United States imperialism: Difference between revisions
Verda.Majo (talk | contribs) (→Economic domination: moved a misplaced paragraph from World Bank section to IMF section and added quotation about each) Tag: Visual edit |
(Added map) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:US military | [[File:US military interventions map.png|thumb|388x388px|Red countries have been invaded or militarily intervened in by the United States since 1798.]] | ||
''' | '''United States imperialism''' consists of policies aimed at extending the economic, political, cultural and military influence of the [[United States of America|United States]] over areas beyond its boundaries, especially considering the [[Marxism|Marxist]] definition of [[imperialism]] as originally defined by [[Vladimir Lenin|Lenin]], but other aspects of imperialism as well, such as military operations and economic terrorism. | ||
Doctrines followed (and sometimes proposed by the U.S. government itself since its inception) such as [[Manifest Destiny]], Monroe and his Roosevelt Chorolary, the Big Stick, the National Security Doctrine, etc. and events such as the conquest of the West, the Mexican war, the banana wars, the Spanish-Cuban-American war and, more recently, the [[Vietnam War]], the U.S. blockade against [[Republic of Cuba|Cuba]], the [[war in Afghanistan]], etc. have made "American imperialism" a term accepted by the greater part of the international community. | Doctrines followed (and sometimes proposed by the U.S. government itself since its inception) such as [[Manifest Destiny]], Monroe and his Roosevelt Chorolary, the Big Stick, the National Security Doctrine, etc. and events such as the conquest of the West, the Mexican war, the banana wars, the Spanish-Cuban-American war and, more recently, the [[Vietnam War]], the U.S. blockade against [[Republic of Cuba|Cuba]], the [[war in Afghanistan]], etc. have made "American imperialism" a term accepted by the greater part of the international community. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Military bases == | == Military bases == | ||
[[File:US military bases.png|thumb|Map of U.S. military bases and troops deployed abroad.|374x374px]] | |||
