More languages
More actions
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin Владимир Ильич Ленин | |
|---|---|
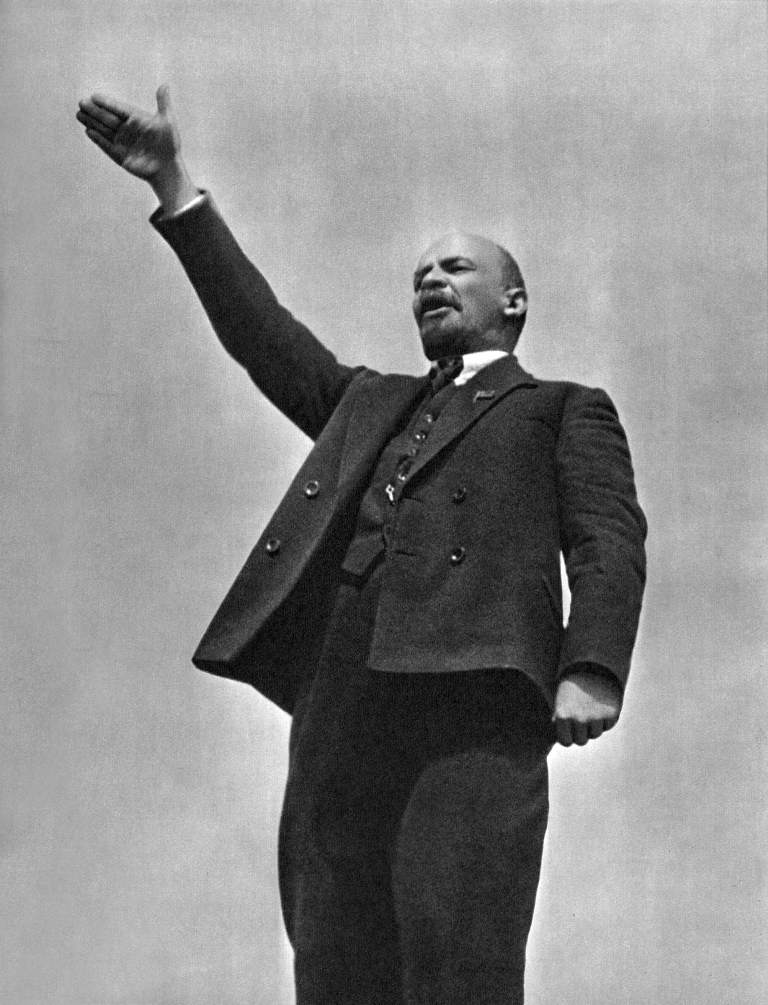 Photo of comrade Lenin | |
| Born | Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov 22 April 1870 Simbirsk, Russian Empire |
| Died | 21 January 1924 (aged 53) Gorki, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union |
| Nationality | Russian Soviet |
| Political orientation | Marxism (developed what is now known as Marxism-Leninism) |
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov[a] (22 April 1870 — 21 January 1924), also known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary leader, political and economic theorist, and philosopher. He is considered one of the most important figures of the 20th century especially as it relates to the socialist movement. Author of several books contributing to Marxist theory, Lenin was responsible for the development of the understanding of the imperialist phenomenon in capitalist mode of production and was a key figure in the 1917 revolution that led to the establishment of the Soviet Union.
Lenin's political and theoretical activity, his writings of the 1890s and the beginning of the 20th century, his resolute struggle against opportunism and revisionist attempts to distort Marxist theory, his struggle for the creation of a revolutionary political party is considered the Leninist contribution to Marxism, now commonly referred to as Marxism-Leninism.
