More languages
More actions

Anti-base movement is a term which refers to various movements which focus on opposing aspects of military bases, which can range from opposition to specific activities of bases or base personnel, to opposing their presence or construction in particular locations, to opposing their existence in general. It can also refer to these movements collectively.[1][2]
Given that the majority of foreign military bases around the world are United States bases,[3][4][5] many anti-base movements around the world have been directed at U.S. bases.
Among the many grievances expressed by anti-base movement activists are issues such as criminal and negligent activity of base personnel, the environmental pollution and destruction generated by U.S. bases, the erosion of national sovereignty that occurs with the U.S. military presence in host locations, and the international provocations and tensions that occur when countries host US bases and collaborate with US military exercises.[6]
Background[edit | edit source]
Prevalence of US bases[edit | edit source]
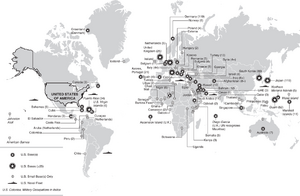
As of a 2021 estimate, the U.S. has approximately 750 bases around the world in at least 80 countries, with the largest concentration of them being in Japan (especially in Okinawa), followed by Germany and south Korea,[7] resulting in many corresponding anti-base movements. There are also anti-base movements within locations claimed by the U.S. as its own territory, some examples being Guam and Hawaiʻi.[8][9] A 2024 study by The Tricontinental described 902 known US military bases.[10]
Cooperative security locations[edit | edit source]
Additionally, some anti-base movements oppose bases which are not formally considered to be a US base by law, but which effectively serve as a US base, many in the form of cooperative security locations (CSL) or forward operating locations, or other such formations sometimes referred to as "lily-pad" bases.[11]
An example of this type of location would be the Military-Civilian Port Complex in south Korea, technically a south Korean base, but which local activists have explained is a place where "strategic assets in the US military can stop by whenever they please according to American interests."[12]
Another example of a legally ambiguous de facto base is the West Africa Logistics Network (WALN) at Kotoka International Airport in Ghana, a "cooperative security location" where the US military and related personnel are afforded numerous privileges, including the ability to conduct construction activities and store defense equipment, supplies, and materiel, enter into Ghana without visa or passport nor customs inspection for U.S. personnel, and protection for U.S. soldiers from being prosecuted by Ghanaian authorities for crimes, following a 2018 Status of Forces Agreement.[13][14]
History of US bases[edit | edit source]

The US settler-colonial state was established on North America through a series of military forts expanding across the continent. The settler state used its military force to defend and advance "civilian" settlers (and their volunteer militias) in their encroachment on more and more land, including punishing indigenous peoples' defense of their borders agreed on in treaties with the settler state, and used its military presence to "force compliance" when indigenous tribes and bands refused to live on reservations or make treaties on the invading settlers' terms.[15]
By this process of expanding military power across the continent, the US occupied much of North America, and then began expanding its base presence to numerous other locations throughout the world starting in the 1890s, leading to further resistance movements. For example, the US military "faced opposition and an insurgency seeking independence almost immediately after seizing the Philippines in 1898".[1] As it expanded its empire in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, the U.S. built bases in Alaska, Hawaiʻi, Puerto Rico, the Philippines, Guam, Panama, and Guantánamo Bay, Cuba.[16]
Author David Vine describes the dynamics of coercion and power imbalance which has accompanied the establishment of many of the U.S.'s post-WWII bases which had, "to one degree or another" been "consented to" by the host nations' governments in the context of "gaping power disparities" and inflated fears about the Soviet Union:
Although the United States has been an empire occupying Native American lands with military bases since independence, its post–World War II collection of foreign bases has been distinguished by the fact that most national governments have, to one degree or another, consented to the country’s presence [...] Importantly, however, this consent has come in a context of often gaping power disparities, where US officials have used US dominance, forms of political-economic coercion, and fears of the Soviet Union (at times, intentionally inflated) to ensure national governments consented to a US base presence.[1]
Issues with US bases[edit | edit source]
Violence toward local population[edit | edit source]
