More languages
More actions
| Great Mongol Nation ᠶᠡᠬᠡ ᠮᠣᠩᠭᠣᠯ ᠤᠯᠤᠰ | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital | Avarga (1206–1235) Karakorum (1235–1260) Khanbaliq (1271–1368) |
| Dominant mode of production | Feudalism |
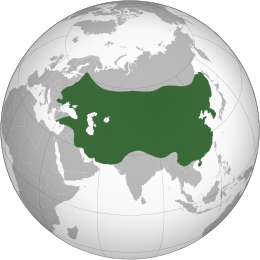
| Area | |
• Total | 24,000,000 km² |
The Great Mongol Nation, commonly known as the Mongol Empire, was the largest contiguous land-based state in history.
History
Background
In the early 11th century, feudal states began forming in Mongolia. Khabul Khan, great-grandfather of Chinggis (Genghis) Khan, became the first khan (leader) of the Khamag confederation, which collapsed in 1166 after his grandson Yesugei was poisoned.[1]:106
Temüjin (later named Chinggis Khan) made an alliance with Jamukha and Toghrul to retake his father's vassals and defeated the Merkit confederation. He then fought with Jamukha over who would rule the Khamag and defeated him in 1090, becoming khan.[1]106–7
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 A. A. Guber, et al. (1973). History of the Mongolian People's Republic. Moscow: USSR Academy of Sciences.