Life and work
Early life (1870–1888)
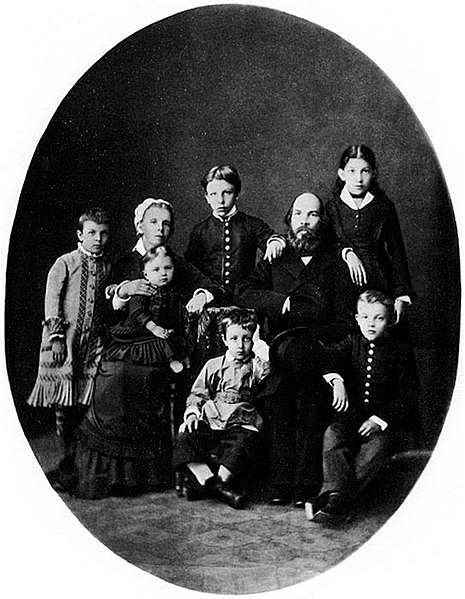

Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov was born in Simbirsk[b] on 22 April 1870[c], the fourth of eight children of Ilya Ulyanov, a respected figure in public education and son of former serf, and Maria Alexandrovna, a woman who came from a family of nobility background.[1] Although Lenin's father was not a revolutionary himself, he shared progressive views and opposed autocracies, and both his father and mother contributed greatly with his intellectual upbringing. Besides his mother and father, a big intellectual influence on Lenin was his brother Alexander, who first introduced him to Marxist literature.[2]
Lenin's youth and childhood coincided with a reactionary period in Russia, when civilians were commonly arrested for expressing criticism of the czarist regime.[2] In May 1887, when Lenin was 17 years old, his brother Alexander Ulyanov was publicly executed for an attempt to assassinate the tzar Alexander III, and event which had an impact in Lenin's radicalization towards revolutionary action.[3]
Lenin was admitted to the Faculty of Law at Kazan University in 13 August 1886, and a month later he joined the Samara-Simbirsk Fraternity, a student society, at the time prohibited by the University Statutes and punishable by expulsion.[2][4] A year after he began his studies, he joined student campaigns and demonstrations demanding that student societies be permitted, that students who had been expelled be reinstated and those responsible for their expulsion be called to account.[2] As a result of participation in the student demonstrations, on December 1887, Lenin was arrested, expelled from University and exiled to a nearby village for one year, becoming under strict police surveillance since then.[2]
Throughout his exile in the village of Kokushkino, Lenin studied extensively political economy works and other literature. Later in his life, he wrote about this period: “I don't think I ever afterwards read so much in my life, not even during my imprisonment in St. Petersburg or exile in Siberia, as I did in the year when I was banished to the village from Kazan; I read voraciously from early morning till late at night.”[2]
In the autumn of 1888, Lenin was permitted to return to Kazan and shortly after returning, but unable to readmit to the university. He was also prohibited from attending universities abroad. Back in Kazan, he joined a Marxist study-circle organized by Nikolai Fedoseyev, beginning his political and revolutionary activities. It was during this period of 1888–89 that Lenin studied for the first time Karl Marx's Capital, vol. I.[2]
Early revolutionary activities (1889–1895)
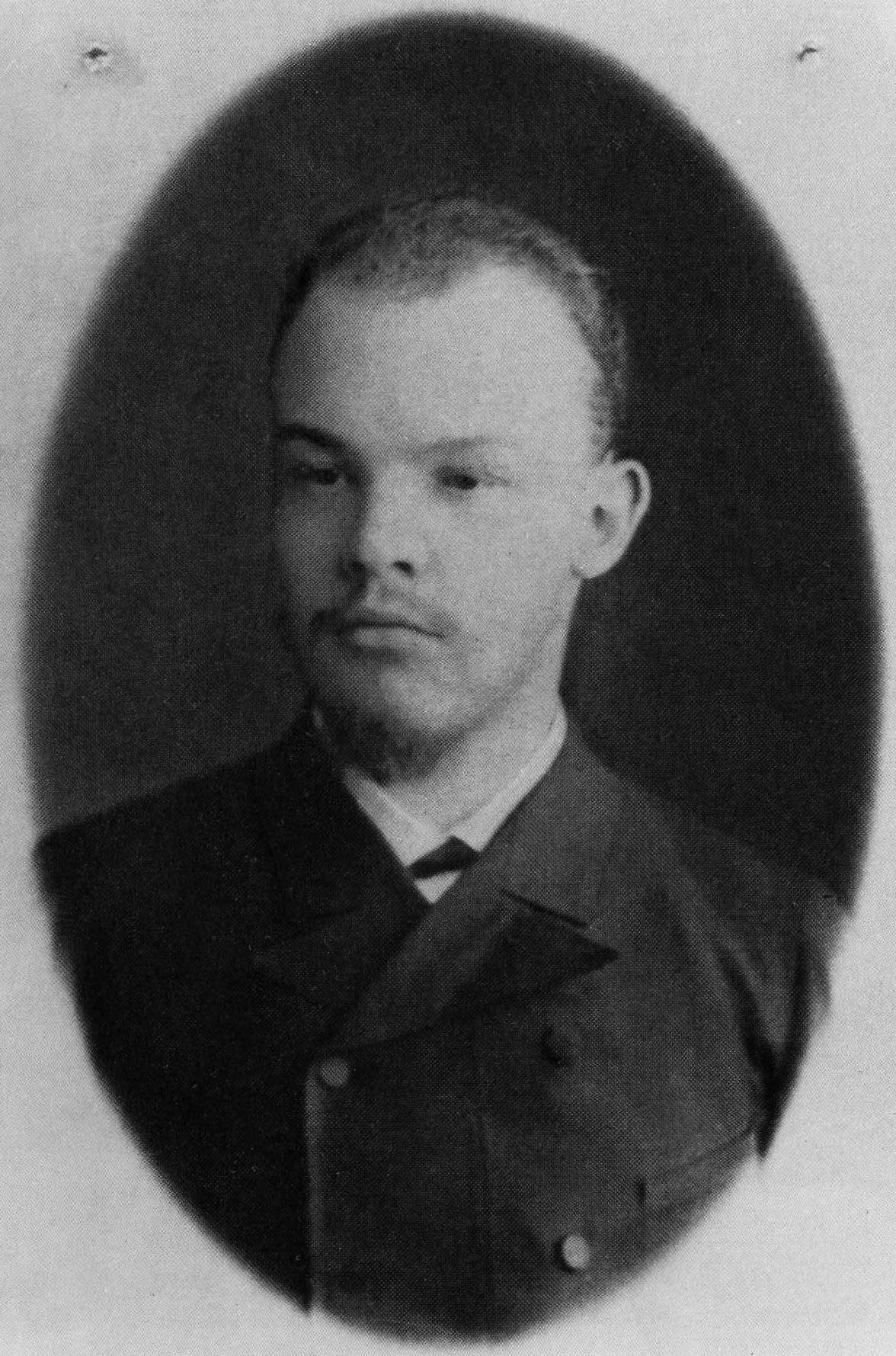
In May 1889, the Ulyanov family moved to a village next to the city of Samara, with Lenin narrowly escaping another arrest by the secret police, which arrested and imprisoned members of Fedoseyev Marxist study-circles of Kazan a month later. In Samara, Lenin earned a living by giving lessons. Considering he was prohibited from attending university, Lenin sent several applications requesting permission to pass his university examinations without attending lectures, until 1890, when he received the permission to do so, along with the task of studying for 18 months independently. After hard work and intense study schedule, he took his examinations in 1891, achieving the highest marks in all subjects, receiving a first-class diploma.[5]
