(→Early revolutionary activities (1889–1904): Added two more paragraphs. Perhaps a summarization will be needed later, and this information may be transferred to an article specifically about the life of Lenin) Tag: Visual edit |
(→Early revolutionary activities (1889–1904): Added text into lede and updated some section titles) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov'''<ref group="lower-alpha">Russian: Владимир Ильич Ульянов</ref> (22 April 1870 — 21 January 1924), also known as '''Vladimir Lenin''', was a [[Russia|Russian]] revolutionary leader, [[Political economy|political and economic]] theorist, and philosopher. He is considered one of the most important figures of the 20th century especially as it relates to the [[socialism|socialist]] movement. Author of several books contributing to [[Marxism|Marxist theory]], Lenin was responsible for the development of the understanding of the [[Imperialism|imperialist]] phenomenon in capitalist mode of production and was a key figure in the [[October Revolution|1917 revolution]] that led to the establishment of the [[Soviet Union]]. | '''Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov'''<ref group="lower-alpha">Russian: Владимир Ильич Ульянов</ref> (22 April 1870 — 21 January 1924), also known as '''Vladimir Lenin''', was a [[Russia|Russian]] revolutionary leader, [[Political economy|political and economic]] theorist, and philosopher. He is considered one of the most important figures of the 20th century especially as it relates to the [[socialism|socialist]] movement. Author of several books contributing to [[Marxism|Marxist theory]], Lenin was responsible for the development of the understanding of the [[Imperialism|imperialist]] phenomenon in capitalist mode of production and was a key figure in the [[October Revolution|1917 revolution]] that led to the establishment of the [[Soviet Union]]. | ||
Lenin's political and theoretical activity, his writings of the 1890s and the beginning of the 20th century, his resolute struggle against [[opportunism]] and [[Revisionism|revisionist]] attempts to distort Marxist theory, his struggle for the creation of a revolutionary [[political party]] is considered the Leninist contribution to Marxism, now commonly referred to as [[Marxism–Leninism|Marxism-Leninism]]. | |||
==Life and work== | ==Life and work== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 33: | ||
In the autumn of 1888, Lenin was permitted to return to Kazan and shortly after returning, but unable to readmit to the university. He was also prohibited from attending universities abroad. Back in Kazan, he joined a Marxist study-circle organized by Nikolai Fedoseyev, beginning his political and revolutionary activities. It was during this period of 1888–89 that Lenin studied for the first time [[Karl Marx]]'s [[Capital, vol. I]].<ref name="cpsubio1-2" /> | In the autumn of 1888, Lenin was permitted to return to Kazan and shortly after returning, but unable to readmit to the university. He was also prohibited from attending universities abroad. Back in Kazan, he joined a Marxist study-circle organized by Nikolai Fedoseyev, beginning his political and revolutionary activities. It was during this period of 1888–89 that Lenin studied for the first time [[Karl Marx]]'s [[Capital, vol. I]].<ref name="cpsubio1-2" /> | ||
===Early revolutionary activities ( | ===Early revolutionary activities (1889–1895)=== | ||
[[File:Vladimir Lenin (1891).png|thumb|227x227px|Lenin in 1891]] | [[File:Vladimir Lenin (1891).png|thumb|227x227px|Lenin in 1891]] | ||
In May 1889, the Ulyanov family moved to a village next to the city of Samara, with Lenin narrowly escaping another arrest by the secret police, which arrested and imprisoned members of Fedoseyev [[Marxism|Marxist]] study-circles of Kazan a month later. In Samara, Lenin earned a living by giving lessons. Considering he was prohibited from attending university, Lenin sent several applications requesting permission to pass his university examinations without attending lectures, until 1890, when he received the permission to do so, along with the task of studying for 18 months independently. After hard work and intense study schedule, he took his examinations in 1891, achieving the highest marks in all subjects, receiving a first-class diploma.