Co-operative Republic of Guyana: Difference between revisions
More languages
More actions
(Created.) Tag: Visual edit |
RedCustodian (talk | contribs) No edit summary Tag: Visual edit |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox country| | {{Infobox country|name=Co-operative Republic of Guyana|image_flag=Guyana flag.png|image_coat=Coat of arms of Guyana.svg|capital=Georgetown|largest_city=Georgetown|image_map=Guyana map.svg|map_width=260|official_languages=English|mode_of_production=[[Capitalism]]|government_type=Assembly-independent republic|leader_title1=President|leader_title2=Prime Minister|leader_name1=[[Irfaan Ali]]|leader_name2=[[Mark Phillips]]|population_estimate=743,700|population_estimate_year=2019|area_km2=214,970}} | ||
'''Guyana''', officially the '''Co-operative Republic of Guyana''', is a country | '''Guyana''', officially the '''Co-operative Republic of Guyana''', is a country on the north coast of [[South America]]. It is surrounded by [[Federative Republic of Brazil|Brazil]] to the south, [[Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela|Venezuela]] to the west, [[Republic of Suriname|Suriname]] to the east and the Atlantic ocean to the north. In the 1950s and 1960s, the [[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]] attempted to undermine the government of democratic socialist [[Cheddi Jagan]], who was the prime minister of [[British Guiana]] at the time.<ref name=":0">{{Citation|year=2005|title=Foreign Relations, 1964-1968, Volume XXXII, | ||
Dominican Republic; Cuba; Haiti; Guyana|chapter=Guyana|title-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070212125256/http://www.guyana.org/govt/US-declassifed-documents-1964-1968.html}}</ref> | Dominican Republic; Cuba; Haiti; Guyana|chapter=Guyana|title-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070212125256/http://www.guyana.org/govt/US-declassifed-documents-1964-1968.html}}</ref> | ||
== History == | |||
=== Spanish and Dutch colonialism === | |||
The [[Monarchy of Spain (1516–1700)|Spanish]] were the first country to colonize what is now Guyana. In the early 17th century, the [[Kingdom of the Netherlands|Dutch]] took over what is now [[Republic of Suriname|Suriname]] and eastern Guyana. In 1777, the Captaincy General of Venezuela signed a treaty defining the Esequibo River as the border between Dutch and British territories.<ref name=":2">{{Web citation|author=Saheli Chowdhury|newspaper=[[Orinoco Tribune]]|title=Essequibo and Other Border Issues: Venezuela’s Territorial Losses to Imperialist Powers Through the Centuries (Part 1)|date=2023-12-01|url=https://orinocotribune.com/essequibo-and-other-border-issues-venezuelas-territorial-losses-to-imperialist-powers-through-the-centuries-part-1/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231202012125/https://orinocotribune.com/essequibo-and-other-border-issues-venezuelas-territorial-losses-to-imperialist-powers-through-the-centuries-part-1/|archive-date=2023-12-02}}</ref> | |||
=== British colonialism === | |||
After the [[Statesian Revolution]], the British moved their colonial efforts to South America and plotted to take over Guyana from the Dutch.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