Lenin began to practice law in the Samara Regional Court, and he appeared for defense in court about twenty times during the period of 1892–93. His legal practice, however, was secondary only to diligently studying Marxism to prepare himself for revolutionary work. In 1892, Lenin organized the first Marxist circle in Samara. The study group focused on the works of Marx and Engels, the works of Plekhanov and others.[5] Lenin's legal practice enriched his knowledge of the real world, as this enabled him to see concrete examples of class struggle from the perspective of the economically disenfranchised and the limits of the bourgeois law apparatus.[4]
In 1893, Lenin wrote his earliest theoretical work titled New economic developments in peasant life,[d] an analysis of Russia's economy based on data and statistics on peasant farming.[5] During that time, Lenin corresponded with Nikolai Fedoseyev and exchanged views on Marxist theory and the economic and political developments of Russia.[5] He had a deep affection for their friendship, and years later he wrote: "Fedoseyev played a very important role in the Volga area and in certain parts of Central Russia during that period; and the turn towards Marxism at that time was, undoubtedly, very largely due to the influence of this exceptionally talented and exceptionally devoted revolutionary."[6]
In August 1893, Lenin went to St. Petersburg, where he attended to several Marxist circle meetings, where the sharply criticized the liberal Narodniks, serving as a basis for Lenin's 1894 book What the “friends of the people” are and how they fight the social-democrats?, which was illegally distributed in 3 parts throughout cities of Russia, laying down the theoretical foundation for the program and tactics of the Russian revolutionary social-democrats.[7][4] It was during this period that Lenin first met Nadezhda Krupskaya, which was working as a teacher free of charge for workers.[8]
Establishment of a united Marxist organization and arrest (1895–1897)
In March 1895,[9] Lenin attended a conference in St. Petersburg of members of the social-democratic groups of St. Petersburg, Moscow, Kiev and Vilno. The conference discussed the question of changing over from the propaganda of Marxism in narrow circles to mass political agitation, and of publishing popular literature for the workers and establishing close contact with them. It was decided to send two representatives abroad, and Lenin was one of them.[10]
From May to September, Lenin traveled abroad to meet the social-democrats in exile, mainly Plekhanov, in Berlin, Lenin first met Wilhelm Liebknecht a German social-democrat and in Paris, Lenin met Paul Lafargue, Marx's son-in-law and socialist militant.[11][12][4] In the occasion of Friedrich Engels' death, in August 5, 1895, Lenin wrote a small pamphlet highlighting Engels' contribution to the proletarian cause.[13] In the same year, the Marxist circles of St. Petersburg united into a single political organization under Lenin's leadership. In December this organization adopted the name of League of Struggle for the Emancipation of the Working Class.[e][10] The organization had been active months earlier in agitating workers through pamphlets and participated in strikes, which led to the arrest of Lenin and other leaders of the League in 20 December, 1895. Lenin was accused of "crimes against the state" and was given fourteen months of solitary confinement followed by three years of Siberian exile.[10][4]
During his time in prison, Lenin continued to carry on his revolutionary work. He quickly found ways and means of establishing contacts with comrades who were not arrested and through them directing the activities of the League. Inside his cell, he managed to write the draft program for the first congress of the League and began to write and research for his book The development of capitalism in Russia evading censorship by using milk as invisible ink, which would reveal the writing once warmed or dipped in hot water.[10][14] Krupskaya was able to exchange letters with Lenin by describing herself as Lenin's fianceé, and through her he maintained communication with the members of the League.[15]