The United States has 750 military bases around the world in at least 80 countries. It also has 173,000 troops deployed in foreign countries. The country with the most U.S. military presence besides the U.S. itself is [[Japan]], with 120 bases and over 53,000 troops. Japan is followed by [[Federal Republic of Germany|Germany]] and then [[Republic of Korea|South Korea]].<ref>{{News citation|newspaper=[[Monthly Review]]|title=Mapping U.S. Imperialism|date=2022-06-06|url=https://mronline.org/2022/06/06/mapping-u-s-imperialism/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220614004514/https://mronline.org/2022/06/06/mapping-u-s-imperialism/|archive-date=2022-06-14|retrieved=2022-06-17}}</ref> | The United States has 750 military bases around the world in at least 80 countries. It also has 173,000 troops deployed in foreign countries. The country with the most U.S. military presence besides the U.S. itself is [[Japan]], with 120 bases and over 53,000 troops. Japan is followed by [[Federal Republic of Germany|Germany]] and then [[Republic of Korea|South Korea]].<ref>{{News citation|newspaper=[[Monthly Review]]|title=Mapping U.S. Imperialism|date=2022-06-06|url=https://mronline.org/2022/06/06/mapping-u-s-imperialism/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220614004514/https://mronline.org/2022/06/06/mapping-u-s-imperialism/|archive-date=2022-06-14|retrieved=2022-06-17}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 23:05, 22 September 2022
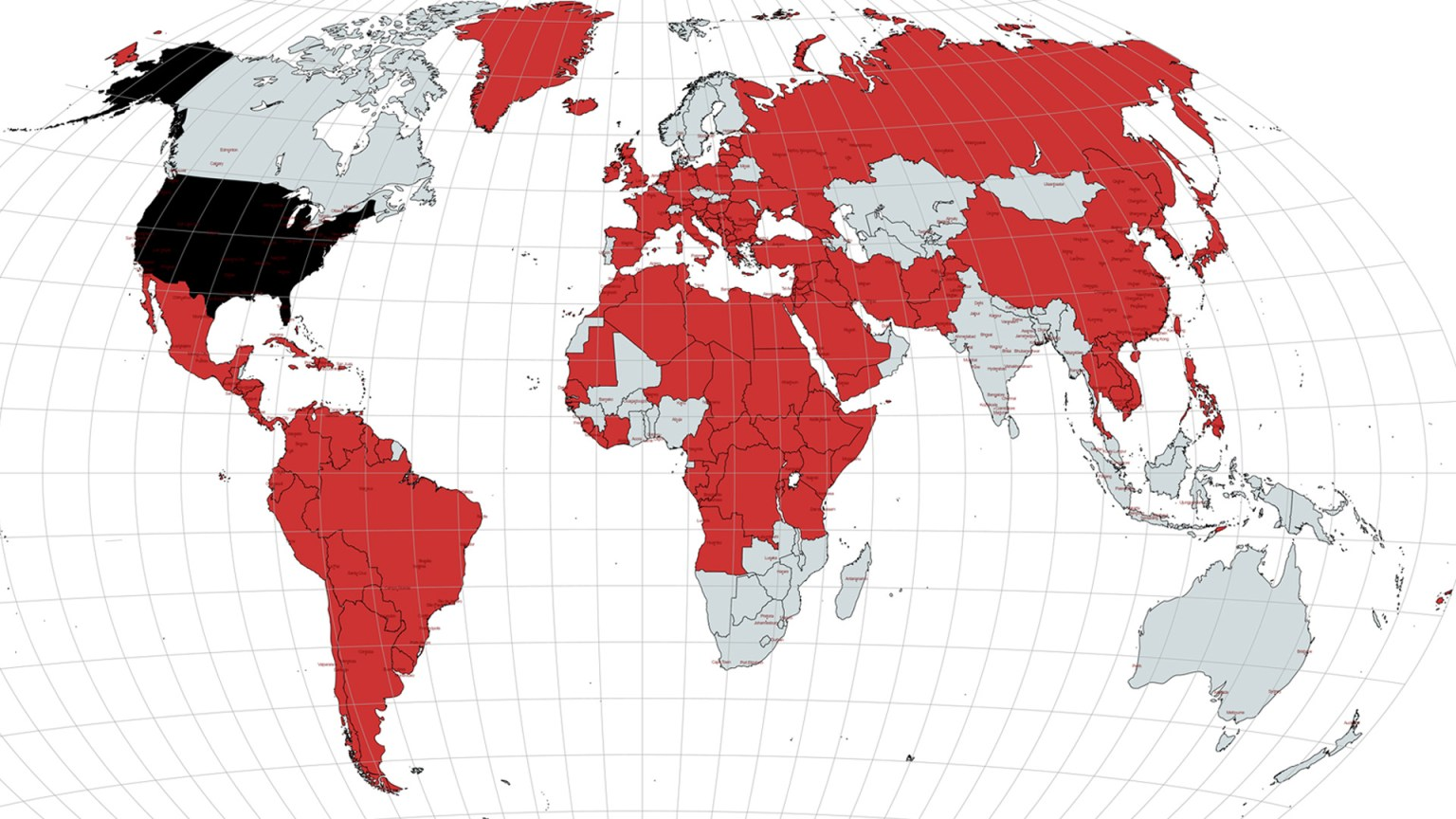
United States imperialism consists of policies aimed at extending the economic, political, cultural and military influence of the United States over areas beyond its boundaries, especially considering the Marxist definition of imperialism as originally defined by Lenin, but other aspects of imperialism as well, such as military operations and economic terrorism.
Doctrines followed (and sometimes proposed by the U.S. government itself since its inception) such as Manifest Destiny, Monroe and his Roosevelt Chorolary, the Big Stick, the National Security Doctrine, etc. and events such as the conquest of the West, the Mexican war, the banana wars, the Spanish-Cuban-American war and, more recently, the Vietnam War, the U.S. blockade against Cuba, the war in Afghanistan, etc. have made "American imperialism" a term accepted by the greater part of the international community.
