m (→History: General structure of the article. Very subject to change) Tag: Visual edit |
(removed extra space) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
| death_place = La Higuera, Vallegrande Province, [[Plurinational State of Bolivia|Bolivia]]. | | death_place = La Higuera, Vallegrande Province, [[Plurinational State of Bolivia|Bolivia]]. | ||
| death_cause = Capture and execution by the Bolivian state | | death_cause = Capture and execution by the Bolivian state | ||
| political_line = [[ | | political_line = [[Marxism–Leninism]]<br>[[Guevarism]]<br>[[Anti-imperialism]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
'''Ernesto''' "'''Che'''" '''Guevara''' {{Datebio|birthday=14th|birthmonth=June|birthyear=1928|deathday=9th|deathmonth=October|deathyear=1967}} was a [[Latin America|Latin-American]] [[Marxism–Leninism| | '''Ernesto''' "'''Che'''" '''Guevara''' {{Datebio|birthday=14th|birthmonth=June|birthyear=1928|deathday=9th|deathmonth=October|deathyear=1967}} was a [[Latin America|Latin-American]] [[Marxism–Leninism|Marxist–Leninist]] revolutionary and a leader of the [[Cuban Revolution]], alongside [[Fidel Castro]]. During his time in the government of [[Republic of Cuba|Cuba]], he was appointed president of the [[Central Bank of Cuba]] in 1959 and later Minister of Industry in 1961.<ref>{{Textcite|author=Richard L. Harris|year=2011|chapter=Timeline: events in the life of Che Guevara|title=Che Guevara: a biography|isbn=978-0-313-35916-3|city=Santa Barbara, Califonia|publisher=Greenwood|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=E894F200B27B2693CC5B5229B5DE50A3}}</ref><ref>{{Web citation|newspaper=teleSUR|title=President Maduro Highlights Ernesto Che Guevara's Legacy|date=2021-10-08|url=https://www.telesurenglish.net/news/President-Maduro-Highlights-Ernesto-Che-Guevaras-Legacy-20211008-0022.html|retrieved=2023-07-09}}</ref> He would also lead the Department of Industrialization and the National Institute for Agrarian Reform.<ref name=":3">{{Web citation|author=Pedro Ríoseco|newspaper=Granma|title=We will be like Che, the motto that belongs to an entire people|date=2023-06-14|url=https://en.granma.cu/cuba/2023-06-14/we-will-be-like-che-the-motto-that-belongs-to-an-entire-people|retrieved=2023-07-09}}</ref> | ||
Che was part of an expedition led by [[Fidel Castro]] that directed the [[armed struggle]] against the [[United States imperialism|US-backed]] | Che was part of an expedition led by [[Fidel Castro]] that directed the [[Cuban Revolution|armed struggle]] against the [[United States imperialism|US-backed]] Cuban dictator [[Fulgencio Batista]]. Guevara also presided over Cuban delegations that visited various countries and was a representative of the revolutionary government in important international conclaves. During the October Crisis he was appointed military chief of the province of Pinar del Río. | ||
In 1965 Che left Cuba to set up guerrilla forces first in the [[Republic of Congo|Congo]] and then later in [[Plurinational State of Bolivia|Bolivia]], where he was ultimately captured and killed in October 1967. | In 1965, Che left Cuba to set up guerrilla forces first in the [[Democratic Republic of the Congo|Congo]] and then later in [[Plurinational State of Bolivia|Bolivia]], where he was ultimately captured and killed in October 1967. Accounts of his execution have varied over the years, but many contemporary accounts indicate some degree of collaboration between Bolivia's government troops and the [[United States of America|United States]]' [[Central Intelligence Agency|CIA]]. Che Guevara developed a theory of primacy of military struggle, in particular concept of guerilla ''foquismo''. Many of Che's theories regarding guerilla tactics are articulated in his 1961 work "[[Guerilla warfare (Che Guevara work)|Guerilla Warfare]]." | ||
