More languages
More actions
Jucheguevara (talk | contribs) m (punctuation) Tags: Visual edit mobile web edit mobile edit advanced mobile edit |
mNo edit summary Tag: Visual edit |
||
| (One intermediate revision by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:Pyramid of Capitalist System.png|thumb|178x178px|Pyramid of the Capitalist System.]] | |||
In sociology, the '''ruling class''' is a [[social class]] who set and decide the political agenda of society. Under [[capitalism]], the ruling class is the [[Bourgeoisie|capitalist class]]; the private owners of industry. | In sociology, the '''ruling class''' is a [[social class]] who set and decide the political agenda of society. Under [[capitalism]], the ruling class is the [[Bourgeoisie|capitalist class]]; the private owners of industry. | ||
In the modern era of [[imperialism]] and capitalist globalization the ruling class is a network of transnational capitalists which do not have allegiance to any nation | In the modern era of [[imperialism]] and capitalist globalization the ruling class is a network of transnational capitalists which do not have allegiance to any nation; their only allegiance is to their personal accumulation of wealth. | ||
== History == | == History == | ||
Latest revision as of 14:06, 17 February 2024
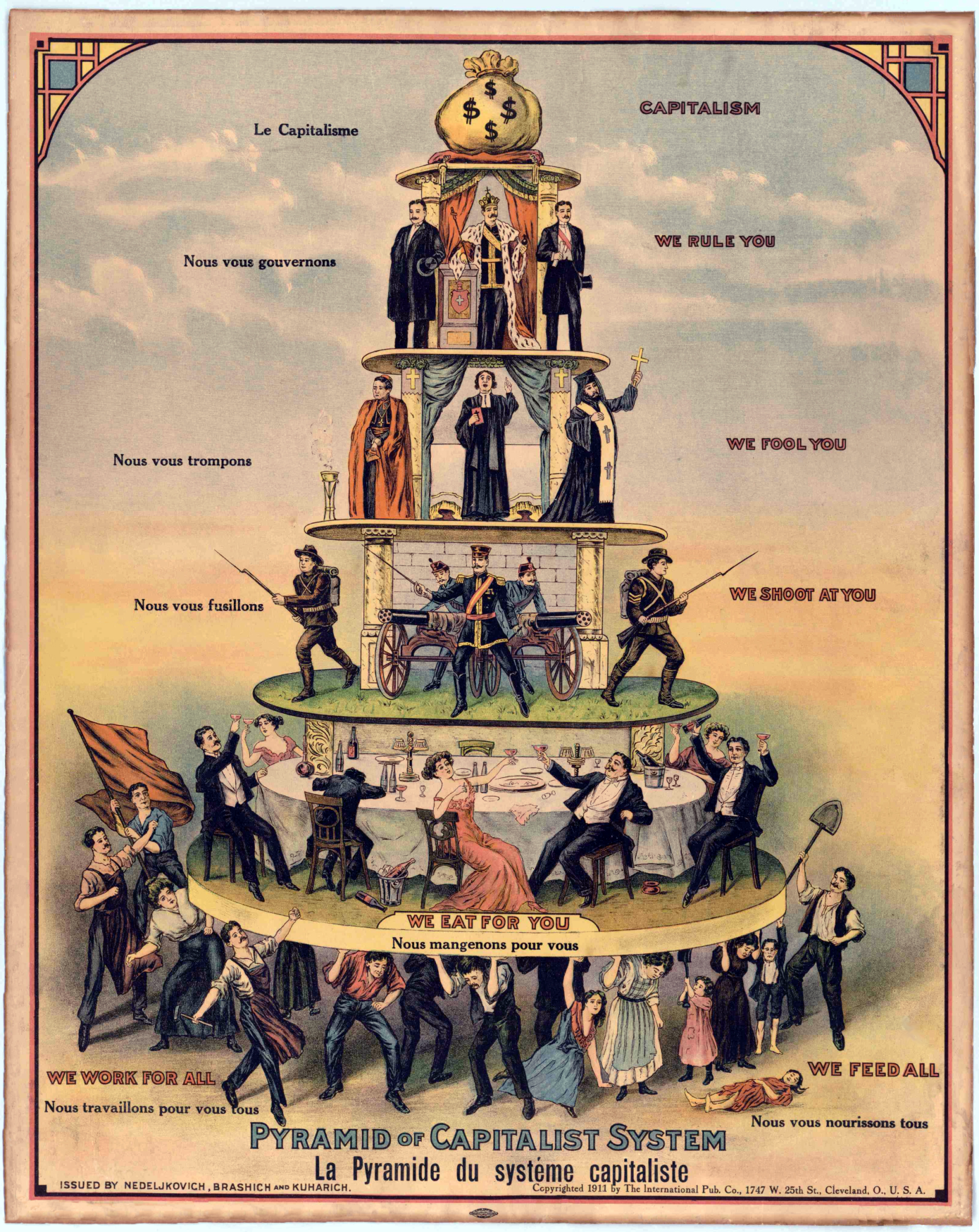
In sociology, the ruling class is a social class who set and decide the political agenda of society. Under capitalism, the ruling class is the capitalist class; the private owners of industry.
In the modern era of imperialism and capitalist globalization the ruling class is a network of transnational capitalists which do not have allegiance to any nation; their only allegiance is to their personal accumulation of wealth.
History[edit | edit source]
Historically, the ruling class has transitioned according to changes in the mode of production. Under feudalism, the ruling class was comprised of feudal lords, under slavery, the ruling class was the slaveowners, and so on.
