More languages
More actions
(Native name) Tag: Visual edit |
General-KJ (talk | contribs) (Expanded the article) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox country|name=New Caledonia|native_name=Kanaky|image_flag=New Caledonian flag.svg|capital=Nouméa|largest_city=Nouméa|image_map=New Caledonia map.png|map_width= | {{Infobox country|name=New Caledonia|native_name=Kanaky|image_flag=New Caledonian flag.svg|image_coat=Emblem of New Caledonia.svg.png|capital=Nouméa|largest_city=Nouméa|government_type=Devolved parliamentary dependency|leader_title1=High Commissioner|leader_name1=[[Louis Le Franc]]|leader_title2=President of the Government|leader_name2=[[Louis Mapou]]|image_map=New Caledonia map.png|map_width=320|official_languages=French|area_km2=18,576|population_census=271,407|population_census_year=2019}} | ||
[[File:Kanaky map.png|thumb|Indigenous groups in New Caledonia]] | [[File:Kanaky map.png|thumb|Indigenous groups in New Caledonia]] | ||
'''Kanky''', officially known as '''New Caledonia''', is a [[French Republic|French]] [[Settler colonialism|settler-colony]] in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The [[Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front]] (FLNKS) has been struggling for [[national liberation]] and independence since the 1980s.<ref name=":1">{{Web citation|author=B. A. Ford|newspaper=[[People's Voice]]|title=Kanaky-New Caledonia independence vote shines light on imperialism in the Pacific|date=2020-10-19|url=https://pvonline.ca/2020/10/19/kanaky-new-caledonia-independence-vote-shines-light-on-imperialism-in-the-pacific/|retrieved=2022-12-22}}</ref> | '''Kanky''', officially known as '''New Caledonia''', is a [[French Republic|French]] [[Settler colonialism|settler-colony]] in the southwest [[Pacific Ocean]]. The [[Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front]] (FLNKS) has been struggling for [[national liberation]] and independence since the 1980s.<ref name=":1">{{Web citation|author=B. A. Ford|newspaper=[[People's Voice]]|title=Kanaky-New Caledonia independence vote shines light on imperialism in the Pacific|date=2020-10-19|url=https://pvonline.ca/2020/10/19/kanaky-new-caledonia-independence-vote-shines-light-on-imperialism-in-the-pacific/|retrieved=2022-12-22}}</ref> | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
James Cook became the first [[Europe|European]] to visit New Caledonia in 1774.<ref name=": | James Cook became the first [[Europe|European]] to visit New Caledonia in 1774, naming the archipelago New Caledonia after the old name for [[Scotland]]; Caledonia.<ref name=":2">{{Citation|author=V. Z. Klepikov|year=1979|title=The Great Soviet Encyclopedia|title-url=https://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/New+Caledonia|chapter=New Caledonia|section=Historical Survey}}</ref> | ||
New Caledonia in 1853 was declared a possession of France and in 1860 became a colony.<ref name=":2" /> The archipelago was a penal colony and many members of the [[Paris Commune]] were exiled to New Caledonia after 1871.<ref>{{Citation|author=Robert Aldrich, John Connell|year=2006|title=France's Overseas Frontier: Départements et territoires d'outre-mer|page=46|publisher=Cambridge University Press|isbn=9780521030366|title-url=https://books.google.com/books?id=vRB3woPa7LAC&pg=PA46}}</ref> New Caledonia became a French Overseas Territory in 1946.<ref name=":0">{{Web citation|newspaper=[[Peoples Dispatch]]|title=Progressive sections denounce outcome of New Caledonia referendum|date=2021-12-20|url=https://peoplesdispatch.org/2021/12/20/progressive-sections-denounce-outcome-of-new-caledonia-referendum/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220116220207/https://peoplesdispatch.org/2021/12/20/progressive-sections-denounce-outcome-of-new-caledonia-referendum/|archive-date=2022-01-16|retrieved=2022-09-09}}</ref> In 1998, the FLNKS signed an agreement with France to extend more rights to indigenous Kanak peoples.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== 2021 independence referendum == | == 2021 independence referendum == | ||
Revision as of 18:04, 21 May 2024
| New Caledonia Kanaky | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Nouméa |
| Official languages | French |
| Government | Devolved parliamentary dependency |
• High Commissioner | Louis Le Franc |
• President of the Government | Louis Mapou |
| Area | |
• Total | 18,576 km² |
| Population | |
• 2019 census | 271,407 |
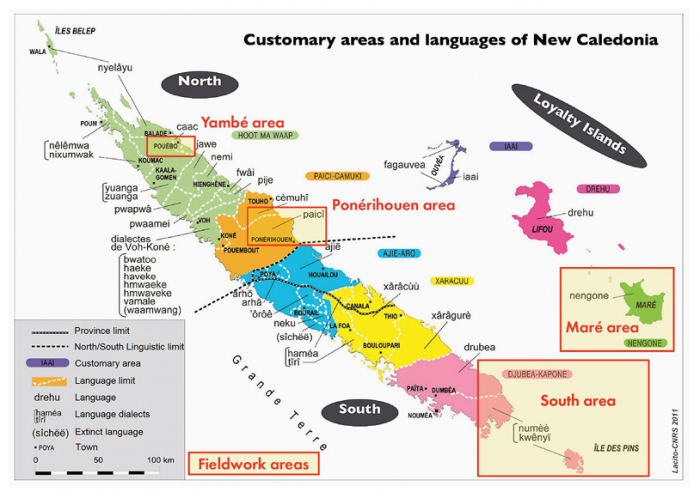
Kanky, officially known as New Caledonia, is a French settler-colony in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The Kanak and Socialist National Liberation Front (FLNKS) has been struggling for national liberation and independence since the 1980s.[1]
History
James Cook became the first European to visit New Caledonia in 1774, naming the archipelago New Caledonia after the old name for Scotland; Caledonia.[2]
New Caledonia in 1853 was declared a possession of France and in 1860 became a colony.[2] The archipelago was a penal colony and many members of the Paris Commune were exiled to New Caledonia after 1871.[3] New Caledonia became a French Overseas Territory in 1946.[4] In 1998, the FLNKS signed an agreement with France to extend more rights to indigenous Kanak peoples.[1]
2021 independence referendum
The FLNKS boycotted a 2021 referendum for independence from France. 96.5% of votes in the referendum were against independence, but only 43.87% of the population voted in the referendum.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 B. A. Ford (2020-10-19). "Kanaky-New Caledonia independence vote shines light on imperialism in the Pacific" People's Voice. Retrieved 2022-12-22.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 V. Z. Klepikov (1979). The Great Soviet Encyclopedia: 'New Caledonia; Historical Survey'.
- ↑ Robert Aldrich, John Connell (2006). France's Overseas Frontier: Départements et territoires d'outre-mer (p. 46). Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521030366
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Progressive sections denounce outcome of New Caledonia referendum" (2021-12-20). Peoples Dispatch. Archived from the original on 2022-01-16. Retrieved 2022-09-09.