== | == Life == | ||
=== Early life in Argentina (1928–1950)=== | === Early life in Argentina (1928–1950)=== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
Ernesto Guevara was born to his father Ernesto Guevara Lynch and his mother Celia de la Serna y Llosa in the city of Rosario, [[Argentine Republic|Argentina]] on May 14th, 1928, despite his birth certificate recording his birth a month later. His mother got pregnant before she was married to his father and they hid baby Che from their families for one month after he was born.<ref name=":0">{{Textcite|author=Jon Lee Anderson|year=2010|title=Che Guevara: a revolutionary life|chapter=A plantation in Misiones|isbn=978-0-8021-9725-2|publisher=Grove Press|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=3E3E1D3A68BF27293A12BC1076076C7B}}</ref> Che spoke Spanish with a typical La Plata accent, common in the regions of [[Uruguay]], south of [[Federative Republic of Brazil|Brazil]] and the northeast region of Argentina, which makes frequent use of the interjection "che" in the speech. This characteristic accent would render Guevara's nickname "Che".<ref name=":1">{{Textcite|author=I. Lavretsky|year=1976|title=Ernesto Che Guevara|chapter=First steps|publisher=Progress Publishers|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=3DA588DC804F57A9857A5A563BB5D2A3}}</ref> | Ernesto Guevara was born to his father Ernesto Guevara Lynch and his mother Celia de la Serna y Llosa in the city of Rosario, [[Argentine Republic|Argentina]] on May 14th, 1928, despite his birth certificate recording his birth a month later. His mother got pregnant before she was married to his father and they hid baby Che from their families for one month after he was born.<ref name=":0">{{Textcite|author=Jon Lee Anderson|year=2010|title=Che Guevara: a revolutionary life|chapter=A plantation in Misiones|isbn=978-0-8021-9725-2|publisher=Grove Press|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=3E3E1D3A68BF27293A12BC1076076C7B}}</ref> Che spoke Spanish with a typical La Plata accent, common in the regions of [[Uruguay]], south of [[Federative Republic of Brazil|Brazil]] and the northeast region of Argentina, which makes frequent use of the interjection "che" in the speech. This characteristic accent would render Guevara's nickname "Che".<ref name=":1">{{Textcite|author=I. Lavretsky|year=1976|title=Ernesto Che Guevara|chapter=First steps|publisher=Progress Publishers|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=3DA588DC804F57A9857A5A563BB5D2A3}}</ref> | ||
Che Guevara's mother had [[Kingdom of Spain|Spanish]] descent, from the Argentine colonial era nobility, and his father had [[Ireland|Irish]] descent, also from an | Che Guevara's mother had [[Kingdom of Spain|Spanish]] descent, from the Argentine colonial era nobility, and his father had [[Republic of Ireland|Irish]] descent, also from an aristocratic family.<ref name=":1" /><ref name=":0" /> During his childhood, Che developed chronic asthma, which would afflict his health for his whole life.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