The violent crimes of U.S. military personnel and U.S. civilian contractors working in base areas include numerous killings and sexual assault crimes committed against the citizens of the countries where they are stationed.[17]
In addition to violence perpetrated by individual personnel against locals, negligence during routine activities of bases have also caused violent damage to local populations, such as people being seriously injured and killed by errant bombs.[18][19]
Areas with a base presence also face issues of increased sex trafficking. For example, in south Korea, a legally-sanctioned prostitution industry was purposely encouraged and maintained by the government in special zones around US bases, with this system persisting for decades.[20]
Environmental destruction[edit | edit source]

The environmental destruction brought about by base presence takes a range of forms, arising from the initial construction of the base and how it alters the environment, to the ongoing activities of the base in that particular location, to the after-effects that remain even after a base has ceased operation. Some examples of environmental hazards are leakages of jet fuel into local drinking water, toxic PFAS foam leaks, litter from practice drills bleeding chemicals into the ground and water, and extreme noise pollution. In addition to physically hazardous pollution, culturally or spiritually significant sites can be destroyed or desecrated by base presence. A 2018 petition by World Can't Wait to stop RIMPAC exercises, addressed to the then-governor of Hawaiʻi, describes further examples:
Retired military ships are towed out to sea and then targeted with missiles and torpedoes until they sink to a watery graveyard on the ocean floor. There they leach toxic chemicals, including PCBs, which accumulate in the bodies of fish, dolphins and whales – and ultimately into our food. Amphibious landing exercises, which include heavy tracked vehicles, damage reefs, erode shoreline, and endanger wildlife. [...] Areas that have been used for live fire training and bombing practice are uninhabitable; bombing and live fire practice is not only continuing but escalating in the age of the “Pacific Pivot”. Indigenous Hawaiian cultural sites have been destroyed. U.S. Military fuel storage tanks are leaking poisons into the drinking water in Hawai`i's most populous city. Vast areas of land and water are so toxic as to be unusable.[21]
National sovereignty concerns[edit | edit source]

Bases may be established and their continuing presence maintained by a variety of methods, ranging from mutual legal agreements to brute force and occupation. Often, a combination of these factors is employed in installing and maintaining a base's presence when its presence is based in imperialist, bourgeois interests not premised on local popular support or when local popular support diminishes and wavers over time.
The presence of foreign bases in one's territory raises concerns over the effect the base presence has on national sovereignty in the host (or occupied) nation. This may range from issues such as which nation has authority to prosecute crimes committed by base personnel in the host country, to what the land area, local resources, and local labor consumed by the base could be otherwise used for by the host nation's populace, to the potential consequences that large concentrations of foreign military personnel and their equipment being present in the location may have on the host nation's overall national security, domestic policymaking, and diplomatic bargaining power.[22]
Status of Forces Agreements[edit | edit source]
The legal agreements made between countries to host foreign military personnel and how domestic laws apply to them are commonly known as Status of Forces Agreements (SOFAs). There is no standard form of SOFA and they may include a variety of provisions. In the case of SOFAs made with the U.S., the most commonly addressed issue in a SOFA is legal protection from prosecution for U.S. personnel while present in a foreign country, and whether the U.S. will exercise sole jurisdiction over U.S. personnel or shared jurisdiction with the host. SOFAs are not themselves security arrangements nor basing agreements. As is noted by a Congressional Research Service report, "a SOFA itself does not constitute a security arrangement; rather, it establishes the rights and privileges of U.S. personnel present in a country in support of the larger security arrangement." The 2012 report noted that, at time of writing, the U.S. was party to more than 100 agreements that may be considered SOFAs.[23]
