More languages
More actions
General-KJ (talk | contribs) (Added Logo, hope we don't get copyrighted!) Tag: Visual edit |
General-KJ (talk | contribs) (Reorganised article and added table of members) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
=== Modern Commonwealth === | === Modern Commonwealth === | ||
In 1949 following the independence of India in 1947, a meeting was held in London where the [[London Declaration]] was made. Following independence India wanted to remove the monarch as head of state but remain in the commonwealth, this declaration allowed republics to remain in the commonwealth, and under British Imperialist control. Following this, as former British colonies declared their independence they joined the Commonwealth. | In 1949 following the independence of India in 1947, a meeting was held in London where the [[London Declaration]] was made. Following independence India wanted to remove the monarch as head of state but remain in the commonwealth, this declaration allowed republics to remain in the commonwealth, and under British Imperialist control. Following this, as former British colonies declared their independence they joined the Commonwealth.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In | In 1961 South Africa left the Commonwealth due to its [[Apartheid]] laws, it would re-join again in 1994 following the official end of apartheid.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In | In 1972 [[Islamic Republic of Pakistan|Pakistan]] withdrew from the Commonwealth in protest at the Commonwealth's recognition, and acceptance of [[People's Republic of Bangladesh|Bangladesh]] into the organisation. It would re-join in 1989.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In | In 1987 [[Republic of Fiji|Fiji]] left following a coup, re-joining in 1997 before being suspended yet again in 2000 following another coup.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In | In 1995 [[Federal Republic of Nigeria|Nigeria]] was suspended following the execution of [[Ken Saro-Wiwa]]. It would be reinstated in 1999.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In 1999 Pakistan was suspended following a military coup.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
In 1999 | |||
In 2001 Fiji was reinstated following bourgeois elections before being suspended again in 2009 following another coup.<ref name=":1" /> | In 2001 Fiji was reinstated following bourgeois elections before being suspended again in 2009 following another coup.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
=== Suspension of Zimbabwe === | === Suspension of Zimbabwe === | ||
In 2002 Zimbabwe was suspended from the Commonwealth and in 2003 withdrew,<ref name=":1" /> following its land reform act. This act redistributed land to subsistence farmers from the estates of wealthy white corporate farmers who had expropriated the land. Naturally this was treated as a threat by British Capitalism, and it expelled Zimbabwe from the organisation, ordering all members to cut ties with Zimbabwe. Following the expulsion the UK enforced harsh sanctions, backed by the [[United States of America|US]], which caused hyperinflation and economic chaos. British capitalism used Zimbabwe as an example for the rest of the Commonwealth of what would happen if they dared to defy the wishes of the Liberal World order.