<ref name="cpsubio1-3">{{Citation|author=Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism|year=1965|title=Lenin: a biography|chapter=Childhood and youth. The beginning of revolutionary activity|section=The Samara period|page=|quote=|pdf=|city=Moscow|publisher=Progress Publishers, CC CPSU|isbn=|doi=|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=EB243CBDFE643F26EEB1360F866F261F|mia=|title-url=|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref> | In May 1889, the Ulyanov family moved to a village next to the city of Samara, with Lenin narrowly escaping another arrest by the secret police, which arrested and imprisoned members of Fedoseyev [[Marxism|Marxist]] study-circles of Kazan a month later. In Samara, Lenin earned a living by giving lessons. Considering he was prohibited from attending university, Lenin sent several applications requesting permission to pass his university examinations without attending lectures, until 1890, when he received the permission to do so, along with the task of studying for 18 months independently. After hard work and intense study schedule, he took his examinations in 1891, achieving the highest marks in all subjects, receiving a first-class diploma.<ref name="cpsubio1-3">{{Citation|author=Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism|year=1965|title=Lenin: a biography|chapter=Childhood and youth. The beginning of revolutionary activity|section=The Samara period|page=|quote=|pdf=|city=Moscow|publisher=Progress Publishers, CC CPSU|isbn=|doi=|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=EB243CBDFE643F26EEB1360F866F261F|mia=|title-url=|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref> | ||
Lenin began to practice law in the Samara Regional Court, and he appeared for defense in court about twenty times during the period of 1892–93. His legal practice, however, was secondary only to diligently studying Marxism to prepare himself for revolutionary work. In 1892, Lenin organized the first Marxist circle in Samara. The study group focused on the works of [[Karl Marx|Marx]] and [[Friedrich Engels|Engels]], the works of [[Plekhanov]] and others.<ref name="cpsubio1-3" /> | Lenin began to practice law in the Samara Regional Court, and he appeared for defense in court about twenty times during the period of 1892–93. His legal practice, however, was secondary only to diligently studying Marxism to prepare himself for revolutionary work. In 1892, Lenin organized the first Marxist circle in Samara. The study group focused on the works of [[Karl Marx|Marx]] and [[Friedrich Engels|Engels]], the works of [[Plekhanov]] and others.<ref name="cpsubio1-3" /> Lenin's legal practice enriched his knowledge of the real world, as this enabled him to see concrete examples of class struggle from the perspective of the economically disenfranchised and the limits of the bourgeois law apparatus.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In 1893, Lenin wrote his earliest theoretical work titled ''New economic developments in peasant life'',<ref group="lower-alpha">The article is available on [https://www.marxists.org/archive/lenin/works/1893/ned/index.htm Marxists Internet Archive].</ref> an analysis of Russia's economy based on data and statistics on peasant farming.<ref name="cpsubio1-3" /> During that time, Lenin corresponded with Nikolai Fedoseyev and exchanged views on Marxist theory and the economic and political developments of [[Russian Empire|Russia]].<ref name="cpsubio1-3" /> He had a deep affection for their friendship, and years later he wrote: "Fedoseyev played a very important role in the Volga area and in certain parts of Central Russia during that period; and the turn towards Marxism at that time was, undoubtedly, very largely due to the influence of this exceptionally talented and exceptionally devoted revolutionary."<ref>{{Citation|author=Vladimir Lenin|year=1922|title=A few words about N. Y. Fedoseyev|chapter=|section=|page=|quote=|pdf=|city=|publisher=|isbn=|doi=|lg=|mia=https://www.marxists.org/archive/lenin/works/1922/dec/06.htm|title-url=|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref> | |||
