More languages
More actions
- Not to be confused with Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau or Papua New Guinea
Republic of Guinea ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫ ߞߊ ߝߊߛߏߦߊߡߊߣߊ
𞤸𞤢𞤱𞤼𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤲'𞤣𞤭 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫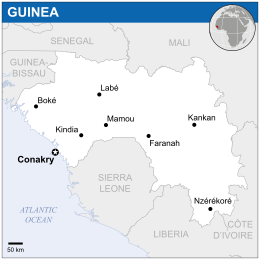
Capital and largest cityConakry Dominant mode of production Capitalism Government Military junta • Interim PresidentMamady Doumbouya • Prime MinisterBah Oury Area • Total245,857 km² Population • 2024 estimate13,986,179 Currency Guinean franc (GNF) Calling code +224 ISO 3166 code GN Internet TLD .gn Guinea, officially the Republic of Guinea, is a country in West Africa with a coast on the Atlantic Ocean to the west. Guinea borders Guinea-Bissau to the northwest, Senegal to the north, Mali to the northeast, Côte d'Ivoire to the east and Sierra Leone and Liberia to the south.
History[edit | edit source]
Precolonial history[edit | edit source]
See main article: Wassoulou Empire
Colonial period[edit | edit source]
Portuguese ships began appearing off the coast of Guinea in the 15th century, and for the next few centuries Europeans would use the people of Guinea in the Transatlantic slave trade, rapidly depopulating the coastal regions. Direct colonial conquest began in the late 19th century with France sending troops in under the pretense of "protecting European traders." France was joined in competition for the territory by Germany and the United Kingdom but France ultimately triumphed and established a protectorate, with colonial rule lasting until 1958.[1]
People's Revolutionary Republic (1958–1984)[edit | edit source]
See main article: People's Revolutionary Republic of Guinea
Conté dictatorship[edit | edit source]
Camara dictatorship[edit | edit source]
Condé presidency[edit | edit source]
2021 coup d'état[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ N. I. Gavrilov (1979). The Great Soviet Encyclopedia: 'Guinea, Republic of; The colonial conquest of Guinea'.