<ref name=":0" /> | In 2002 [[Republic of Zimbabwe|Zimbabwe]] was suspended from the Commonwealth and in 2003 withdrew,<ref name=":1" /> following its land reform act. This act redistributed land to subsistence farmers from the estates of wealthy white corporate farmers who had expropriated the land. Naturally this was treated as a threat by British Capitalism, and it expelled Zimbabwe from the organisation, ordering all members to cut ties with Zimbabwe. Following the expulsion the UK enforced harsh sanctions, backed by the [[United States of America|US]], which caused hyperinflation and economic chaos. British capitalism used Zimbabwe as an example for the rest of the Commonwealth of what would happen if they dared to defy the wishes of the Liberal World order.<ref name=":0" /> | ||
=== 21st Century === | === 21st Century === | ||
2004 Pakistan was reinstated before being suspended again in 2007 following a declared state of emergency and suspension of the | In 2004 Pakistan was reinstated before being suspended again in 2007 following a declared state of emergency and suspension of the constitution. It was reinstated once more in 2008.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In 2016 | In 2013 [[Republic of The Gambia|Gambia]] left followed by [[Republic of Maldives|Maldives]] in 2016 but the former would re-join in 2018 and the latter in 2020.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
In | In 2014 Fiji was reinstated.<ref name=":1" /> | ||
== Member States == | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ | |||
!Country | |||
!First Joined | |||
!Continent | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Antigua and Barbuda.svg.png}} [[Antigua and Barbuda]] | |||
|1 November 1981 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Australia flag.png}} [[Commonwealth of Australia|Australia]] | |||
|19 November 1926 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of the Bahamas.svg.png}} [[Commonwealth of The Bahamas|Bahamas]] | |||
|10 July 1973 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Bangladesh.svg}} [[People's Republic of Bangladesh|Bangladesh]] | |||
|18 April 1972 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Barbados.svg.png}} [[Barbados]] | |||
|30 November 1966 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Belize.svg.png}} [[Belize]] | |||
|21 September 1981 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Botswana.svg}} [[Republic of Botswana|Botswana]] | |||
|30 September 1966 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Brunei.svg}} [[Brunei Darussalam|Brunei]] | |||
|7 May 1984 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Cameroon.svg}} [[Republic of Cameroon|Cameroon]] | |||
|1 November 1995 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Canada.png}} [[Canada]] | |||
|19 November 1926 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Cyprus.svg}} [[Republic of Cyprus|Cyprus]] | |||
|13 March 1961 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Dominica.svg}} [[Commonwealth of Dominica|Dominica]] | |||
|3 November 1978 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Eswatini flag.png}} [[Kingdom of Eswatini|Eswatini]] | |||
|6 September 1968 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Fiji.svg}} [[Republic of Fiji|Fiji]] | |||
|10 October 1970 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Gabon.svg}} [[Gabonese Republic|Gabon]] | |||
|25 June 2022 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of The Gambia.svg}} [[Republic of The Gambia|Gambia]] | |||
|18 February 1965 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Ghana.png}} [[Republic of Ghana|Ghana]] | |||
|6 March 1957 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Grenada flag.png}} [[Grenada]] | |||
|7 February 1974 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Guyana flag.png}} [[Co-operative Republic of Guyana|Guyana]] | |||