In August 1893, Lenin went to St. Petersburg, where he attended to several Marxist circle meetings, where the sharply criticized the [[Liberalism|liberal]] Narodniks, serving as a basis for Lenin's 1894 book [[What the “friends of the people” are and how they fight the social-democrats? (1894)|''What the “friends of the people” are and how they fight the social-democrats?'']], which was illegally distributed throughout cities of Russia, laying down the theoretical foundation for the program and tactics of the Russian revolutionary social-democrats.<ref name="cpsubio2-2">{{Citation|author=Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism|year=1965|title=Lenin: a biography|chapter=Leader of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia|section=The ideological defeat of Narodism|page=|quote=|pdf=|city=Moscow|publisher=Progress Publishers, CC CPSU|isbn=|doi=|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=EB243CBDFE643F26EEB1360F866F261F|mia=|title-url=|chapter-url=|trans-title=|trans-lang=}}</ref><ref name=":1" /> | |||
=== Establishment of a united Marxist organization (1895–1897) === | |||
=== Siberian exile (1897–1900) === | |||
===Revolutions in Russia (1905–1917)=== | ===Revolutions in Russia (1905–1917)=== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 53: | ||
===Declining health and death (1923–1924)=== | ===Declining health and death (1923–1924)=== | ||
== Library works == | ==Library works== | ||
* (1902) [[Library:What is to be done?|What is to be done?]] | *(1902) [[Library:What is to be done?|What is to be done?]] | ||
* (1905) [[Library:Two tactics of social-democracy in the democratic revolution|Two tactics of social-democracy in the democratic revolution]] | *(1905) [[Library:Two tactics of social-democracy in the democratic revolution|Two tactics of social-democracy in the democratic revolution]] | ||
* (1908) [[Library:Materialism and empiriocriticism|Materialism and empiriocriticism]] | *(1908) [[Library:Materialism and empiriocriticism|Materialism and empiriocriticism]] | ||
* (1913) [[Library:The three sources and three component parts of Marxism|The three sources and three component parts of Marxism]] | *(1913) [[Library:The three sources and three component parts of Marxism|The three sources and three component parts of Marxism]] | ||
* (1916) [[Library:Imperialism, the highest stage of capitalism|Imperialism, the highest stage of capitalism]] | *(1916) [[Library:Imperialism, the highest stage of capitalism|Imperialism, the highest stage of capitalism]] | ||
* (1917) [[Library:The state and revolution|The state and revolution]] | *(1917) [[Library:The state and revolution|The state and revolution]] | ||
* (1918) [[Library:The proletarian revolution and the renegade Kautsky|The proletarian revolution and the renegade Kautsky]] | *(1918) [[Library:The proletarian revolution and the renegade Kautsky|The proletarian revolution and the renegade Kautsky]] | ||
* (1920) [[Library:"Left-wing" communism, an infantile disorder|“Left-wing” communism, an infantile disorder]] | *(1920) [[Library:"Left-wing" communism, an infantile disorder|“Left-wing” communism, an infantile disorder]] | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 03:27, 13 December 2021
Vladimir Ilyich Lenin Владимир Ильич Ленин | |
|---|---|
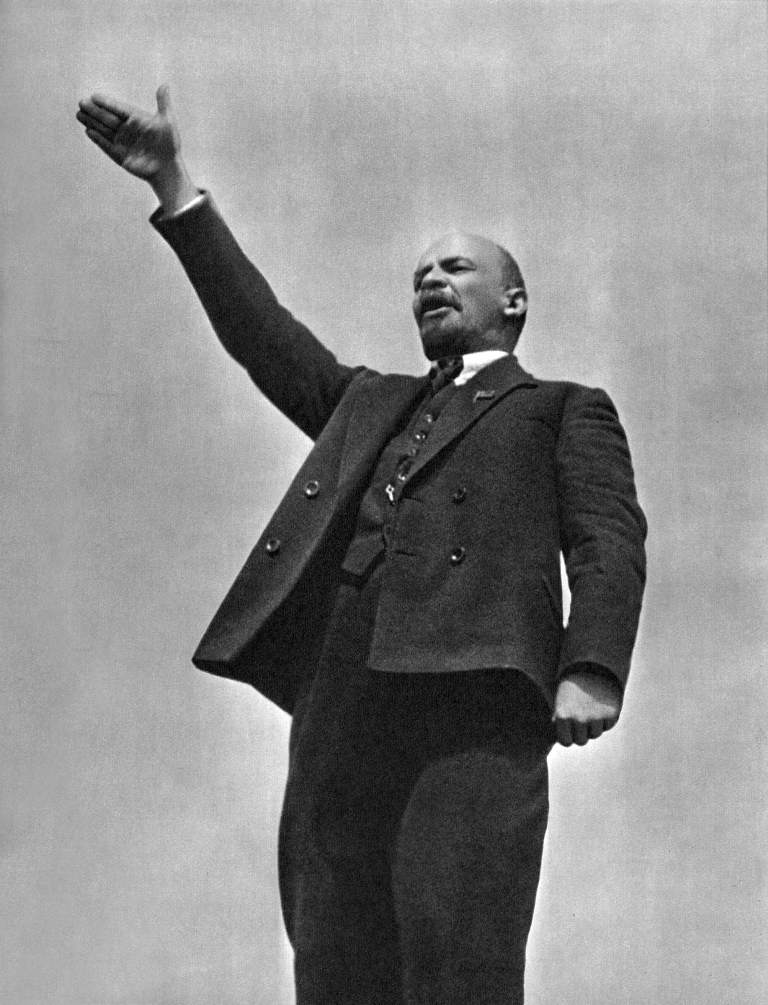 Photo of comrade Lenin | |
| Born | Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov 22 April 1870 Simbirsk, Russian Empire |
| Died | 21 January 1924 (aged 53) Gorki, Russian SFSR, Soviet Union |
| Nationality | Russian Soviet |
| Political orientation | Marxism (developed what is now known as Marxism-Leninism) |
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov[a] (22 April 1870 — 21 January 1924), also known as Vladimir Lenin, was a Russian revolutionary leader, political and economic theorist, and philosopher. He is considered one of the most important figures of the 20th century especially as it relates to the socialist movement. Author of several books contributing to Marxist theory, Lenin was responsible for the development of the understanding of the imperialist phenomenon in capitalist mode of production and was a key figure in the 1917 revolution that led to the establishment of the Soviet Union.