The United States has interfered in the elections of 45 foreign countries[1] and organized over 132 CIA and military interventions around the world since 1890,[2] in addition to almost 100 before 1890.[3]
History
Between 1798 and 1827, the United States participated 23 military interventions, including in Greece, Libya, and Cuba. It did 71 interventions between 1831 and 1896 on all continents except Antarctica. The U.S. did 40 interventions between 1898 and 1919.[3]
According to a report by the Congressional Research Service, a US government institution that compiles information on behalf of Congress, the United States launched at least 251 military interventions between 1991 and 2022. The report documented another 218 US military interventions between 1798 and 1990. This adds up to a total of 469 US military interventions since 1798 that have been acknowledged by the Congress. Of the total 469 documented foreign military interventions, the Congressional Research Service noted that the US government only formally declared war 11 times, in just five separate wars.[4] In an analysis of the report, journalist Benjamin Norton noted that the data excludes the independence war been US settlers and the British empire, any military deployments between 1776 and 1798, excludes the deployment of the US military forces against Indigenous peoples, when they were systematically ethnically cleansed in the violent process of westward settler-colonial expansion, and the US Civil War, and further noted that all of these numbers are conservative estimates, because they do not include US special operations, covert actions, or domestic deployments.[5]
Death toll
Austin Murphy estimates that U.S. imperialism and colonialism have intentionally killed over 11 million unarmed civilians, including five million indigenous people, a million Filipinos, 500,000 German and Japanese people, over 500,000 Indonesians, over a million each of Vietnamese, Iraqis, and Koreans, and over 500,000 Cambodians. This is a low estimate and Murphy acknowledges that the deaths of indigenous people in North America alone is over 18 million.[6]
Military bases
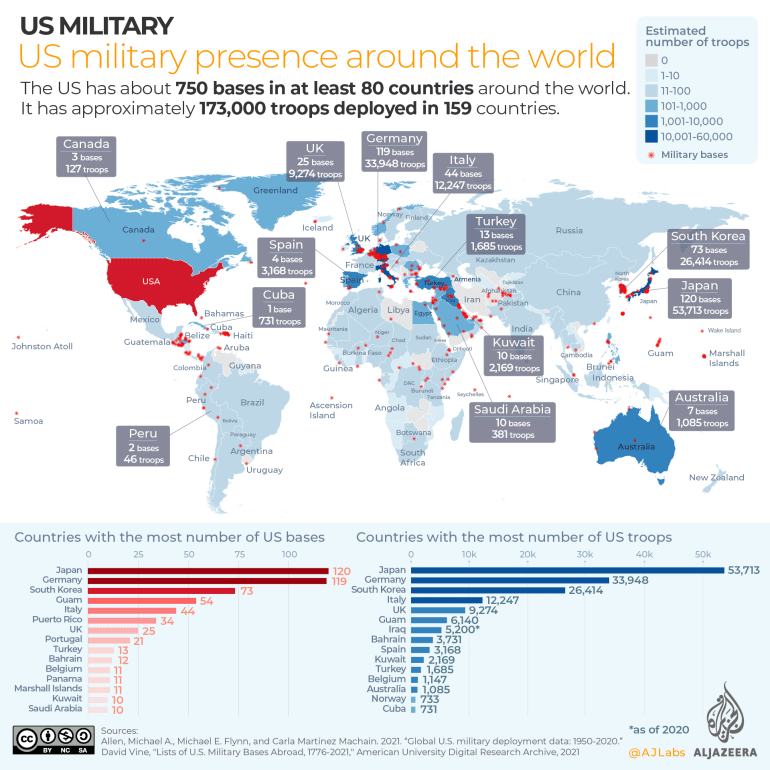
The United States has 750 military bases around the world in at least 80 countries. It also has 173,000 troops deployed in foreign countries. The country with the most U.S. military presence besides the U.S. itself is Japan, with 120 bases and over 53,000 troops. Japan is followed by Germany and then South Korea.[7]
In addition to having bases and troops in South Korea, the U.S. military has maintained command over the South Korean military since the Korean War in the 1950s. South Korea has operational control of its military under armistice conditions, but the United States would take over in wartime, and the U.S. combatant commander would be able to direct, organize, employ, assign command functions to, or suspend the duty of subordinate South Korean commanders and forces. In essence, if war breaks out on the Korean Peninsula, South Korea would supply the overwhelming majority of the fighting force, which would then be placed under U.S. operational control.[8][9][10]
Economic domination
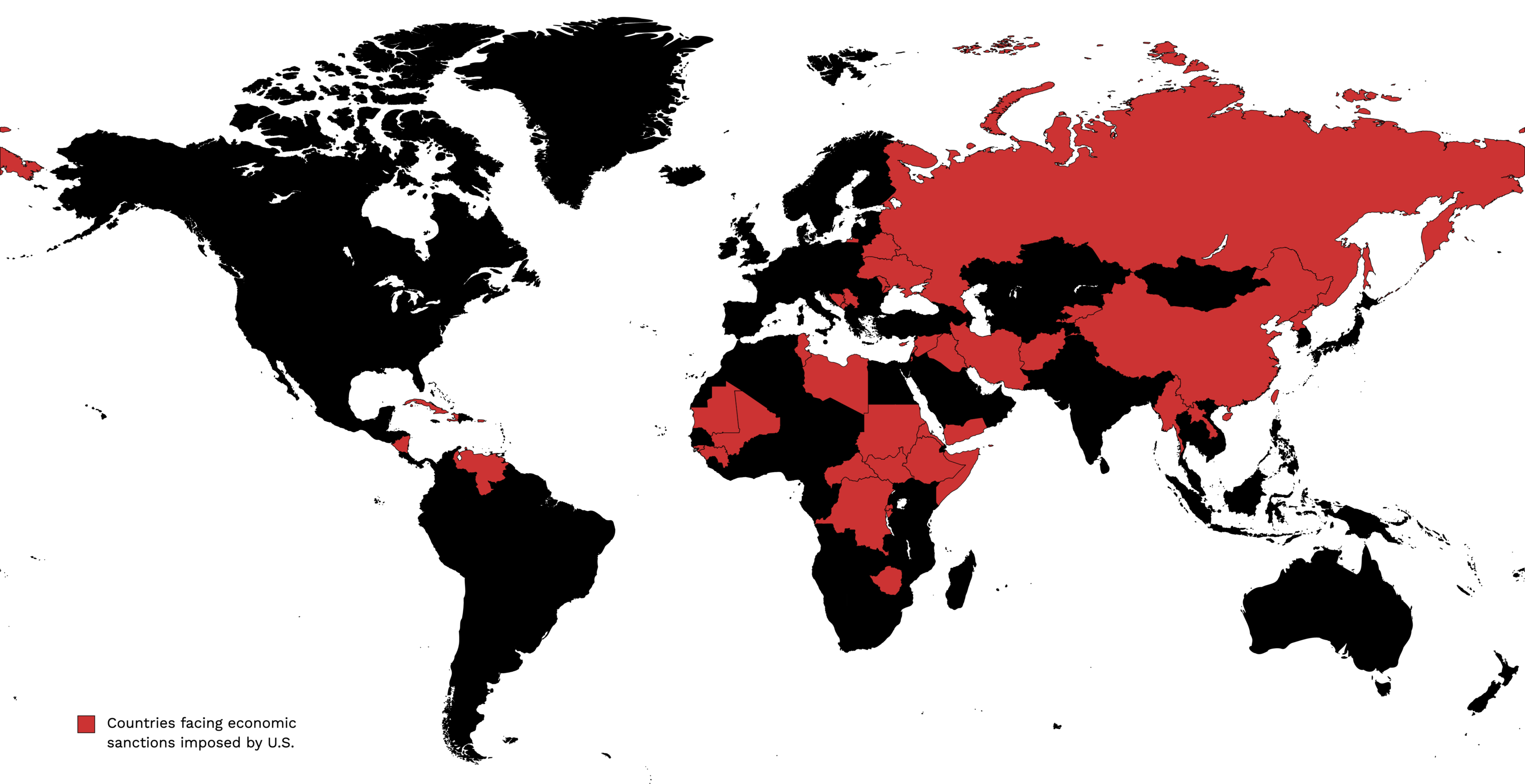
The United States bourgeoisie uses various economic methods to shape and control the development and economic policies of other nations and force them into subordination and perpetual debt and under-development. This can be seen through institutions such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), institutions in which the U.S. plays a key role in managing. Economic sanctions are another major method by which the United States manipulates and destroys the economic development of other countries. Freezing or seizure of assets, often under the guise of sanctions, is another method commonly used by the United States to stifle and disrupt foreign economies and enrich its own by excluding its own companies and institutions from sanctions while freezing and confiscating the assets of the target country.[11][12][13]
