More languages
More actions
No edit summary |
(→Territory: I added an extensive background and Arab revolt section to the article, under a section I started about the Israeli occupation of palestine.) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
'''Palestine''', officially the '''State of Palestine''', is an independent state in Western Asia that is partially occupied by [[Israel]]. | '''Palestine''', officially the '''State of Palestine''', is an independent state in Western Asia that is partially occupied by [[Israel]]. | ||
== Territory == | == Israeli Occupation (1948 - Present) == | ||
=== Background === | |||
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, a movement known as Zionism was formed, advocating a homeland for [[Judaism|Jewish]] people in the, then [[United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland|British]] occupied, land of Palestine. At the same time, the majority Arabic population, who had lived in Palestine for generations, desired independence from the British in the form of an independent Arabic state. In 1917 the British released the Balfour Declaration, which expressed full support to the Zionist movement. The Palestinian people, angered by the British completely ignoring their interests, began protests and rioting against Jewish occupation as early as 1920. These protests were largely led by Amin al-Husseini, the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem. | |||
=== The Arab Revolt (1936 - 1939) === | |||
Starting April 19, 1936, a mass strike against the British instatement of Zionism in the region was formulated. The strike was organized by the Arab Higher Committee, a Palestinian independence movement under the leadership of Amin al-Husseini. This strike eventually led to violent insurgency against British rule in the countryside. The British reacted to these strikes as any imperialist power would; through violent suppression. The British seized and searched property, often without warrants, tortured Palestinian prisoners, and deported Palestinian people from their homeland. There were also many violent encounters between Palestinian resistance, the British army, and Zionist paramilitary groups. | |||
By the time it concluded in September 1939, more than 5,000 Arabs, over 300 Jews, and 262 Britons had been killed and at least 15,000 Arabs were wounded. | |||
=== Territory === | |||
[[File:West Bank.png|left|thumb|325x325px|Green: Palestinian control<br>Red: Joint control<br>Blue and pink: Israeli control]] | [[File:West Bank.png|left|thumb|325x325px|Green: Palestinian control<br>Red: Joint control<br>Blue and pink: Israeli control]] | ||
Before 1948, Palestine consisted of all of the land on the land on the Sinai Peninsula outside of Egypt. In 1948, the area was partitioned into two states, Israel and Palestine. Israel was not satisfied with its territory and soon annexed 60% of Palestinian land in the Arab–Israeli War.<ref>{{Citation|author=|year=1948|title=Area of Jurisdiction and Powers Ordinance (1948)|chapter=|section=|page=57|quote=|pdf=|city=|publisher=israellawresourcecenter.org|isbn=|doi=|lg=|mia=|title-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624062229/http://www.israellawresourcecenter.org/israellaws/fulltext/areajurisdictionpowersord.htm|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref> During the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel invaded the rest of Palestine and annexed East Jerusalem.<ref>{{Citation|author=|year=2018|title=Milestones: 1961–1968|chapter=|section=|page=|quote=|pdf=|city=|publisher=Office of the Historian|isbn=|doi=|lg=|mia=|title-url=|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref> Most of the West Bank is now occupied by Israel.<ref>{{News citation|journalist=|date=2003-12-17|title=Applicability of the Geneva Convention relative to the Protection of Civilian Persons in Time of War, of 12 August 1949, to the Occupied Palestinian Territory, including Jerusalem, and the other occupied Arab territories|url=http://domino.un.org/unispal.nsf/97360ee7a29e68a085256df900723485/d6f5d7049734efff85256e1200677754|newspaper=United Nations|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070603050844/http://domino.un.org/unispal.nsf/97360ee7a29e68a085256df900723485/d6f5d7049734efff85256e1200677754|archive-date=2007-06-03|retrieved=2022-01-03}}</ref> | Before 1948, Palestine consisted of all of the land on the land on the Sinai Peninsula outside of Egypt. In 1948, the area was partitioned into two states, Israel and Palestine. Israel was not satisfied with its territory and soon annexed 60% of Palestinian land in the Arab–Israeli War.<ref>{{Citation|author=|year=1948|title=Area of Jurisdiction and Powers Ordinance (1948)|chapter=|section=|page=57|quote=|pdf=|city=|publisher=israellawresourcecenter.org|isbn=|doi=|lg=|mia=|title-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20170624062229/http://www.israellawresourcecenter.org/israellaws/fulltext/areajurisdictionpowersord.htm|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref> During the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel invaded the rest of Palestine and annexed East Jerusalem.<ref>{{Citation|author=|year=2018|title=Milestones: 1961–1968|chapter=|section=|page=|quote=|pdf=|city=|publisher=Office of the Historian|isbn=|doi=|lg=|mia=|title-url=|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref> Most of the West Bank is now occupied by Israel.<ref>{{News citation|journalist=|date=2003-12-17|title=Applicability of the Geneva Convention relative to the Protection of Civilian Persons in Time of War, of 12 August 1949, to the Occupied Palestinian Territory, including Jerusalem, and the other occupied Arab territories|url=http://domino.un.org/unispal.nsf/97360ee7a29e68a085256df900723485/d6f5d7049734efff85256e1200677754|newspaper=United Nations|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070603050844/http://domino.un.org/unispal.nsf/97360ee7a29e68a085256df900723485/d6f5d7049734efff85256e1200677754|archive-date=2007-06-03|retrieved=2022-01-03}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 02:47, 7 May 2023
Palestine, officially the State of Palestine, is an independent state in Western Asia that is partially occupied by Israel.