Lenin's political and theoretical activity, his writings of the 1890s and the beginning of the 20th century, his resolute struggle against opportunism and revisionist attempts to distort Marxist theory, his struggle for the creation of a revolutionary political party is considered the Leninist contribution to Marxism, now commonly referred to as Marxism-Leninism.
Life and work
Early life (1870–1888)
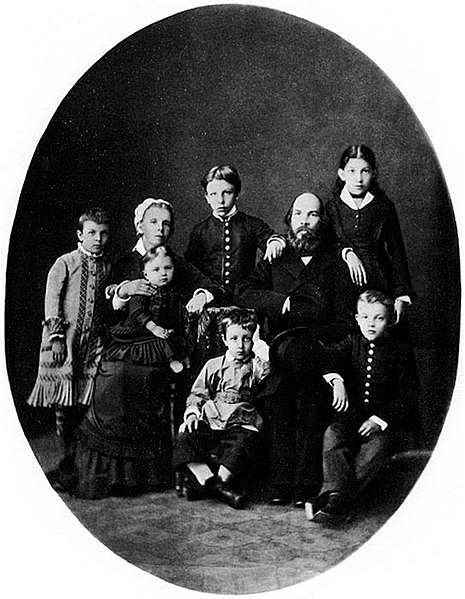

Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov was born in Simbirsk[b] on 22 April 1870[c], the fourth of eight children of Ilya Ulyanov, a respected figure in public education and son of former serf, and Maria Alexandrovna, a woman who came from a family of nobility background.[1] Although Lenin's father was not a revolutionary himself, he shared progressive views and opposed autocracies, and both his father and mother contributed greatly with his intellectual upbringing. Besides his mother and father, a big intellectual influence on Lenin was his brother Alexander, who first introduced him to Marxist literature.[2]
Lenin's youth and childhood coincided with a reactionary period in Russia, when civilians were commonly arrested for expressing criticism of the czarist regime.[2] In May 1887, when Lenin was 17 years old, his brother Alexander Ulyanov was publicly executed for an attempt to assassinate the tzar Alexander III, and event which had an impact in Lenin's radicalization towards revolutionary action.[3]
Lenin was admitted to the Faculty of Law at Kazan University in 13 August 1886, and a month later he joined the Samara-Simbirsk Fraternity, a student society, at the time prohibited by the University Statutes and punishable by expulsion.[2][4] A year after he began his studies, he joined student campaigns and demonstrations demanding that student societies be permitted, that students who had been expelled be reinstated and those responsible for their expulsion be called to account.[2] As a result of participation in the student demonstrations, on December 1887, Lenin was arrested, expelled from University and exiled to a nearby village for one year, becoming under strict police surveillance since then.[2]
Throughout his exile in the village of Kokushkino, Lenin studied extensively political economy works and other literature. Later in his life, he wrote about this period: “I don't think I ever afterwards read so much in my life, not even during my imprisonment in St. Petersburg or exile in Siberia, as I did in the year when I was banished to the village from Kazan; I read voraciously from early morning till late at night.”[2]
