More languages
More actions
No edit summary |
General-KJ (talk | contribs) (Expanded the article) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox country|name=State of Qatar|native_name=دولة قطر|image_flag=Flag of Qatar.svg|image_coat=Emblem of Qatar.svg|capital=Doha|largest_city=Doha|mode_of_production=[[Capitalism]]|government_type=Unitary Semi-constitutional [[monarchy]]|leader_title1=Emir|leader_name1=[[Tanim bin Hamad]]|leader_title2=Prime Minister|leader_name2=[[Mohammed bin Abdulrahman]]|image_map=Qatar map.svg|map_width=260|official_languages=Arabic|established_event1=Independence from the United Kingdom|established_date1=1971|area_km2=11,581|population_estimate=2,795,484|population_estimate_year=2020}} | |||
'''Qatar''', officially the '''State of Qatar''', is a monarchy on the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia. 85% of | '''Qatar''', officially the '''State of Qatar''', is a monarchy occupying the Qatar Peninsula on the north-eastern coast of the [[Arabian Peninsula]] in [[West Asia|Western Asia]]. It shares its only land border with [[Kingdom of Saudi Arabia|Saudi Arabia]] with the rest of the territory surrounded by the [[Persian Gulf]]. The Gulf of Bahrain separates it from the nearby island nation of [[Kingdom of Bahrain|Bahrain]]. Qatar is a [[United States of America|US]] ally and allows the [[Imperialism|imperialist]] power to use its airbases to bomb the region.<ref name=":0">{{Web citation|author=Proletarian Writers|newspaper=Proletarian|title=Qatar at the crossroads?|date=2022-12-31|url=https://thecommunists.org/2022/12/31/news/qatar-iran-nato-crossroads/|retrieved=2023-11-30}}</ref> | ||
The capital of Doha is home to over 80% of the country's inhabitants with the land area mostly being made up of flat, low-lying desert. 85% of Qatar's inhabitants are migrant workers with almost no [[trade union]] activity.<ref>{{Web citation|author=Vince Hawkins|newspaper=[[Counterfire]]|title=Sporting values built on bloodied sand: Qatar 2022|date=2022-11-18|url=https://www.counterfire.org/articles/opinion/23611-sporting-values-built-on-bloodied-sand-qatar-2022-world-cup|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20221118223051/https://www.counterfire.org/articles/opinion/23611-sporting-values-built-on-bloodied-sand-qatar-2022-world-cup|archive-date=2022-11-18|retrieved=2022-11-23}}</ref> | |||
== History == | |||
=== Ottoman Rule === | |||
The region submitted to [[Ottoman Empire (1299–1922)|Ottoman]] rule in 1871 who held the region until 1914 when it renounced its rights to Qatar in favour of the British.<ref name=":1">{{Citation|author=A. A. Ershov|year=1979|title=The Great Soviet Encyclopedia|title-url=https://encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com/qatar|chapter=Qatar|section=Historical Survey}}</ref> | |||
=== British Rule === | |||
Qatar became a [[United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland|British]] Protectorate on November 3, 1916 after the British imposed an unequal treaty on the Qatari.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
=== Independence === | |||
In 1968, with the imminent withdrawal of the British on the horizon, Qatar entered negotiations with Bahrain and the [[Trucial States]] for the potential formation of a Federation of Persian Gulf Emirates, but these talks ultimately failed and the Trucial States instead became the [[United Arab Emirates]]. A provisional constitution of Qatar was adopted on April 2, 1970, and the first Qatari government of ten ministers, seven of them from the Thani royal family, was formed on May 29, 1970. On September 1, 1971, Qatar was proclaimed an independent state with the UK recognising the move soon after and concluding a "friendship treaty". In September 1971, Qatar became a member of the [[United Nations|UN]] and the [[Arab League]].<ref name=":1" /> | |||
=== 21st Century === | |||
The US made use of the Al Udeid air base during its imperialist [[war in Afghanistan]] in 2001 and Qatar has remained loyal to the US to the present day.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