He initially studied engineering in the Argentine city of Córdoba. In 1947, his paternal grandmother, who he taken care of, died. This death caused him to start studying medicine at the School of Medicine in Buenos Aires. He received his degree at the age of 24.<ref name=":2">{{Web citation|author=Ángel Freddy Pérez Cabrera|newspaper=Granma|title=Che, an extraordinarily human man|date=2023-06-14|url=https://en.granma.cu/cuba/2023-06-14/che-an-extraordinarily-human-man|retrieved=2023-07-07}}</ref> | |||
=== Continental motorcycle travels (1950–1952)=== | === Continental motorcycle travels (1950–1952)=== | ||
Guevara made two motorcycle trips across South America.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
The first trip was during a time when he was a student. He made the trip with Alberto Granado. They worked in hospitals in Lima and São Paulo to help cure those afflicted with leprosy.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
He made another trip on his motorcycle to help those in need after graduating. That trip ended in [[Guatemala]].<ref name=":2" /> | |||
His motorcycle trips across [[Latin America]] helped inspire him against imperialism. This was due to seeing mistreatment of workers in Chilean copper mines run by the Anaconda Company and hearing about the actions of the United Fruit Company. Both United Fruit and Anaconda were Statesian companies. He understood that the actions of foreign imperialists was inherently tied to the bourgeoisie in the local countries. This lead him to support both [[Marxism]] and national liberation.<ref>{{Web citation|newspaper=teleSUR|title=Che Guevara's Socialism Against Revolutionary Dogma|date=2019-10-09|url=https://www.telesurenglish.net/analysis/Che-Guevaras-Socialism-Against-Revolutionary-Dogma-20181006-0005.html|retrieved=2023-07-09}}</ref> | |||
===Guatemala and Mexico (1952–1955)=== | ===Guatemala and Mexico (1952–1955)=== | ||
He would meet [[Raúl Castro|Raúl]] and [[Fidel Castro]] as well as other future Cuban revolutionaries in [[Mexico]].<ref name=":2" /><ref>{{Web citation|author=Yisel Martínez|newspaper=Granma|title=Ernesto Guevara: The man who gave himself|date=2018-06-13|url=https://en.granma.cu/cuba/2018-06-13/ernesto-guevara-the-man-who-gave-himself|retrieved=2023-07-09}}</ref> Guevara was inspired to join them in their revolution by Fidel Castro and was decided to be the doctor of the [[Granma]] yacht.<ref name=":2" /> | |||
=== Cuban Revolution (1956–1958)=== | === Cuban Revolution (1956–1958)=== | ||
Guevara was involved in the [[Cuban revolution]] and was a member of the Granma yacht expedition to Cuba. He fought in Sierra Maestra and was at the head of the invasion.<ref name=":3" /> | |||
===Governance in Cuba (1959–1965)=== | ===Governance in Cuba (1959–1965)=== | ||
During the [[Bay of Pigs|Bay of Pigs invasion]] of Cuba, Guevara almost was killed by an accidental discharge of his pistol. While leading the Rebel Army Command at the previous headquarters of the Rural Guard in Consolación del Sur in Pinar del Río, he fell on a pipe which loosened his pistol from his belt which proceeded to discharge. The bullet entered his right cheekbone and exited by his ear. He received a tetanus vaccine due to the shot, to which he was allergic.<ref>{{Web citation|author=Ronald Suárez Rivas|newspaper=Granma|title=The shot that almost took Che's life|date=2017-09-28|url=https://en.granma.cu/cuba/2017-08-28/the-shot-that-almost-took-ches-life|retrieved=2023-07-09}}</ref> | |||