|26 May 1966 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of India.svg}} [[Republic of India|India]] | |||
|15 August 1947 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Jamaican flag.svg}} [[Jamaica]] | |||
|6 August 1962 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Kenya.svg}} [[Republic of Kenya|Kenya]] | |||
|12 December 1963 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Kiribati.svg}} [[Republic of Kiribati|Kiribati]] | |||
|12 July 1979 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Lesotho.svg}} [[Kingdom of Lesotho|Lesotho]] | |||
|4 October 1966 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Malawi.svg}} [[Republic of Malawi|Malawi]] | |||
|6 July 1964 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Malaysia.svg}} [[Malaysia]] | |||
|31 August 1957 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Maldives.svg}} [[Republic of Maldives|Maldives]] | |||
|9 July 1982 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Malta.svg}} [[Republic of Malta|Malta]] | |||
|21 September 1964 | |||
|Europe | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Mauritius.svg}} [[Republic of Mauritius|Mauritius]] | |||
|12 March 1968 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Mozambique.svg.png}} [[Republic of Mozambique|Mozambique]] | |||
|13 November 1995 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Namibia.svg}} [[Republic of Namibia|Namibia]] | |||
|21 March 1990 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Nauru.svg}} [[Republic of Nauru|Nauru]] | |||
|29 November 1968 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Aotearoa.svg}} [[New Zealand]] | |||
|19 November 1926 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Nigeria.svg}} [[Federal Republic of Nigeria|Nigeria]] | |||
|1 October 1960 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Pakistan.svg}} [[Islamic Republic of Pakistan|Pakistan]] | |||
|14 August 1947 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Papua New Guinea.svg}} [[Independent State of Papua New Guinea|Papua New Guinea]] | |||
|16 September 1975 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Rwanda.svg}} [[Republic of Rwanda|Rwanda]] | |||
|29 November 2009 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Saint Kitts and Nevis.svg}} [[Federation of Saint Christopher and Nevis|Saint Kitts and Nevis]] | |||
|19 September 1983 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Saint Lucia.svg}} [[Saint Lucia]] | |||
|22 February 1979 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Saint Vincent and the Grenadines.svg}} [[Saint Vincent and the Grenadines]] | |||
|27 October 1979 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Samoa.svg}} [[Independent State of Samoa|Samoa]] | |||
|28 August 1970 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Seychelles.svg}} [[Republic of Seychelles|Seychelles]] | |||
|28 June 1976 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Sierra Leone.svg.png}} [[Republic of Sierra Leone|Sierra Leone]] | |||
|27 April 1961 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Singapore.svg}} [[Republic of Singapore|Singapore]] | |||
|15 October 1965 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of the Solomon Islands.svg.png}} [[Solomon Islands]] | |||
|7 July 1978 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of South Africa.png}} [[Republic of South Africa|South Africa]] | |||
|19 November 1926 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of sri lanka.png}} [[Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka|Sri Lanka]] | |||