Siberian exile (1897–1900)
After more than fourteen months of imprisonment Lenin was sentenced to three years in exile in the village of Shushenskoye in Eastern Siberia under police surveillance. The sentence was announced to him on February 13, 1897.[16] In a 1897 letter to his mother and sister during his exile, Lenin asked them to bring him works written by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels published in French, The poverty of philosophy, Critique of Hegel's philosophy of right, and a chapter of Anti-Dühring.[17] Krupskaya, who was in prison since August 1896 in the same case as Lenin, received permission to join Lenin in Shushenskoye by describing herself as his fianceé in December 1897,[18] and in May 1898 she finally arrived, marrying Lenin a month later.[19][20]
In 1899, Lenin made a profound study on the history of philosophy, reading works by Kant and Hegel, among other philosophers.[21]
Revolutions in Russia (1905–1917)
Soviet government (1918–1923)
Declining health and death (1923–1924)
Library works
- (1902) What is to be done?
- (1905) Two tactics of social-democracy in the democratic revolution
- (1908) Materialism and empiriocriticism
- (1913) The three sources and three component parts of Marxism
- (1916) Imperialism, the highest stage of capitalism
- (1917) The state and revolution
- (1918) The proletarian revolution and the renegade Kautsky
- (1920) “Left-wing” communism, an infantile disorder
References
- ↑ Tamás Krausz (2015). Reconstructing Lenin: an intellectual biography: 'Family'. ISBN 9781583674499 [LG]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Childhood and youth. The beginning of revolutionary activity; The shaping of revolutionary views'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ Robert Service (2000). A biography of Lenin: 'Deaths in the family'. ISBN 9780333726259 [LG]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Tamás Krausz (2015). Reconstructing Lenin: an intellectual biography: 'Who was Lenin?; Education'. ISBN 9781583674499 [LG]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Childhood and youth. The beginning of revolutionary activity; The Samara period'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ Vladimir Lenin (1922). A few words about N. Y. Fedoseyev. [MIA]
- ↑ Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Leader of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia; The ideological defeat of Narodism'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Leader of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia; Among the St. Petersburg Proletariat'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ “2 or 3 March: Lenin takes part in a meeting of members of social democratic groups from St Petersburg, Moscow, Kiev and Vilno. Passing from propaganda work in Marxist circles to mass agitation work is debated.”
Gerda Weber & Hermann Weber (1974). Lenin: life and works: '1895' (p. 7). [LG] - ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Leader of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia; The League of Struggle for the Emancipation of the Working Class'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ “15 May-8 June: Lenin travels to Switzerland; he meets Potresov in Geneva and travels with him to see Plekhanov who is on holiday in the mountain village of Les Ormonts, near Les Diablerets. [...]
Before 8 June: Lenin travels to Paris and gets to know Paul Lafargue, Karl Marx's son-in-law, there. [...]