In December 1964, Che spoke at the [[United Nations]] and encouraged the UN to take action against [[imperialism]].<ref name=":122">{{Citation|author=[[Vijay Prashad]]|year=2008|title=The Darker Nations: A People's History of the Third World|chapter=Belgrade|page=104|pdf=https://cloudflare-ipfs.com/ipfs/bafykbzaceascnzh26r5d6uitjjs2z7rflhaxlt7rboz5whzdf76qg6xxvecqq?filename=%28A%20New%20Press%20People%27s%20history%29%20Vijay%20Prashad%20-%20The%20darker%20nations_%20a%20people%27s%20history%20of%20the%20third%20world-The%20New%20Press%20%282008%29.pdf|publisher=The New Press|isbn=9781595583420|lg=https://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=9B40B96E830128A7FE0E0E887C06829F}}</ref> | |||
On 24 February 1965, he addressed the Second Economic Seminar of Afro-Asian Solidarity in [[People's Democratic Republic of Algeria|Algeria]]. He called for [[Socialist state|socialist countries]] to support post-colonial states in order to protect them from [[Imperialism|imperialist]] [[Bank|banks]]. He said trade between socialist countries should help both countries develop.<ref name=":022">{{Citation|author=[[Vijay Prashad]]|year=2017|title=Red Star over the Third World|chapter=Colonial Fascism|page=113|pdf=https://cloudflare-ipfs.com/ipfs/bafykbzacecu7gb2ei65us6ip3r2ugcgkblneqcftbm456mb6bzvprkbqk55qm?filename=Vijay%20Prashad%20-%20Red%20Star%20Over%20the%20Third%20World-LeftWord%20Books%20%282018%29.pdf|city=New Delhi|publisher=LeftWord Books}}</ref> | |||
===Struggle in Congo (1965–1966)=== | ===Struggle in Congo (1965–1966)=== | ||
Che left Cuba before he could attend the [[Tricontinental Conference]] and fought in the revolutionary movement in the [[Republic of the Congo (1960–1964)|Congo]].<ref name=":1222">{{Citation|author=[[Vijay Prashad]]|year=2008|title=The Darker Nations: A People's History of the Third World|chapter=Havana|page=108–109|pdf=https://cloudflare-ipfs.com/ipfs/bafykbzaceascnzh26r5d6uitjjs2z7rflhaxlt7rboz5whzdf76qg6xxvecqq?filename=%28A%20New%20Press%20People%27s%20history%29%20Vijay%20Prashad%20-%20The%20darker%20nations_%20a%20people%27s%20history%20of%20the%20third%20world-The%20New%20Press%20%282008%29.pdf|publisher=The New Press|isbn=9781595583420|lg=https://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=9B40B96E830128A7FE0E0E887C06829F}}</ref> | |||
===Struggle in Bolivia and capture (1966–1967)=== | ===Struggle in Bolivia and capture (1966–1967)=== | ||
[[Mario Monje]], leader of the [[Bolivian Communist Party]], agreed to support Che's struggle in Bolivia.<ref name=":1222" /> The CIA, working with [[Gusano|wealthy Cuban exiles]], captured and murdered Che Guevara in Quebrada del Yuro near La Higuera in Bolivia on the 8th of October, 1967.<ref name=":2" /><ref>{{Citation|author=William Blum|year=2002|title=Rogue State: A Guide to the World's Only Superpower|chapter=A Concise History of United States Global Interventions, | |||