World Bank
Main article: World Bank
Since its origin, the president of the World Bank has been a US citizen proposed by its government. The US is also the only country to have a de facto right of veto at the World Bank, which is headquartered in Washington, D.C.[14] Countries must also join the International Monetary Fund to be eligible to join the World Bank Group.[15]
Historian and political scientist Eric Toussaint asserts that the unstated agenda of the World Bank is to "subordinate the public and private spheres of all human societies to the capitalist imperative of seeking maximum profit" which results in stagnation and deterioration of the living conditions of a great majority of the world’s population, concurrently with greater and greater concentration of wealth, as well as contributing to the deterioration of the natural environment.[16]
International Monetary Fund
Main article: International Monetary Fund
According to a 2016 article by the Center for Economic and Policy Research (CEPR) regarding voting shares in the IMF, the U.S. "dwarfs all other member countries’ voting shares" and the CEPR's co-director stated that "IMF governance structure [...] ensures that the U.S. and Europe will continue to control the Fund."[17]
Former IMF senior economist Davison Budhoo wrote that through extensive and systematic statistical fraud the IMF imposes its policies on developing countries. He explained that the IMF "manipulated, blatantly and systematically, certain key statistical indices so as to put ourselves in a position where we could make very false pronouncements about economic and financial performance" and that the consequences of these policies led to massive poverty and starvation, noting that the IMF's policies are made in "utter disregard to local conditions" and lead countries to "self destruct" and "unleash unstoppable economic and social chaos". He also stated that the routine policy packages of the IMF "can never serve, under any set of circumstances, the cause of financial balance and economic growth" and "can only serve to accentuate world tensions, expand even further the already bulging ranks of the poverty-stricken and destitute of the South".[18]
During the 1980s and 90s, the IMF dramatically expanded its reach by making assistance conditional on borrowers committing to extensive market reforms. During what are known as the Third World Debt Crisis, the Asian Financial Crisis of 1997–98, and the collapse of the Soviet Union, the IMF exercised enormous pressure on states in receipt of loans, demanding they commit to austerity and major transformations of their domestic economies. Failing to agree to these terms not only jeopardized the IMF’s assistance; it also jeopardized access to other sources of foreign capital, since the existence of a prior arrangement with the IMF was used by other lenders to determine a country’s creditworthiness. It is by this method that the IMF brings countries into subordination under U.S. dominance. Although the IMF's policies are certainly heavily influenced by neoliberalism, they are also an extension of older colonial and imperialist methods of domination that can be traced back to long before the 1980s and 90s.[19]
Economic sanctions
Main article: Economic sanctions