Israeli Occupation (1948 - Present)
Background
In the 19th and early 20th centuries, a movement known as Zionism was formed, advocating a homeland for Jewish people in the, then British occupied, land of Palestine. At the same time, the majority Arabic population, who had lived in Palestine for generations, desired independence from the British in the form of an independent Arabic state. In 1917 the British released the Balfour Declaration, which expressed full support to the Zionist movement. The Palestinian people, angered by the British completely ignoring their interests, began protests and rioting against Jewish occupation as early as 1920. These protests were largely led by Amin al-Husseini, the Grand Mufti of Jerusalem.
The Arab Revolt (1936 - 1939)
Starting April 19, 1936, a mass strike against the British instatement of Zionism in the region was formulated. The strike was organized by the Arab Higher Committee, a Palestinian independence movement under the leadership of Amin al-Husseini. This strike eventually led to violent insurgency against British rule in the countryside. The British reacted to these strikes as any imperialist power would; through violent suppression. The British seized and searched property, often without warrants, tortured Palestinian prisoners, and deported Palestinian people from their homeland. There were also many violent encounters between Palestinian resistance, the British army, and Zionist paramilitary groups.
By the time it concluded in September 1939, more than 5,000 Arabs, over 300 Jews, and 262 Britons had been killed and at least 15,000 Arabs were wounded.
Territory
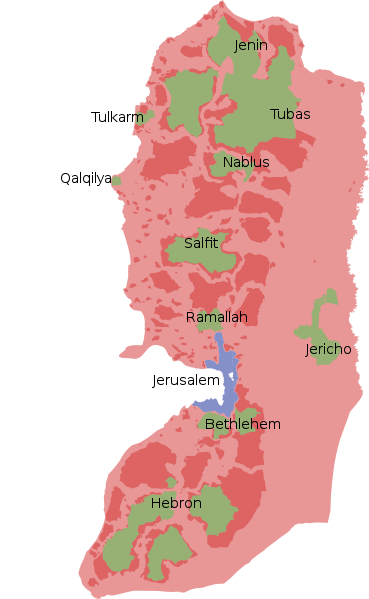
Red: Joint control
Blue and pink: Israeli control
Before 1948, Palestine consisted of all of the land on the land on the Sinai Peninsula outside of Egypt. In 1948, the area was partitioned into two states, Israel and Palestine. Israel was not satisfied with its territory and soon annexed 60% of Palestinian land in the Arab–Israeli War.[1] During the Six-Day War in 1967, Israel invaded the rest of Palestine and annexed East Jerusalem.[2] Most of the West Bank is now occupied by Israel.[3]
References
- ↑ Area of Jurisdiction and Powers Ordinance (1948) (1948) (p. 57). israellawresourcecenter.org.
- ↑ Milestones: 1961–1968 (2018). Office of the Historian.
- ↑ "Applicability of the Geneva Convention relative to the Protection of Civilian Persons in Time of War, of 12 August 1949, to the Occupied Palestinian Territory, including Jerusalem, and the other occupied Arab territories" (2003-12-17). United Nations. Archived from the original on 2007-06-03. Retrieved 2022-01-03.