1945 to the Present|isbn=9781842772201|publisher=Zed Books Ltd|lg=https://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=29EED3C6906FF165E08303B9EAF66B4F|pdf=https://cloudflare-ipfs.com/ipfs/bafykbzacedas5bwprytpzcih6tof3ipede5uzmcvt47tfzwp4cptdau6vmjpy?filename=William%20Blum%20-%20Rogue%20State_%20A%20Guide%20to%20the%20World%27s%20Only%20Superpower-Zed%20Books%20Ltd%20%282002%29.pdf|page=123}}</ref><ref>{{Web citation|author=Yenia Silva Correa|newspaper=Granma|title=What it means to be like Che|date=2017-08-09|url=https://en.granma.cu/cuba/2017-08-09/what-it-means-to-be-like-che|retrieved=2023-07-09}}</ref><ref>{{Web citation|newspaper=teleSUR|title='Che Guevara' Is Remembered 53 Years After His Assassination|date=2020-10-09|url=https://www.telesurenglish.net/news/Cuba-Pays-Honor-to-Che-Guevara-on-53rd-Anniversary-of-His-Death-20201009-0008.html|retrieved=2023-07-09}}</ref> | |||
==Works== | ==Works== | ||
==='' | ===''Guerrilla warfare''=== | ||
===''Reminiscences of the Cuban revolutionary war''=== | ===''Reminiscences of the Cuban revolutionary war''=== | ||
| Line 56: | Line 75: | ||
*{{Textcite|author=Jon Lee Anderson|year=2010|title=Che: a revolutionary life|pdf=|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=3E3E1D3A68BF27293A12BC1076076C7B|publisher=Grove Press|isbn=978-0-8021-9725-2}} | *{{Textcite|author=Jon Lee Anderson|year=2010|title=Che: a revolutionary life|pdf=|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=3E3E1D3A68BF27293A12BC1076076C7B|publisher=Grove Press|isbn=978-0-8021-9725-2}} | ||
*{{Textcite|author=Jorge G. Castañeda|year=1998|title=Compañero: the life and death of Che Guevara|pdf=|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=0C2A7034251A2A2E64A739A11CAD53C4|city=New York|publisher=Vintage Books|isbn=9780679759409}} | *{{Textcite|author=Jorge G. Castañeda|year=1998|title=Compañero: the life and death of Che Guevara|pdf=|lg=http://libgen.rs/book/index.php?md5=0C2A7034251A2A2E64A739A11CAD53C4|city=New York|publisher=Vintage Books|isbn=9780679759409}} | ||
*{{Textcite|author=Pablo Ignacio Taibo II|year=1997|title=Guevara, Also Known as Che|pdf=|lg=http://library.lol/main/CB9369623DEA7690018147DBADE603B3|publisher=Thomas Dunne Books (St. Martin's Press)|isbn=9780312155391}} | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Revolutionaries]] | |||
[[Category:Communists]] | |||
Latest revision as of 15:24, 1 September 2023
Ernesto Guevara | |
|---|---|
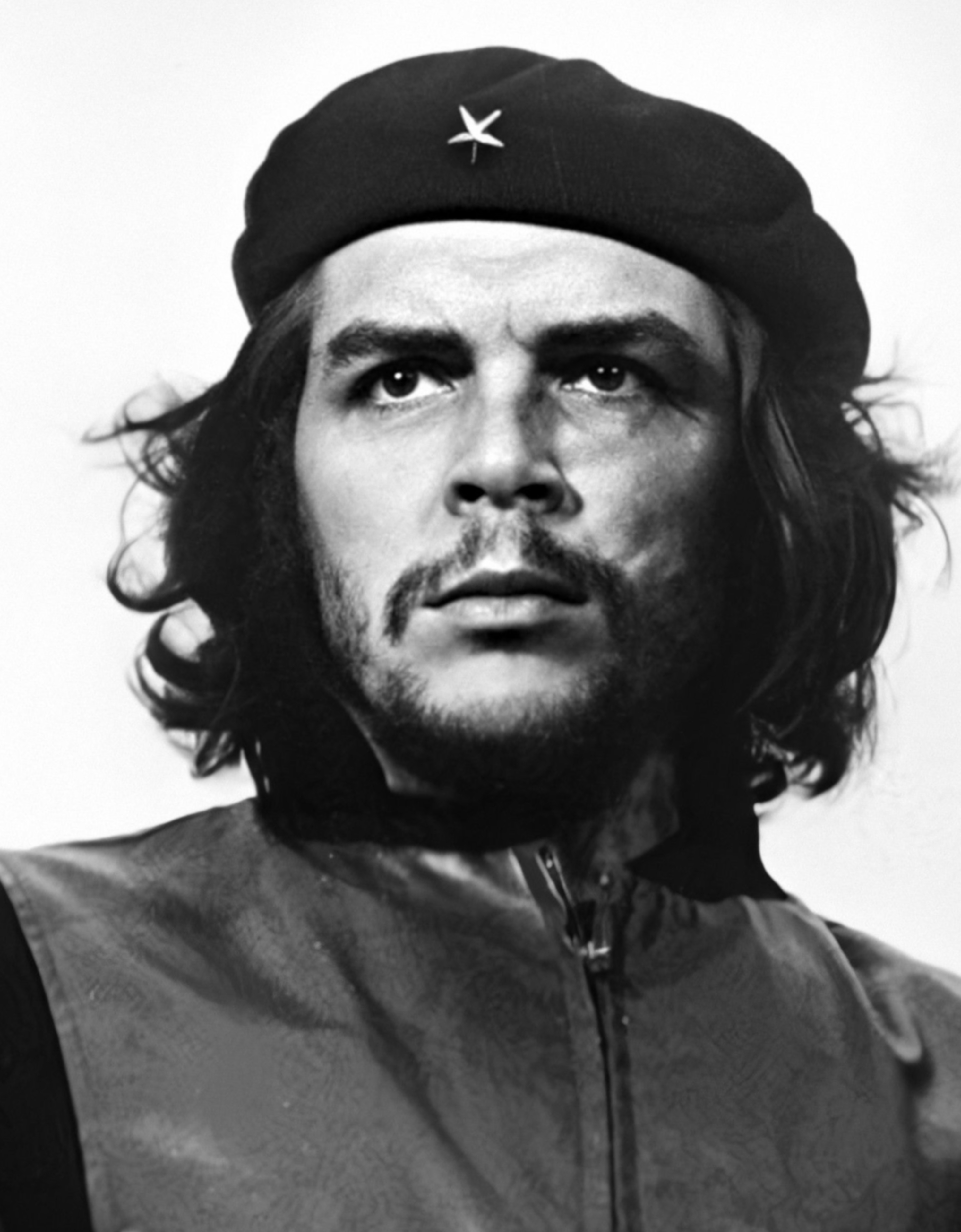 Portrait of comrade Che | |
| Born | Ernesto Guevara June 14, 1928 Rosario, Santa Fé Province, Argentina |
| Died | October 9, 1967 (aged 39) La Higuera, Vallegrande Province, Bolivia. |
| Cause of death | Capture and execution by the Bolivian state |
| Nationality | Argentinian |
| Political orientation | Marxism–Leninism Guevarism Anti-imperialism |
Ernesto "Che" Guevara (June 14th, 1928 — October 9th, 1967) was a Latin-American Marxist–Leninist revolutionary and a leader of the Cuban Revolution, alongside Fidel Castro. During his time in the government of Cuba, he was appointed president of the Central Bank of Cuba in 1959 and later Minister of Industry in 1961.[1][2] He would also lead the Department of Industrialization and the National Institute for Agrarian Reform.[3]
Che was part of an expedition led by Fidel Castro that directed the armed struggle against the US-backed Cuban dictator Fulgencio Batista. Guevara also presided over Cuban delegations that visited various countries and was a representative of the revolutionary government in important international conclaves. During the October Crisis he was appointed military chief of the province of Pinar del Río.