Following the 1794 [[Batavian Revolution]] in the Netherlands, Guyanese [[Slavery|slave]] owners allowed the [[Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1801)|British]] to take over Guyana because they worried that the Dutch would abolish slavery like [[French Republic (1792–1804)|France]] did. In 1823, following a slave revolt, the British declared martial law and killed 250 rebels.<ref name=":122">{{Citation|author=[[Domenico Losurdo]]|year=2011|title=Liberalism: A Counter-History|chapter=Crisis of the English and American Models|page=157–158|publisher=Verso|isbn=9781844676934|lg=https://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=5BB3406BC2E64972831A1C00D5D4BFE4|pdf=https://cloudflare-ipfs.com/ipfs/bafykbzacebhsj2yxuoudkhkjp6lzgr5jvgyhu76zxe4gw3d65gpg32a6nded4?filename=Domenico%20Losurdo%2C%20Gregory%20Elliott%20-%20Liberalism_%20A%20Counter-History-Verso%20%282011%29.pdf}}</ref> | |||
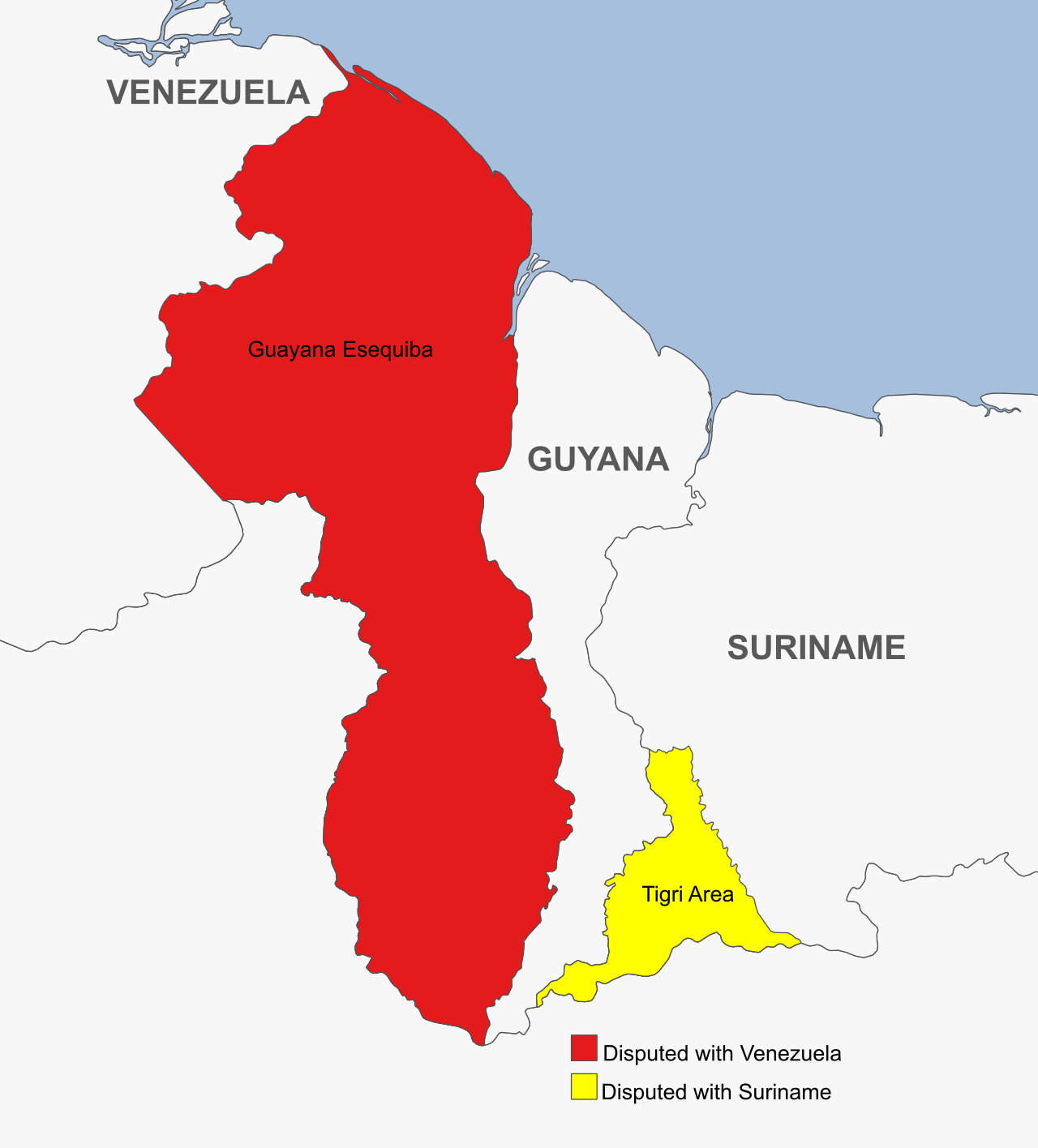
In 1815, Britain recognized the 1777 borders of Venezuela. In 1822, under the orders of [[Simón Bolívar]], Ambassador [[José Rafael Revenga]] criticized British intrusions west of the Esequibo. After [[Gran Colombia]] broke apart, the Michelena-Pombo Treaty of 1833 divided the Guajira Peninsula roughly in half between Colombia and Venezuela. The Venezuelan parliament rejected the treaty and continued to dispute the region until 1883. The British also annexed the Dutch region of Tigri, which Suriname still claims to this day.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
In 1840, the Royal Geographic Society of London sent [[Robert Schomburgk]], a [[Holy Roman Empire (800–1806)|German]] geographer, to map the border between Venezuela and British Guyana. His map claimed the sparsely populated Guayana Esequiba and Tigri regions as part of Guyana. In 1841, [[Alejo Fortique]], the Venezuelan ambassador to the UK, argued the Esequibo issue and made the British agree to future negotiations on the border. After he died in 1845, Venezuela agreed to postpone border negotiations.<ref name=":33">{{Web citation|author=Saheli Chowdhuri|newspaper=[[Orinoco Tribune]]|title=Essequibo and Other Border Issues: Venezuela’s Territorial Losses to Imperialist Powers Through the Centuries (Part 2)|date=2023-12-03|url=https://orinocotribune.com/essequibo-and-other-border-issues-venezuelas-territorial-losses-to-imperialist-powers-through-the-centuries-part-2/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20231204033538/https://orinocotribune.com/essequibo-and-other-border-issues-venezuelas-territorial-losses-to-imperialist-powers-through-the-centuries-part-2/|archive-date=2023-12-04}}</ref> | |||
In 1895, the United States asserted the [[Monroe Doctrine]], which considers the Americas to be territory for colonization by the USA rather than colonization by [[Europe]]. The UK initially refused to negotiate until the USA threatened war. In 1897, after the UK refused to negotiate with Venezuela, which it considered uncivilized, the USA decided to negotiate on Venezuela's behalf without taking its interests into account. The UK and USA created a tribunal of five people: two from the UK and three from the USA. The last member, [[Frederick Fyodor Martens]], was a [[Russian Empire (1721–1917)|Russian]] diplomat who wanted Russia and Britain to cooperate in invading Central Asia. In 1899, the tribunal created the Paris Arbitration Award, which surrendered Guayana Esequibo the British.<ref name=":33" /> The affair was an early instance of the Monroe Doctrine being invoked and the U.S. asserting itself as an imperial power.<ref>[https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/venezuela “Milestones: 1866–1898 - Office of the Historian.”] 2023. State.gov. 2023.</ref><ref name=":02">Wilkins, Brett. [https://www.telesurenglish.net/opinion/The-History--and-Hypocrisy--of-US-Meddling-in-Venezuela--20190128-0016.html “The History - and Hypocrisy - of US Meddling in Venezuela.”] Telesurenglish.net. teleSUR. 2018. [https://web.archive.org/web/20230307033238/https://www.telesurenglish.net/opinion/The-History--and-Hypocrisy--of-US-Meddling-in-Venezuela--20190128-0016.html Archived] 2023-03-07.</ref> | |||