|4 February 1948 | |||
|Asia | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Tanzania.svg}} [[United Republic of Tanzania|Tanzania]] | |||
|9 December 1961 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Togo.svg}} [[Togolese Republic|Togo]] | |||
|25 June 2022 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Tonga.svg}} [[Kingdom of Tonga|Tonga]] | |||
|4 June 1970 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Trinidad and Tobago.svg}} [[Republic of Trinidad and Tobago|Trinidad and Tobago]] | |||
|31 August 1962 | |||
|Americas | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Tuvalu.svg}} [[Tuvalu]] | |||
|1 October 1978 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Uganda.svg}} [[Republic of Uganda|Uganda]] | |||
|9 October 1962 | |||
|Africa | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of the United Kingdom.svg}} [[United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland|United Kingdom]] | |||
|19 November 1926 | |||
|Europe | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Vanuatu.svg}} [[Republic of Vanuatu|Vanuatu]] | |||
|30 July 1980 | |||
|Oceania | |||
|- | |||
|{{Flagicon|Flag of Zambia.svg.png}} [[Republic of Zambia|Zambia]] | |||
|24 October 1964 | |||
|Africa | |||
|} | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
<references /> | <references /> | ||
[[Category:Imperialist intergovernmental organizations]] | [[Category:Imperialist intergovernmental organizations]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:28, 17 January 2024
| Commonwealth of Nations | |
|---|---|
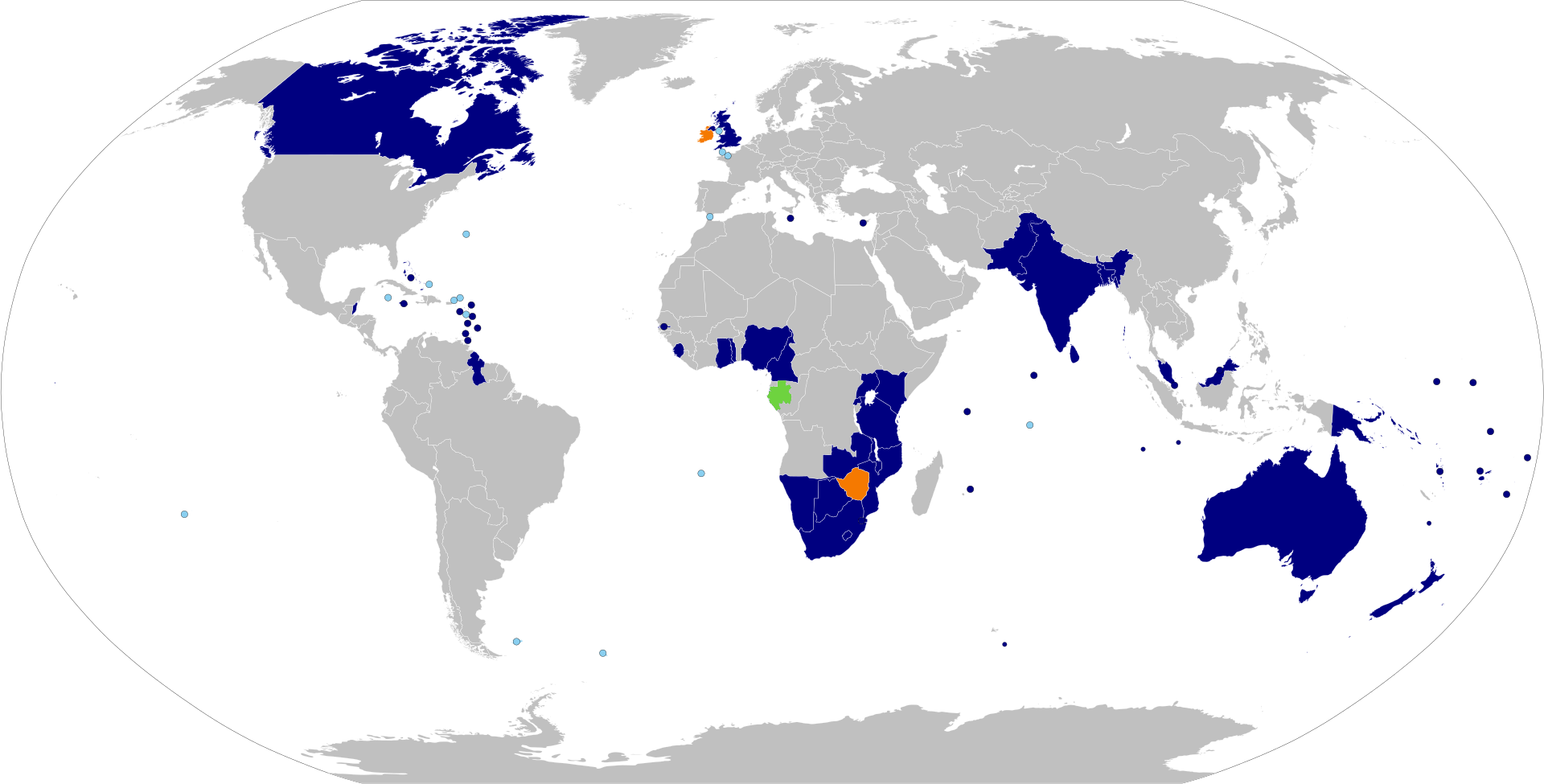 Dark Blue: Current member state Green: Suspended member state Orange: Former member states Light Blue: British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies | |
| Headquarters | Marlborough House, London, United Kingdom |
| Leaders | |
• Head | Charles III |
• Secretary-General | Patricia Scotland |
• Chair-in-Office | Paul Kagame |
| History | |
• Balfour Declaration | 19 November 1926 |
• Statute of Westminster | 11 December 1931 |
• London Declaration | 28 April 1949 |
| Area | |
• Total | 29,958,050 km² |
The Commonwealth, officially the Commonwealth of Nations, is an imperialist intergovernmental organisation made up mostly of former British colonies. The organisation is used by the British to tie itself to its former colonies, and maintain the liberal world order, with 15 out of the 56 members still using the British monarch as head of state.[1]
History[edit | edit source]
Foundation[edit | edit source]
In the 19th century Britain started reforming its most important colonies into dominions, allowing them to be semi-autonomous. From 1887 leaders of these dominions attended conferences with Britain with the 1926 Imperial Conference being attended by the leaders of Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, Newfoundland, New Zealand, and South Africa. At the 1926 conference the Balfour Declaration was made which declared that supposedly all members were "equal members of the community of the British Empire", thus beginning the reformation of the Empire into the Commonwealth.[2]
Modern Commonwealth[edit | edit source]
In 1949 following the independence of India in 1947, a meeting was held in London where the London Declaration was made. Following independence India wanted to remove the monarch as head of state but remain in the commonwealth, this declaration allowed republics to remain in the commonwealth, and under British Imperialist control. Following this, as former British colonies declared their independence they joined the Commonwealth.[2]