In 1965, Che left Cuba to set up guerrilla forces first in the Congo and then later in Bolivia, where he was ultimately captured and killed in October 1967. Accounts of his execution have varied over the years, but many contemporary accounts indicate some degree of collaboration between Bolivia's government troops and the United States' CIA. Che Guevara developed a theory of primacy of military struggle, in particular concept of guerilla foquismo. Many of Che's theories regarding guerilla tactics are articulated in his 1961 work "Guerilla Warfare."
Life
Early life in Argentina (1928–1950)
Ernesto Guevara was born to his father Ernesto Guevara Lynch and his mother Celia de la Serna y Llosa in the city of Rosario, Argentina on May 14th, 1928, despite his birth certificate recording his birth a month later. His mother got pregnant before she was married to his father and they hid baby Che from their families for one month after he was born.[4] Che spoke Spanish with a typical La Plata accent, common in the regions of Uruguay, south of Brazil and the northeast region of Argentina, which makes frequent use of the interjection "che" in the speech. This characteristic accent would render Guevara's nickname "Che".[5]
Che Guevara's mother had Spanish descent, from the Argentine colonial era nobility, and his father had Irish descent, also from an aristocratic family.[5][4] During his childhood, Che developed chronic asthma, which would afflict his health for his whole life.[4]
He initially studied engineering in the Argentine city of Córdoba. In 1947, his paternal grandmother, who he taken care of, died. This death caused him to start studying medicine at the School of Medicine in Buenos Aires. He received his degree at the age of 24.[6]
Continental motorcycle travels (1950–1952)
Guevara made two motorcycle trips across South America.[6]
The first trip was during a time when he was a student. He made the trip with Alberto Granado. They worked in hospitals in Lima and São Paulo to help cure those afflicted with leprosy.[6]
He made another trip on his motorcycle to help those in need after graduating. That trip ended in Guatemala.[6]
His motorcycle trips across Latin America helped inspire him against imperialism. This was due to seeing mistreatment of workers in Chilean copper mines run by the Anaconda Company and hearing about the actions of the United Fruit Company. Both United Fruit and Anaconda were Statesian companies. He understood that the actions of foreign imperialists was inherently tied to the bourgeoisie in the local countries. This lead him to support both Marxism and national liberation.[7]
Guatemala and Mexico (1952–1955)
He would meet Raúl and Fidel Castro as well as other future Cuban revolutionaries in Mexico.[6][8] Guevara was inspired to join them in their revolution by Fidel Castro and was decided to be the doctor of the Granma yacht.[6]
Cuban Revolution (1956–1958)
Guevara was involved in the Cuban revolution and was a member of the Granma yacht expedition to Cuba. He fought in Sierra Maestra and was at the head of the invasion.[3]
Governance in Cuba (1959–1965)
During the Bay of Pigs invasion of Cuba, Guevara almost was killed by an accidental discharge of his pistol. While leading the Rebel Army Command at the previous headquarters of the Rural Guard in Consolación del Sur in Pinar del Río, he fell on a pipe which loosened his pistol from his belt which proceeded to discharge. The bullet entered his right cheekbone and exited by his ear. He received a tetanus vaccine due to the shot, to which he was allergic.[9]
In December 1964, Che spoke at the United Nations and encouraged the UN to take action against imperialism.[10]
