More languages
More actions
Jucheguevara (talk | contribs) (linked to cuba) Tag: Visual edit |
Jucheguevara (talk | contribs) (fixing up references) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{External article cleanup|date=November 2021}} | {{External article cleanup|date=November 2021}} | ||
[[File:One-belt-one-road.svg.png|alt=Map of Transportation routes in the Belt and Road Initiative|thumb|Transportation routes in the Belt and Road Initiative]] | [[File:One-belt-one-road.svg.png|alt=Map of Transportation routes in the Belt and Road Initiative|thumb|Transportation routes in the Belt and Road Initiative]] | ||
The '''Belt and Road Initiative''' ('''BRI''', or '''B&R'''), known in Chinese and formerly in English as '''One Belt One Road''' or '''OBOR''' for short, is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the [[China#Governance|Chinese government]] in 2013 to invest in nearly 70 countries and international organizations. It is considered a centerpiece of [[Communist Party of China]] general secretary and paramount leader [[Xi Jinping]]'s | The '''Belt and Road Initiative''' ('''BRI''', or '''B&R'''), known in Chinese and formerly in English as '''One Belt One Road''' or '''OBOR''' for short, is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the [[China#Governance|Chinese government]] in 2013 to invest in nearly 70 countries and international organizations. It is considered a centerpiece of [[Communist Party of China]] general secretary and paramount leader [[Xi Jinping]]'s foreign policy.<ref>{{News citation|title=President Xi proposes Silk Road economic belt|url=https://www.chinadaily.com.cn/china/2013xivisitcenterasia/2013-09/07/content_16951811.htm}}</ref> | ||
The BRI is one of the many factors which is leading to [[de-dollarization]], the transition away from the dependence on the US dollar as a global reserve asset and means of exchange.<ref>https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2018/04/09/the-de-dollarization-in-china/</ref> | The BRI is one of the many factors which is leading to [[de-dollarization]], the transition away from the dependence on the US dollar as a global reserve asset and means of exchange.<ref>https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2018/04/09/the-de-dollarization-in-china/</ref> | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
The project has a target completion date of 2049.<ref>https://www.pr.com/press-release/780645</ref> | The project has a target completion date of 2049.<ref>https://www.pr.com/press-release/780645</ref> | ||