According to Sanctions Kill in a 2021 article, US sanctions affect a third of humanity with more than 8,000 measures impacting more than 40 countries and that the U.S. far exceeds any other country in the number of countries they have strangled with economic sanctions.[20] Lauren Smith notes in Monthly Review Online that it is not unilateral sanctions imposed by the U.S. alone that devastate a targeted country, it is the imposition of secondary sanctions upon foreign third parties that represents the final blow to its economy and people. These measures threaten to cut off foreign countries, governments, companies, financial institutions and individuals from the U.S. financial system if they engage in prohibited transactions with a sanctioned target—irrespective as to whether or not that activity impacts the United States directly.[11]
In an internal memo regarding Cuba, U.S. officials discussed how imposing "economic dissatisfaction and hardship" on Cuba would be an effective means of deposing the communist government, stating that because Castro enjoyed majority support among the people, their only option to reduce support for him would be "to bring about hunger, desperation and overthrow of government" by "denying money and supplies to Cuba, to decrease monetary and real wages".[21] The US embargo of Cuba is one of the oldest and strictest of all US sanctions regimes, prohibiting nearly all trade, travel, and financial transactions since the early 1960s.[13]
Freezing and seizure of assets
Russian Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov claims that the U.S. simply confiscates Venezuela’s money under the guise of sanctions, noting that the U.S. is experienced in such illegal affairs, giving Iraq, Libya, Iran, Cuba, Nicaragua, and Panama as examples. According to Lavrov, "US companies operating in Venezuela are excluded from the sanctions regime. Simply put they want to overthrow the government and gain profits at the same time."[12]
In 2003, President Bush signed an order to take possession of the Iraqi government assets that were frozen in 1990, before the Persian Gulf War. As a result, seventeen of the world’s biggest financial institutions were told by the Treasury Department to hand over $1.7 billion in frozen Iraqi assets that the U.S. government intended to place in an account at the NY Fed.[11]
In 2015, it was announced that $67 billion in Libya’s assets remained frozen from 2011. In 2018, it was announced that Libya’s assets had decreased to $34 billion. The UN Libya Experts Panel is “looking for answers” to explain the disappearance of $33 billion in frozen assets.[11]
Since 2021, the U.S. Biden administration has blocked Afghanistan’s central bank from accessing roughly $7 billion in its foreign reserves held in the US. Along with sanctions on government officials and a cutoff of aid, this has contributed to a severe collapse of Afghanistan’s economy.[13]
By country
Iraq
The U.S. bombing of Iraq directly killed approximately 50,000 civilians. The U.S. sanctions and destruction of infrastructure and farmland caused over a million civilians, including many civilians.[6]
Philippines
When the United States seized the Philippines from Spain in 1898, most of its territory was controlled by a Filipino resistance army. The United States fought a war against the resistance until 1902 and sporadic uprisings continued until 1915. The United States killed over 600,000 people on the island of Luzon alone and hundreds of thousands more died from starvation and disease throughout the Philippines.[6]
Vietnam
The United States killed at least a million Vietnamese civilians with bombing campaigns in the Vietnam War. The U.S. killed about ten times as many civilians as actual Viet Minh soldiers during the bombings. The total number of Vietnamese people killed, including soldiers and civilians killed indirectly through starvation, may be more than three million.[6]
Korea