In the autumn of 1888, Lenin was permitted to return to Kazan and shortly after returning, but unable to readmit to the university. He was also prohibited from attending universities abroad. Back in Kazan, he joined a Marxist study-circle organized by Nikolai Fedoseyev, beginning his political and revolutionary activities. It was during this period of 1888–89 that Lenin studied for the first time Karl Marx's Capital, vol. I.[2]
Early revolutionary activities (1889–1895)
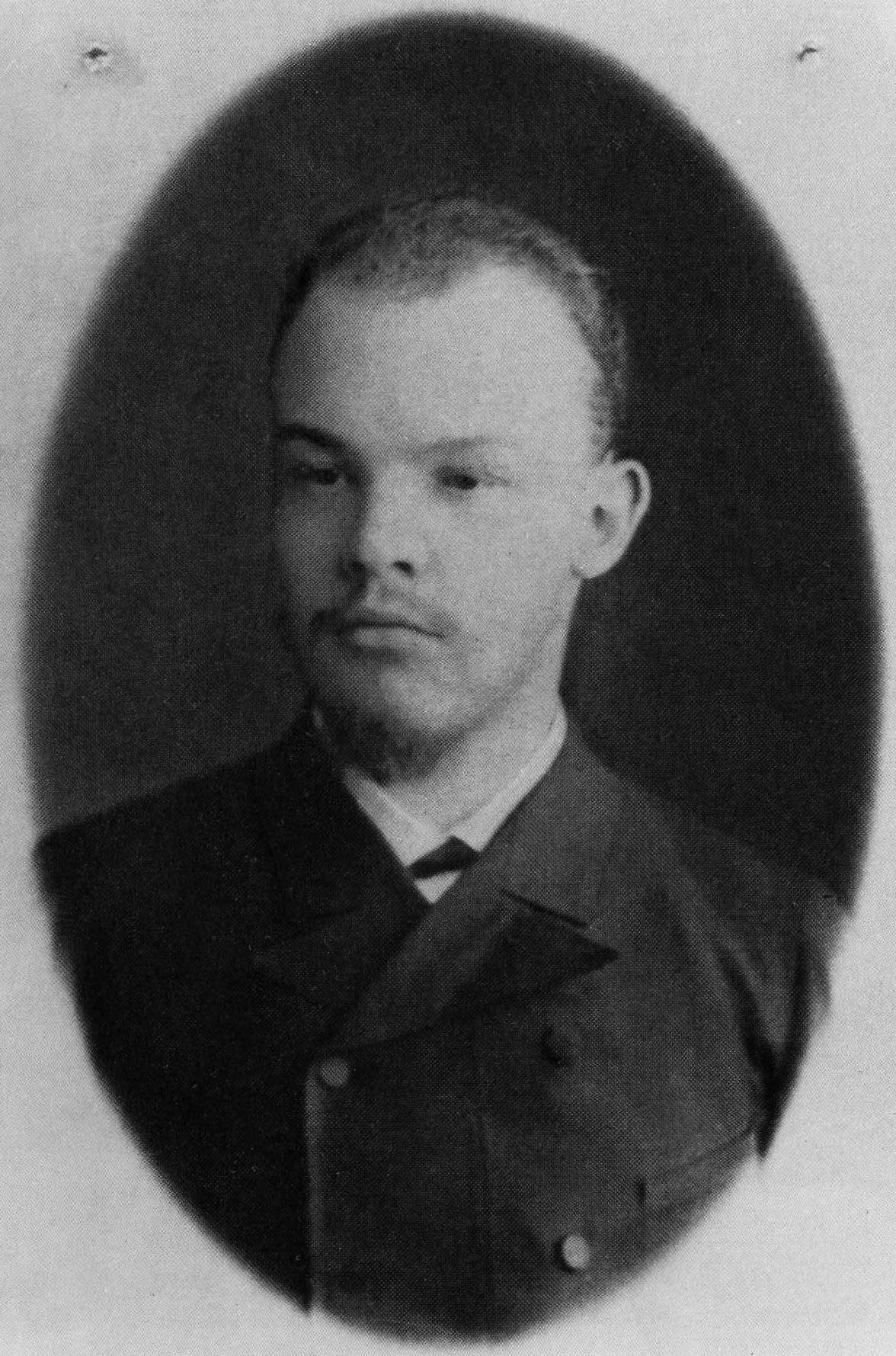
In May 1889, the Ulyanov family moved to a village next to the city of Samara, with Lenin narrowly escaping another arrest by the secret police, which arrested and imprisoned members of Fedoseyev Marxist study-circles of Kazan a month later. In Samara, Lenin earned a living by giving lessons. Considering he was prohibited from attending university, Lenin sent several applications requesting permission to pass his university examinations without attending lectures, until 1890, when he received the permission to do so, along with the task of studying for 18 months independently. After hard work and intense study schedule, he took his examinations in 1891, achieving the highest marks in all subjects, receiving a first-class diploma.[5]
Lenin began to practice law in the Samara Regional Court, and he appeared for defense in court about twenty times during the period of 1892–93. His legal practice, however, was secondary only to diligently studying Marxism to prepare himself for revolutionary work. In 1892, Lenin organized the first Marxist circle in Samara. The study group focused on the works of Marx and Engels, the works of Plekhanov and others.[5] Lenin's legal practice enriched his knowledge of the real world, as this enabled him to see concrete examples of class struggle from the perspective of the economically disenfranchised and the limits of the bourgeois law apparatus.[4]
In 1893, Lenin wrote his earliest theoretical work titled New economic developments in peasant life,[d] an analysis of Russia's economy based on data and statistics on peasant farming.[5] During that time, Lenin corresponded with Nikolai Fedoseyev and exchanged views on Marxist theory and the economic and political developments of Russia.[5] He had a deep affection for their friendship, and years later he wrote: "Fedoseyev played a very important role in the Volga area and in certain parts of Central Russia during that period; and the turn towards Marxism at that time was, undoubtedly, very largely due to the influence of this exceptionally talented and exceptionally devoted revolutionary."[6]