Qatar was suspended from the [[Gulf Cooperation Council]] (GCC) in 2017 accused of supporting [[terrorism]]. In 2021 Qatar was readmitted to the GCC though with strengthened ties to [[Islamic Republic of Iran|Iran]] and [[Republic of Türkiye|Turkey]].<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== Economy == | |||
Qatar and Iran jointly own the [[South Pars North Dome]] natural gas field, the largest such maritime field in the world making Qatar one of the most natural gas rich countries in the world. It holds an estimated 50.97tn cubic metres of in-situ gas and some 50bn barrels of condensates and covers an area of 9,700 square kilometres.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
[[Category:Countries]] | [[Category:Countries]] | ||
[[Category:Asian countries]] | [[Category:Asian countries]] | ||
Latest revision as of 22:25, 21 May 2024
| State of Qatar دولة قطر | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Doha |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Dominant mode of production | Capitalism |
| Government | Unitary Semi-constitutional monarchy |
• Emir | Tanim bin Hamad |
• Prime Minister | Mohammed bin Abdulrahman |
| History | |
• Independence from the United Kingdom | 1971 |
| Area | |
• Total | 11,581 km² |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 2,795,484 |
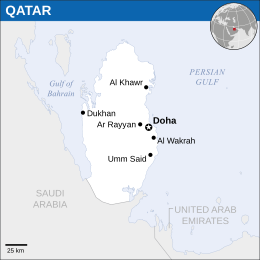
Qatar, officially the State of Qatar, is a monarchy occupying the Qatar Peninsula on the north-eastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia. It shares its only land border with Saudi Arabia with the rest of the territory surrounded by the Persian Gulf. The Gulf of Bahrain separates it from the nearby island nation of Bahrain. Qatar is a US ally and allows the imperialist power to use its airbases to bomb the region.[1]
The capital of Doha is home to over 80% of the country's inhabitants with the land area mostly being made up of flat, low-lying desert. 85% of Qatar's inhabitants are migrant workers with almost no trade union activity.[2]
History[edit | edit source]
Ottoman Rule[edit | edit source]
The region submitted to Ottoman rule in 1871 who held the region until 1914 when it renounced its rights to Qatar in favour of the British.[3]
British Rule[edit | edit source]
Qatar became a British Protectorate on November 3, 1916 after the British imposed an unequal treaty on the Qatari.[3]
Independence[edit | edit source]
In 1968, with the imminent withdrawal of the British on the horizon, Qatar entered negotiations with Bahrain and the Trucial States for the potential formation of a Federation of Persian Gulf Emirates, but these talks ultimately failed and the Trucial States instead became the United Arab Emirates. A provisional constitution of Qatar was adopted on April 2, 1970, and the first Qatari government of ten ministers, seven of them from the Thani royal family, was formed on May 29, 1970. On September 1, 1971, Qatar was proclaimed an independent state with the UK recognising the move soon after and concluding a "friendship treaty". In September 1971, Qatar became a member of the UN and the Arab League.[3]
21st Century[edit | edit source]
The US made use of the Al Udeid air base during its imperialist war in Afghanistan in 2001 and Qatar has remained loyal to the US to the present day.[1]
Qatar was suspended from the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) in 2017 accused of supporting terrorism. In 2021 Qatar was readmitted to the GCC though with strengthened ties to Iran and Turkey.[1]
Economy[edit | edit source]
Qatar and Iran jointly own the South Pars North Dome natural gas field, the largest such maritime field in the world making Qatar one of the most natural gas rich countries in the world. It holds an estimated 50.97tn cubic metres of in-situ gas and some 50bn barrels of condensates and covers an area of 9,700 square kilometres.[1]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Proletarian Writers (2022-12-31). "Qatar at the crossroads?" Proletarian. Retrieved 2023-11-30.
- ↑ Vince Hawkins (2022-11-18). "Sporting values built on bloodied sand: Qatar 2022" Counterfire. Archived from the original on 2022-11-18. Retrieved 2022-11-23.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 A. A. Ershov (1979). The Great Soviet Encyclopedia: 'Qatar; Historical Survey'.