The division of Korea into north and south occurred after Korea's liberation from Japan. Meant only to be a temporary division while Korea stabilized, the U.S. has never given up military control over the South. The U.S. military government in Korea re-instated Japanese colonial-era collaborators to their positions, re-instated Japanese colonial-era grain collection policies, violently disbanded the widely popular Korean People's Committees,[22][23] and solidified the division of Korea despite widespread opposition among the populace at the time of division. This is exemplified by the events of the Jeju uprising, where the people expressed their opposition to the U.S.-led decision to officially split Korea via the formation of the southern Republic of Korea, and were met with violence that killed approximately one-tenth of the island's population. The U.S. installed the dictator Syngman Rhee in the ROK, an expat who had been living in the U.S. for decades, while an internal document of the CIA at the time acknowledged that "imported expatriate" Rhee would most likely begin "ruthless suppression of all non-Rhee Rightist, Moderate, and Leftist opposition" after coming to power.[24]
During the Korean War, The United States dropped "635,000 tons of bombs in Korea (not counting 32,557 tons of napalm), compared to 503,000 tons in the entire Pacific Theater in World War II" and "at least 50 percent of eighteen out of the North's twenty-two major cities were obliterated."[25]
Several of the massacres of civilians conducted or observed by the U.S. military in Korea as well as by the U.S.-backed Southern regime have since been officially admitted to by the U.S. or the South Korean government, or by both, or corroborated by Koreans, U.S. veterans, journalists, and other eyewitnesses.[26] Regarding the Korean War, U.S. Air Force General Curtis LeMay stated "Over a period of three years or so, we killed off—what—twenty percent of the population of Korea as direct casualties of war, or from starvation and exposure?"[27]
According to the South Korean People's Democracy Party (민중민주당), writing in a 2020 Liberation School article, South Korea "is a complete colony occupied by the U.S. military, is politically oppressed by the U.S., and is economically subordinate to imperialist countries, including the U.S." and states that "true peace is possible only without imperialism; the head of imperialism is the U.S. We have an opinion that a true peace movement should be an anti-imperialist movement and an anti-U.S. movement. We believe that the progressive and peace-loving forces of the world can and must conduct an anti-imperialist, anti-war struggle, to halt all wars in the world by U.S. troops and to withdraw all U.S. troops stationed overseas."[28]
References
- ↑ Dov Levin (2020). Meddling in the Ballot Box. Carnegie Mellon University.
- ↑ Zoltán Grossman. U.S. Military Interventions since 1890: From Wounded Knee to Syria. [PDF]
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States: 'US Triumphalism and Peacetime Colonialism' (p. 162). ReVisioning American History. [PDF] Boston: Beacon Press Books.
- ↑ Barbara Salazar and Sofia Plagakis. "Instances of Use of United States Armed Forces Abroad, 1798-2022." R42738. March 8, 2022. Congressional Research Service. Archived 2022-08-09.
- ↑ Norton, Benjamin. 2022. “US Launched 251 Military Interventions since 1991, and 469 since 1798.” Multipolarista. September 13, 2022. Archived 2022-09-16.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Austin Murphy (2000). The Triumph of Evil: 'Introduction' (pp. 22–24, 37–40). [PDF] European Press Academic Publishing. ISBN 8883980026
- ↑ "Mapping U.S. Imperialism" (2022-06-06). Monthly Review. Archived from the original on 2022-06-14. Retrieved 2022-06-17.