In August 1893, Lenin went to St. Petersburg, where he attended to several Marxist circle meetings, where the sharply criticized the liberal Narodniks, serving as a basis for Lenin's 1894 book What the “friends of the people” are and how they fight the social-democrats?, which was illegally distributed throughout cities of Russia, laying down the theoretical foundation for the program and tactics of the Russian revolutionary social-democrats.[7][4]
Establishment of a united Marxist organization (1895–1897)
Siberian exile (1897–1900)
Revolutions in Russia (1905–1917)
Soviet government (1918–1923)
Declining health and death (1923–1924)
Library works
- (1902) What is to be done?
- (1905) Two tactics of social-democracy in the democratic revolution
- (1908) Materialism and empiriocriticism
- (1913) The three sources and three component parts of Marxism
- (1916) Imperialism, the highest stage of capitalism
- (1917) The state and revolution
- (1918) The proletarian revolution and the renegade Kautsky
- (1920) “Left-wing” communism, an infantile disorder
References
- ↑ Tamás Krausz (2015). Reconstructing Lenin: an intellectual biography: 'Family'. ISBN 9781583674499 [LG]
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Childhood and youth. The beginning of revolutionary activity; The shaping of revolutionary views'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ Robert Service (2000). A biography of Lenin: 'Deaths in the family'. ISBN 9780333726259 [LG]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Tamás Krausz (2015). Reconstructing Lenin: an intellectual biography: 'Education'. ISBN 9781583674499 [LG]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Childhood and youth. The beginning of revolutionary activity; The Samara period'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
- ↑ Vladimir Lenin (1922). A few words about N. Y. Fedoseyev. [MIA]
- ↑ Pyotr Pospelov & Institute of Marxism-Leninism (1965). Lenin: a biography: 'Leader of the revolutionary proletariat of Russia; The ideological defeat of Narodism'. Moscow: Progress Publishers, CC CPSU. [LG]
Notes
- ↑ Russian: Владимир Ильич Ульянов
- ↑ Russian: Симбирск
The city of Simbirsk was the administrative center of Simbirsk Governorate, which was one of the administrative divisions of the Russian Empire. The city is now known as Ulyanovsk, of the Ulyanovsk Region in the Russian Federation, in honor of Lenin. - ↑ Current calendar (Gregorian)
- ↑ The article is available on Marxists Internet Archive.