=== Independence === | |||
In 1944 the [[United States of America|USA]] feared the potential of a communist government taking power once independence was declared, so intervened along with the British to change the electoral system to prevent Jagan's [[People's Progressive Party]] (PPP) being re-elected. The plan worked and [[Linden Forbes Burnham]] leader of the [[People's National Congress]] (PNC) took power. Following this the British lent their support to the new government and granted them independence in May 1966.<ref name=":0" /> | |||
When Guyana became independent from the British in 1966, Venezuela agreed to temporarily leave the Esequibo region under Guyana's control until they could reach a permanent solution. However, Venezuela did not recognize Guyananese authority over the disputed region. In 1970, with the Port of Spain Protocol, Prime Minister [[Eric Williams]] of Trinidad and Tobago made an agreement that Guyana and Venezuela would maintain bilateral ties and that Venezuela would not claim the Esequibo until 1982.<ref name=":33" /> | |||
== Border disputes == | |||
[[File:Guyana Disputed Areas.svg.png|thumb]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
[[Category:Countries]] | [[Category:Countries]] | ||
Latest revision as of 21:25, 23 May 2024
| Co-operative Republic of Guyana | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Georgetown |
| Official languages | English |
| Dominant mode of production | Capitalism |
| Government | Assembly-independent republic |
• President | Irfaan Ali |
• Prime Minister | Mark Phillips |
| Area | |
• Total | 214,970 km² |
| Population | |
• 2019 estimate | 743,700 |
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the north coast of South America. It is surrounded by Brazil to the south, Venezuela to the west, Suriname to the east and the Atlantic ocean to the north. In the 1950s and 1960s, the CIA attempted to undermine the government of democratic socialist Cheddi Jagan, who was the prime minister of British Guiana at the time.[1]
History[edit | edit source]
Spanish and Dutch colonialism[edit | edit source]
The Spanish were the first country to colonize what is now Guyana. In the early 17th century, the Dutch took over what is now Suriname and eastern Guyana. In 1777, the Captaincy General of Venezuela signed a treaty defining the Esequibo River as the border between Dutch and British territories.[2]
British colonialism[edit | edit source]
After the Statesian Revolution, the British moved their colonial efforts to South America and plotted to take over Guyana from the Dutch.[2]
Following the 1794 Batavian Revolution in the Netherlands, Guyanese slave owners allowed the British to take over Guyana because they worried that the Dutch would abolish slavery like France did. In 1823, following a slave revolt, the British declared martial law and killed 250 rebels.[3]
In 1815, Britain recognized the 1777 borders of Venezuela. In 1822, under the orders of Simón Bolívar, Ambassador José Rafael Revenga criticized British intrusions west of the Esequibo. After Gran Colombia broke apart, the Michelena-Pombo Treaty of 1833 divided the Guajira Peninsula roughly in half between Colombia and Venezuela. The Venezuelan parliament rejected the treaty and continued to dispute the region until 1883. The British also annexed the Dutch region of Tigri, which Suriname still claims to this day.[2]