14 September: In a letter to Wilhelm Liebknecht, Plekhanov recommends Lenin as 'one of our best Russian friends' and requests that Lenin be received because of an 'important matter' as he is returning to Russia. Lenin visits Wilhelm Liebknecht in Charlottenburg between 14-19 September.”
Gerda Weber & Hermann Weber (1974). Lenin: life and works: '1895' (pp. 7-9). [LG] - ↑ “In Europe in 1895, he met the elders of Russian Marxism: Plekhanov and Axelrod in Switzerland, Paul Lafargue (Marx’s son-in-law) in Paris and Wilhelm Liebknecht in Berlin.”
Tariq Ali (2017). The dilemmas of Lenin: 'Terrorism and utopia; The younger brother' (pp. 44-45). [LG] - ↑ Vladimir Lenin (1895). Friedrich Engels. [MIA]
- ↑ “They came written in milk every Saturday, which was book-receiving day. A glance at the secret mark would tell you that the book contained a message. Hot water for tea would be handed round at six o'clock, and then the wardress would conduct the non-political criminals to church. By that time you bad the letter cut up in strips, and your tea brewed, and the moment the wardress went away you would begin dipping the strips in the hot tea to develop the text.”
Nadezhda Krupskaya (1933). Reminiscences of Lenin: 'St. Petersburg'. [MIA] - ↑ “So-and-so had no one coming to visit him – it was necessary to get him a "fiancee": or so-and-so had to be told through visiting relatives to look for letters in such-and-such a book in the prison library, on such-and-such a page; another needed warm boots, and so on.”
Nadezhda Krupskaya (1933). Reminiscences of Lenin: 'St. Petersburg'. [MIA] - ↑ Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Siberian exile' (p. 51). Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ “I should like to have Saint-Simon and also the following books in French:
K. Marx. Misère de la philosophie. 1896. Paris.
Fr. Engels. La force et l’ économic dans le développement social.
K. Marx. Critique de la philosophie du droit de Hegel. 1895.
all these are from the “bibliothèque socialiste internationale” where Labriola came from.
All the best,
V. U.”
Vladimir Lenin (1897). December 21, 1897 letter to his mother and sister. [MIA] - ↑ “I was banished to the Ufa Gubernia for three years, but obtained a transfer to the village of Shushenskoye in the Minusinsk Uyezd, where Vladimir Ilyich lived, by describing myself as his fiancee.”
Nadezhda Krupskaya (1933). Reminiscences of Lenin: 'St. Petersburg'. [MIA] - ↑ “Krupskaya arrived in Shushenskoye early in May 1898 together with her mother Yelizaveta Vasilyevna. Lenin and Krupskaya were married on July 10. They set up house together, started a small kitchen garden, planted flowers and hops in the yard. The young couple lived in peace and harmony.”
Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Siberian exile' (p. 54). Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG] - ↑ “The name of his love, Nadezhda Konstantinovna Krupskaya—who was arrested in the same case as Vladimir Ilyich albeit much later, on 12 August 1896—came up often in his letters. In his letters from 19 October, 10 December, and 21 December 1896 (from Shusha to Moscow, addressed to his mother, Manya, and Anyuta), he wrote to his relatives that Nadezhda Konstantinovna might join him soon, for she had received permission to choose Shushenskoye instead of northern Russia”
Tamás Krausz (2015). Reconstructing Lenin: an intellectual biography: 'Who was Lenin?; The personality of Lenin as a young man in exile and as an émigré'. ISBN 9781583674499 [LG] - ↑ “I have started with Holbach and Helvètius, and am now taking up Kant. I have got hold of the chief works of the chief classical philosophers, but I do not have the neo-Kantian books (I have only ordered Lange). Tell me, please, whether you or your comrades have them and whether you could not share them with me.”
Vladimir Lenin (1899). June 27, 1899 letter to A.N. Potresov. [MIA]
Notes
- ↑ Russian: Владимир Ильич Ульянов
- ↑ Russian: Симбирск
The city of Simbirsk was the administrative center of Simbirsk Governorate, which was one of the administrative divisions of the Russian Empire. The city is now known as Ulyanovsk, of the Ulyanovsk Region in the Russian Federation, in honor of Lenin. - ↑ Current calendar (Gregorian)
- ↑ The article is available on Marxists Internet Archive.
- ↑ Russian: Союз борьбы за освобождение рабочего класса, lit. Union of Struggle for the Emancipation of the Working Class