- ↑ Swanström, N. (2021, April 27). Not a Sovereignty Issue: Understanding the Transition of Military Operational Control between the United States and South Korea. Institute for Security and Development Policy. https://isdp.eu/publication/not-a-sovereignty-issue-understanding-the-transition-of-military-operational-control-between-the-united-states-and-south-korea/
- ↑ "Combined Forces Command". United States Forces Korea. Archived from the original on 2022-07-28.
- ↑ Kelly, R. E. (2017, February 27). Why US control of the South Korean military is here to stay. The Interpreter. https://www.lowyinstitute.org/the-interpreter/why-us-control-south-korean-military-here-stay
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Smith, Lauren. “United States Imposed Economic Sanctions: The Big Heist” MR Online. March 10, 2020. Archived 2022-09-08.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 “‘Cynical’ US Sanctions Meant to Confiscate Venezuela’s Assets – Lavrov.” RT International. RT. January 29, 2019. Archived version.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Galant, Michael. “CEPR Sanctions Watch, May-June 2022” Center for Economic and Policy Research. July 8, 2022. Archived 2022-09-07.
- ↑ Toussaint, Eric. 2020. “Domination of the United States on the World Bank – CADTM.” Committee for the Abolition of Illegitimate Debt.
- ↑ “The World Bank Group and the International Monetary Fund (IMF).” 2018. World Bank. Archived 2022-07-20.
- ↑ Toussaint, Eric. 2022. “World Bank and IMF: 76 Years Is Enough! Abolition! – CADTM.” CADTM. August 11, 2022. Archive.
- ↑ “US and Europe Continue to Maintain Control of IMF despite Small Changes in Voting Structure - Center for Economic and Policy Research.” February 6, 2020. .
- ↑ Budhoo, Davison. "Enough is Enough." 1988. Archived 2022-05-16.
- ↑ Daniel Steinmetz-Jenkins. “The Rotten Roots of the IMF and the World Bank.” The Nation, 15 June 2022. Archived.
- ↑ W, Jim. Feb. 2, 2021. “Sanctions Fact Sheet/over 40 Countries | Sanctions Kill.” Sanctionskill.org. Archived 2022-09-07.
- ↑ "Memorandum From the Deputy Assistant Secretary of State for Inter-American Affairs (Mallory) to the Assistant Secretary of State for Inter-American Affairs (Rubottom)." Foreign Relations of the United States, 1958–1960, Cuba, Volume vi - Office of the Historian. State.gov. U.S. Department of State. Archived 2022-08-14.
- ↑ Robinson, Richard. Cited in Mark J. Scher (1973) U.S. policy in Korea 1945–1948: A Neocolonial model takes shape. Bulletin of Concerned Asian Scholars, 5:4, 17-27, DOI: 10.1080/14672715.1973.10406346. https://doi.org/10.1080/14672715.1973.1040634 URL: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/14672715.1973.10406346
- ↑ Jay Hauben (2011-08-20). "People's Republic of Korea: Jeju, 1945-1946" The Jeju Weekly. Archived from the original on 2022-07-23. Retrieved 2022-07-23.
- ↑ "March 18, 1948 Central Intelligence Agency, ORE 15/48, 'The Current Situation in Korea'". Wilson Center Digital Archive. Archived from the original. Retrieved 2022-07-29.
- ↑ Bruce Cumings (2010). The Korean War: A History: '"The Most Disproportionate Result:" The Air War' (pp. 159-160). New York: Modern Library. ISBN 978-0-679-64357-9
- ↑ “AP: U.S. Allowed Korean Massacre in 1950.” 2008. Cbsnews.com. CBS News. July 5, 2008. https://www.cbsnews.com/news/ap-us-allowed-korean-massacre-in-1950/. Archive.
- ↑ Richard H. Kohn and Joseph P. Harahan (1988). Strategic Air Warfare: an interview with generals Curtis E. LeMay, Leon W. Johnson, David A. Burchinal, and Jack J. Catton (p. 88). Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, United States Air Force. ISBN 0-912799-56-0
- ↑ People's Democracy Party and Liberation School. “70 Years Too Long: The Struggle to End the Korean War – Liberation School.” Liberation School – Revolutionary Marxism for a New Generation of Fighters, 25 June 2020. Archived