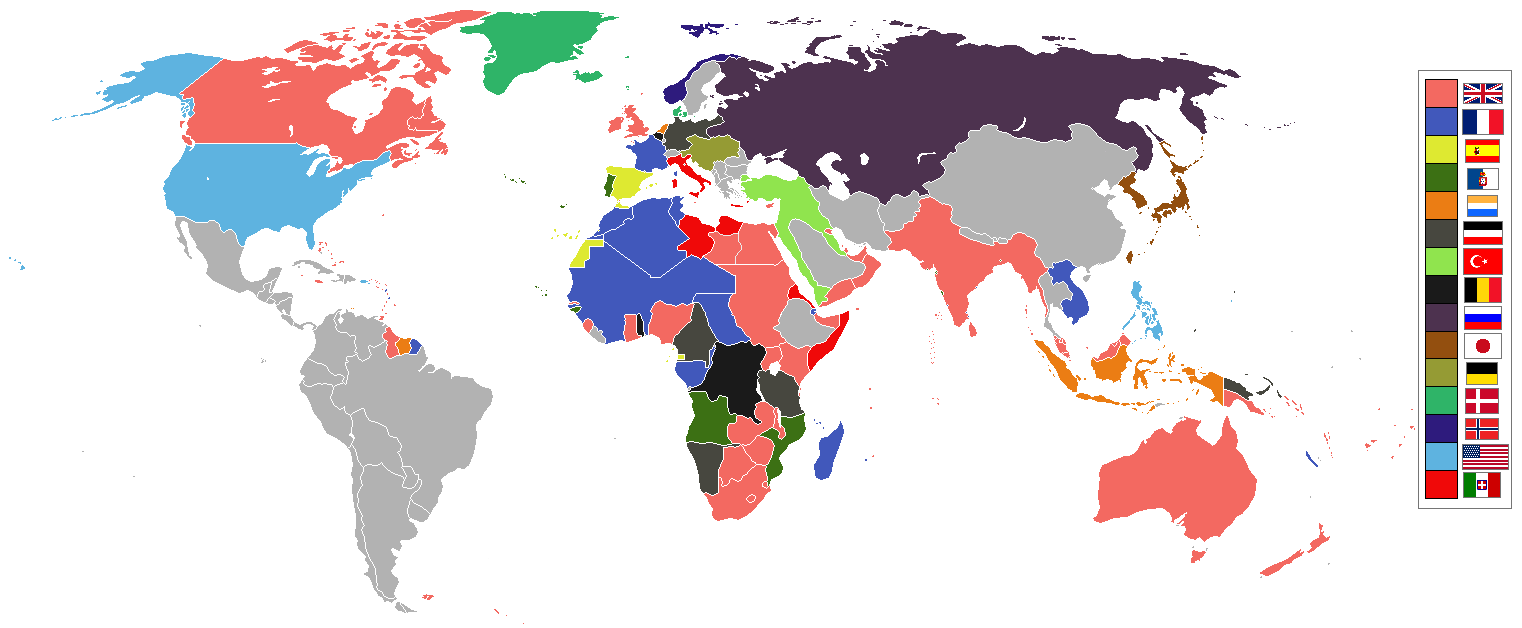
Although the German 'blank check' for Austro-Hungary to initiate aggression against Serbia was the immediate cause, structural issues of the world capitalist order at the time can be identified. The main branches of bourgeois historiography pin down Imperial Germany as responsible for the war , noting the firebrand nature of Kaiser Wilhelm II (The Fischer thesis), or surmise that the war occurred due to a diplomatic breakdown, with each side 'sleepwalking' into the war. As the Industrial Revolution was winding down and several countries were turning towards imperialism to keep capitalism afloat, others were going to their industrial revolution still, which they had started at a later date (such as Germany). The former countries had already colonised the world and so had enjoyed the benefits of imperialism for decades. The latter countries on the other hand were barely reaching their imperialist phase, and as such entered the war to redistribute colonial possessions to their advantage.
Alliances
Two major alliances faced off in the conflict. The Triple Entente, composed of:
- France,
- the British Empire,
- and Tsarist Russia
Against the Triple Alliance, composed of:
- the German Empire,
- Austria-Hungary,
- and Italy
Major Events
The 'July Crisis'
Entry of Italy and the Battles of the Isonzo
The Brest-Litovsk Treaty and withdrawal of Russia
Reliance on colonies
Colonies played a primordial role in this conflict, with their masters requiring soldiers and resources be sent to aid in the war effort.
A major rebellion against the Tsarist colonial government broke out in the Central Asian region in 1916. Another uprising against the British colonists, the Easter uprising also took place in 1916.
In his book The Wretched of the Earth, Franz Fanon recalled a poem by Keita Fodeba, African Dawn, in which a Malian youth is sent to fight for France in World War 1. Picked by the village for his bravery, he leaves in a ship soon after heading for the French front. During his time in the army, his wife receives sparse letters from him and fears for the worst every day. Eventually near the end of the war, she learns that he will be coming back. But on the day his ship arrives back in his home country, he is killed in an undisclosed altercation with two white colonial police officers.
Fanon notes that "There is not a single colonized person who will not receive the message that this poem holds." He further writes that "this is Sétif in 1945, this is Fort-le-France, this is Saigon, Dakar, and Lagos".
Consequences of World War I
Ultimately, the forces of the Triple Alliance failed to upset the balance like they sought to, instead surrendering in 1918 and losing their meagre colonial possessions. The infamous Versailles treaty was imposed upon members of the Alliance.
Faced with heavy penalties from the victors and coupled with the fact that they had become unable to enter an imperialist phase and sustain capitalism, fascism was able to take hold in Germany, Italy, and Austria, ultimately leading to World War 2. It should be noted that fascism was already starting to appear in Italy under an ultranationalist veneer, and as such it wasn't WW1 by itself that was the triggering factor for fascism as an ideology to exist.
Resistance to World War I
Several European socialist parties confirmed their commitment against the warmongering machinations of their respective ruling classes at the Basel Conference in 1912. However, most parties turned back on this commitment and joined their ruling classes to wage war against workers from other countries. Russia, after having undergone the Bolshevik Revolution, withdrew from the war in 1917 and appealed to all countries to cease the war.