In 1840, the Royal Geographic Society of London sent Robert Schomburgk, a German geographer, to map the border between Venezuela and British Guyana. His map claimed the sparsely populated Guayana Esequiba and Tigri regions as part of Guyana. In 1841, Alejo Fortique, the Venezuelan ambassador to the UK, argued the Esequibo issue and made the British agree to future negotiations on the border. After he died in 1845, Venezuela agreed to postpone border negotiations.[4]
In 1895, the United States asserted the Monroe Doctrine, which considers the Americas to be territory for colonization by the USA rather than colonization by Europe. The UK initially refused to negotiate until the USA threatened war. In 1897, after the UK refused to negotiate with Venezuela, which it considered uncivilized, the USA decided to negotiate on Venezuela's behalf without taking its interests into account. The UK and USA created a tribunal of five people: two from the UK and three from the USA. The last member, Frederick Fyodor Martens, was a Russian diplomat who wanted Russia and Britain to cooperate in invading Central Asia. In 1899, the tribunal created the Paris Arbitration Award, which surrendered Guayana Esequibo the British.[4] The affair was an early instance of the Monroe Doctrine being invoked and the U.S. asserting itself as an imperial power.[5][6]
Independence[edit | edit source]
In 1944 the USA feared the potential of a communist government taking power once independence was declared, so intervened along with the British to change the electoral system to prevent Jagan's People's Progressive Party (PPP) being re-elected. The plan worked and Linden Forbes Burnham leader of the People's National Congress (PNC) took power. Following this the British lent their support to the new government and granted them independence in May 1966.[1]
When Guyana became independent from the British in 1966, Venezuela agreed to temporarily leave the Esequibo region under Guyana's control until they could reach a permanent solution. However, Venezuela did not recognize Guyananese authority over the disputed region. In 1970, with the Port of Spain Protocol, Prime Minister Eric Williams of Trinidad and Tobago made an agreement that Guyana and Venezuela would maintain bilateral ties and that Venezuela would not claim the Esequibo until 1982.[4]
Border disputes[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [https://web.archive.org/web/20070212125256/http://www.guyana.org/govt/US-declassifed-documents-1964-1968.html Foreign Relations, 1964-1968, Volume XXXII, Dominican Republic; Cuba; Haiti; Guyana]: 'Guyana' (2005).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Saheli Chowdhury (2023-12-01). "Essequibo and Other Border Issues: Venezuela’s Territorial Losses to Imperialist Powers Through the Centuries (Part 1)" Orinoco Tribune. Archived from the original on 2023-12-02.
- ↑ Domenico Losurdo (2011). Liberalism: A Counter-History: 'Crisis of the English and American Models' (pp. 157–158). [PDF] Verso. ISBN 9781844676934 [LG]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Saheli Chowdhuri (2023-12-03). "Essequibo and Other Border Issues: Venezuela’s Territorial Losses to Imperialist Powers Through the Centuries (Part 2)" Orinoco Tribune. Archived from the original on 2023-12-04.
- ↑ “Milestones: 1866–1898 - Office of the Historian.” 2023. State.gov. 2023.
- ↑ Wilkins, Brett. “The History - and Hypocrisy - of US Meddling in Venezuela.” Telesurenglish.net. teleSUR. 2018. Archived 2023-03-07.