In 2021, [[Republic of Cuba|Cuba]] has joined the BRI project for the purpose of expanding its telecommunications and green energy industries.<ref>{{News citation|journalist=|date=2021-10-18|title=Cuba Formally Joins China's Belt and Road Energy Partnership|url=https://www.telesurenglish.net/news/Cuba-Formally-Joins-Chinas-Belt-and-Road-Energy-Partnership-20211018-0016.html|newspaper=[[TeleSUR]]|archive-url=|archive-date=|retrieved=}}</ref> | In 2021, [[Republic of Cuba|Cuba]] has joined the BRI project for the purpose of expanding its telecommunications and green energy industries.<ref>{{News citation|journalist=|date=2021-10-18|title=Cuba Formally Joins China's Belt and Road Energy Partnership|url=https://www.telesurenglish.net/news/Cuba-Formally-Joins-Chinas-Belt-and-Road-Energy-Partnership-20211018-0016.html|newspaper=[[TeleSUR]]|archive-url=|archive-date=|retrieved=}}</ref> Syria has also joined.<ref>{{News citation|date=2022-12-01|title=Syria Officially Joins China's Belt and Road, Seeking Lifeline to Defy U.S. Sanctions|url=https://www.newsweek.com/syria-officially-joins-chinas-belt-road-seeking-lifeline-defy-us-sanctions-1668849}}</ref> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 20:27, 20 January 2022
 | Some parts of this article were copied from external sources and may contain errors or lack of appropriate formatting. You can help improve this article by editing it and cleaning it up. (November 2021) |
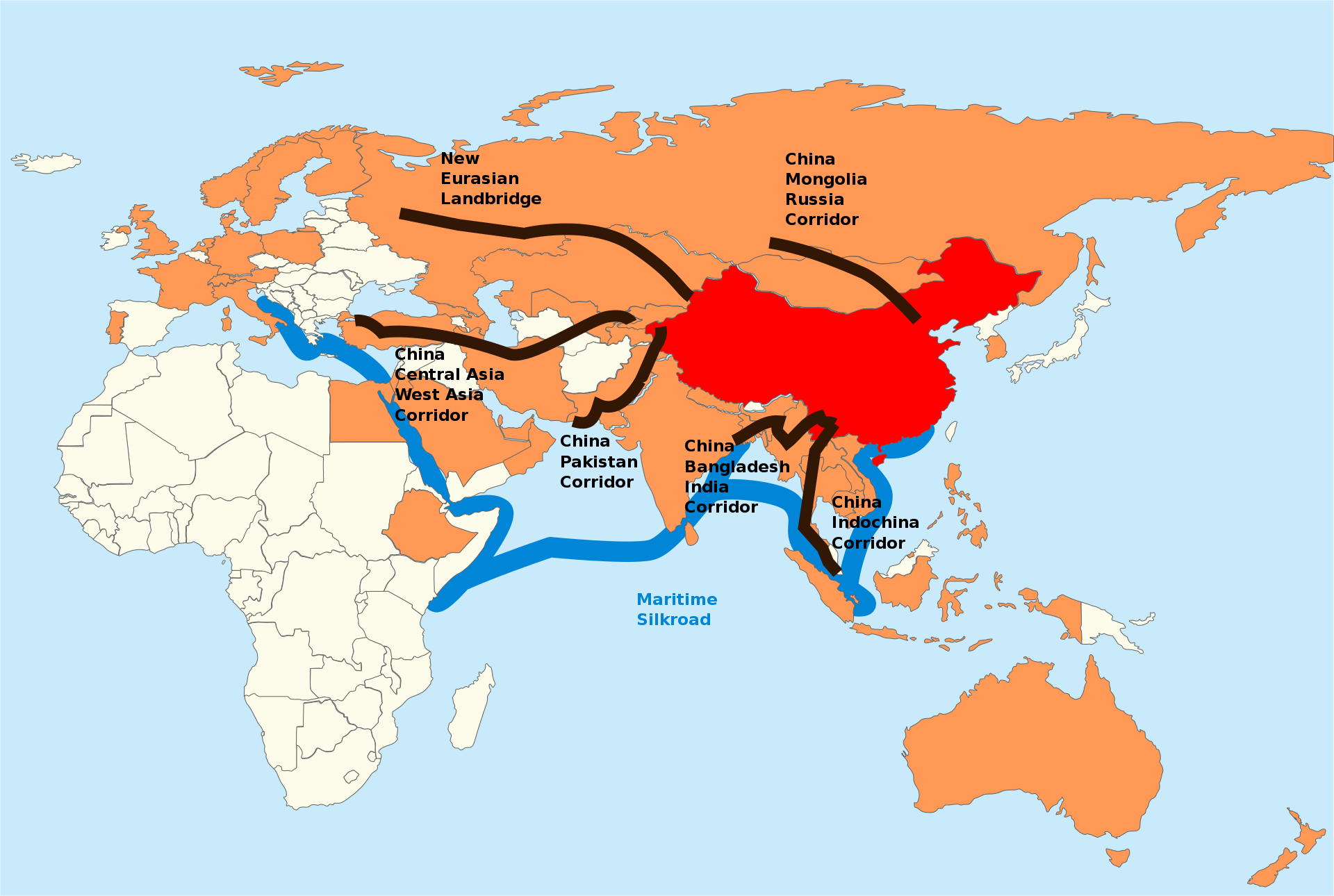
The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI, or B&R), known in Chinese and formerly in English as One Belt One Road or OBOR for short, is a global infrastructure development strategy adopted by the Chinese government in 2013 to invest in nearly 70 countries and international organizations. It is considered a centerpiece of Communist Party of China general secretary and paramount leader Xi Jinping's foreign policy.[1]
The BRI is one of the many factors which is leading to de-dollarization, the transition away from the dependence on the US dollar as a global reserve asset and means of exchange.[2]
The project has a target completion date of 2049.[3]
In 2021, Cuba has joined the BRI project for the purpose of expanding its telecommunications and green energy industries.[4] Syria has also joined.[5]
References
- ↑ "President Xi proposes Silk Road economic belt".
- ↑ https://moderndiplomacy.eu/2018/04/09/the-de-dollarization-in-china/
- ↑ https://www.pr.com/press-release/780645
- ↑ "Cuba Formally Joins China's Belt and Road Energy Partnership" (2021-10-18). TeleSUR.
- ↑ "Syria Officially Joins China's Belt and Road, Seeking Lifeline to Defy U.S. Sanctions" (2022-12-01).