In 1961 South Africa left the Commonwealth due to its Apartheid laws, it would re-join again in 1994 following the official end of apartheid.[2]
In 1972 Pakistan withdrew from the Commonwealth in protest at the Commonwealth's recognition, and acceptance of Bangladesh into the organisation. It would re-join in 1989.[2]
In 1987 Fiji left following a coup, re-joining in 1997 before being suspended yet again in 2000 following another coup.[2]
In 1995 Nigeria was suspended following the execution of Ken Saro-Wiwa. It would be reinstated in 1999.[2]
In 1999 Pakistan was suspended following a military coup.[2]
In 2001 Fiji was reinstated following bourgeois elections before being suspended again in 2009 following another coup.[2]
Suspension of Zimbabwe[edit | edit source]
In 2002 Zimbabwe was suspended from the Commonwealth and in 2003 withdrew,[2] following its land reform act. This act redistributed land to subsistence farmers from the estates of wealthy white corporate farmers who had expropriated the land. Naturally this was treated as a threat by British Capitalism, and it expelled Zimbabwe from the organisation, ordering all members to cut ties with Zimbabwe. Following the expulsion the UK enforced harsh sanctions, backed by the US, which caused hyperinflation and economic chaos. British capitalism used Zimbabwe as an example for the rest of the Commonwealth of what would happen if they dared to defy the wishes of the Liberal World order.[1]
21st Century[edit | edit source]
In 2004 Pakistan was reinstated before being suspended again in 2007 following a declared state of emergency and suspension of the constitution. It was reinstated once more in 2008.[2]
In 2013 Gambia left followed by Maldives in 2016 but the former would re-join in 2018 and the latter in 2020.[2]
In 2014 Fiji was reinstated.[2]
Member States[edit | edit source]
| Country | First Joined | Continent |
|---|---|---|
| 1 November 1981 | Americas | |
| 19 November 1926 | Oceania | |
| 10 July 1973 | Americas | |
| 18 April 1972 | Asia | |
| 30 November 1966 | Americas | |
| 21 September 1981 | Americas | |
| 30 September 1966 | Africa | |
| 7 May 1984 | Asia | |
| 1 November 1995 | Africa | |
| 19 November 1926 | Americas | |
| 13 March 1961 | Asia | |
| 3 November 1978 | Americas | |
| 6 September 1968 | Africa | |
| 10 October 1970 | Oceania | |
| 25 June 2022 | Africa | |
| 18 February 1965 | Africa | |
| 6 March 1957 | Africa | |
| 7 February 1974 | Americas | |
| 26 May 1966 | Americas | |
| 15 August 1947 | Asia | |
| 6 August 1962 | Americas | |
| 12 December 1963 | Africa | |
| 12 July 1979 | Oceania | |
| 4 October 1966 | Africa | |
| 6 July 1964 | Africa | |
| 31 August 1957 | Asia | |
| 9 July 1982 | Asia | |
| 21 September 1964 | Europe | |
| 12 March 1968 | Africa | |
| 13 November 1995 | Africa | |
| 21 March 1990 | Africa | |
| 29 November 1968 | Oceania | |
| 19 November 1926 | Oceania | |
| 1 October 1960 | Africa | |
| 14 August 1947 | Asia | |
| 16 September 1975 | Oceania | |
| 29 November 2009 | Africa | |
| 19 September 1983 | Americas | |
| 22 February 1979 | Americas | |
| 27 October 1979 | Americas | |
| 28 August 1970 | Oceania | |
| 28 June 1976 | Africa | |
| 27 April 1961 | Africa | |
| 15 October 1965 | Asia | |
| 7 July 1978 | Oceania | |
| 19 November 1926 | Africa | |
| 4 February 1948 | Asia | |
| 9 December 1961 | Africa | |
| 25 June 2022 | Africa | |
| 4 June 1970 | Oceania | |
| 31 August 1962 | Americas | |
| 1 October 1978 | Oceania | |
| 9 October 1962 | Africa | |
| 19 November 1926 | Europe | |
| 30 July 1980 | Oceania | |
| 24 October 1964 | Africa |