On 24 February 1965, he addressed the Second Economic Seminar of Afro-Asian Solidarity in Algeria. He called for socialist countries to support post-colonial states in order to protect them from imperialist banks. He said trade between socialist countries should help both countries develop.[11]
Struggle in Congo (1965–1966)
Che left Cuba before he could attend the Tricontinental Conference and fought in the revolutionary movement in the Congo.[12]
Struggle in Bolivia and capture (1966–1967)
Mario Monje, leader of the Bolivian Communist Party, agreed to support Che's struggle in Bolivia.[12] The CIA, working with wealthy Cuban exiles, captured and murdered Che Guevara in Quebrada del Yuro near La Higuera in Bolivia on the 8th of October, 1967.[6][13][14][15]
Works
Guerrilla warfare
Reminiscences of the Cuban revolutionary war
On revolutionary medicine
Bibliography
Che Guevara biographies
- Richard L. Harris (2011). Che Guevara: a biography. Santa Barbara, Califonia: Greenwood. ISBN 978-0-313-35916-3 [LG]
- Fidel Castro (2006). Che: a memoir. Melbourne: Ocean Press. ISBN 978-1-921700-83-5 [LG]
- Jon Lee Anderson (2010). Che: a revolutionary life. Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-9725-2 [LG]
- Jorge G. Castañeda (1998). Compañero: the life and death of Che Guevara. New York: Vintage Books. ISBN 9780679759409 [LG]
- Pablo Ignacio Taibo II (1997). Guevara, Also Known as Che. Thomas Dunne Books (St. Martin's Press). ISBN 9780312155391 [LG]
References
- ↑ Richard L. Harris (2011). 'Timeline: events in the life of Che Guevara' in Che Guevara: a biography. Santa Barbara, Califonia: Greenwood. ISBN 978-0-313-35916-3 [LG]
- ↑ "President Maduro Highlights Ernesto Che Guevara's Legacy" (2021-10-08). teleSUR. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Pedro Ríoseco (2023-06-14). "We will be like Che, the motto that belongs to an entire people" Granma. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Jon Lee Anderson (2010). 'A plantation in Misiones' in Che Guevara: a revolutionary life. Grove Press. ISBN 978-0-8021-9725-2 [LG]
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 I. Lavretsky (1976). 'First steps' in Ernesto Che Guevara. Progress Publishers. [LG]
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 Ángel Freddy Pérez Cabrera (2023-06-14). "Che, an extraordinarily human man" Granma. Retrieved 2023-07-07.
- ↑ "Che Guevara's Socialism Against Revolutionary Dogma" (2019-10-09). teleSUR. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- ↑ Yisel Martínez (2018-06-13). "Ernesto Guevara: The man who gave himself" Granma. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- ↑ Ronald Suárez Rivas (2017-09-28). "The shot that almost took Che's life" Granma. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- ↑ Vijay Prashad (2008). The Darker Nations: A People's History of the Third World: 'Belgrade' (p. 104). [PDF] The New Press. ISBN 9781595583420 [LG]
- ↑ Vijay Prashad (2017). Red Star over the Third World: 'Colonial Fascism' (p. 113). [PDF] New Delhi: LeftWord Books.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Vijay Prashad (2008). The Darker Nations: A People's History of the Third World: 'Havana' (pp. 108–109). [PDF] The New Press. ISBN 9781595583420 [LG]
- ↑ William Blum (2002). Rogue State: A Guide to the World's Only Superpower: 'A Concise History of United States Global Interventions, 1945 to the Present' (p. 123). [PDF] Zed Books Ltd. ISBN 9781842772201 [LG]
- ↑ Yenia Silva Correa (2017-08-09). "What it means to be like Che" Granma. Retrieved 2023-07-09.
- ↑ "'Che Guevara' Is Remembered 53 Years After His Assassination" (2020-10-09). teleSUR. Retrieved 2023-07-09.