Though SOFAs are not formally basing agreements, a 2021 article in The Tricontinental explains how Ghana's 2018 SOFA agreement nonetheless allows the U.S. such a level of authority over facilities in Ghana so as to be able to effectively set up a base through Articles 5 and 6 of the agreement, designating agreed facilities to be of "unimpeded" and "exclusive" use to the U.S. and that Ghana "shall also provide access to and use of a runway that meets the requirements of United States forces."[14] Furthermore, the agreement gives the U.S. forces and U.S. contractors the ability to "undertake construction activities" and make alterations to agreed facilities and to "preposition and store defense equipment, supplies, and materiel" at agreed facilities and areas,[24] gives U.S. soldiers the right to carry arms on duty, allows U.S. army and civilians to enter Ghana without a passport nor a visa but just identification cards, allows the U.S. army to not take responsibility for the death of any other person aside from U.S. military personnel, and third party issues involving U.S. military personnel will only be resolved according to the laws of the United States, among other preferential treatments.[24][25][13] Such agreements between the U.S. and Ghana have led to the establishment of the West Africa Logistics Network (WALN) at Kotoka International Airport in Accra to "ferry supplies and arms to special forces troops across the region".[26]
War provocations[edit | edit source]
The presence of military bases in a location leads to the concern of that location becoming a strategically significant location with regard to international tensions involving the host country, the hosted country, and their various neighbors, allies, targets, and/or rivals. People who live in the host nation are confronted with the potential wartime actions resulting from the presence of a base in their territory in addition to the peacetime concern of the base's potential to provoke international tensions, such as through military build-up, exercises, and shows of force. Individuals and organizations within anti-base movements may express a variety of perspectives on such issues, such as locals' urgent safety concerns over their location becoming a diplomatic pawn or wartime hotspot or launch pad, general anti-war or pacifist sentiments, promotion of non-alignment, and explicitly anti-imperialist sentiment.[1]
In the present-day context, of high concern in host locations of US bases is what this portends in regard to conflicts between the US-led imperialist bloc on one hand, and the imperialists' perceived or declared targets and rivals on the other, sometimes referred to as the New Cold War.[27]
As political scientist and Guam independence advocate[28] Kenneth Gofigan Kuper has described, writing about the highly militarized US colony of Guam:
In the coming years, I am afraid things will get worse for the people of Guam unless restraint enters the picture. [...] One of Guam’s former non-voting representatives in Congress, Ben Blaz, once said of our island, “We are equal in war, but not in peace.” I think he was only half-right. While we are clearly not equal in peace, as no colony can be, we are NOT equal in war. We in Guam bear the brunt of U.S. power projection in the Indo-Pacific, both as provocative threat and as a target. The task of securing a “free and open” Indo-Pacific is disproportionately on our backs.[29]
Representing Oceania Rising at a 2017 talk about militarization and resistance in the Pacific, Kuper gave an example of the dynamic at play in US-occupied Guam, where the U.S. military presence threatens Guam more than protects it. Explaining that Guam is within range of China's IRBM the DF-26, as well as within the range of the DPRK's precision strike means, Kuper stated "I remember, when all this news was coming out, you had people on Facebook and social media saying, 'Thank God the U.S. military is here. They're gonna protect us from these threats.' And I countered, saying, 'Why the Hell are these threats here to begin with--in Guam? It's exactly the United States military presence.'" Kuper continued, clarifying that rather than offering protection, the military presence "makes everything so much more dangerous." He added that the people of Guam experience periodic threats over geopolitical tensions, stating "we are pawns in a game we don't even want to be a part of."[30]
Bases and anti-base movements by location[edit | edit source]
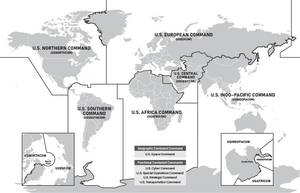
The United States Department of Defense (DoD) divides its commands into various areas of responsibility (AOR), with seven combatant commands covering geographic areas (one of them being US Space Command), while the remaining commands cover functions such as transportation and special operations.[31][32] As US bases are generally managed and strategically conceptualized according to this structure, and likewise anti-base movements in different nations are thus strategically linked and affected by which areas of responsibility they fall under or adjoin, this section will be divided roughly following its scheme and some of its terminology.
Africa[edit | edit source]
U.S. Africa Command (USAFRICOM) began its operations on October 1, 2007 and became fully operational on October 1, 2008. It is headquartered at Kelley Barracks in Stuttgart, Germany.[33] The US's main "enduring" base in Africa is Camp Lemonnier in Djibouti.[34] A 2024 article in World Beyond War estimated that the US maintains around 52 bases in Africa.[35]
The US justifies its military presence in Africa by claiming to assist African governments in building capacity in their armed forces to deal with violent extremists and to respond to crises.[33] However, despite claiming to combat terrorism, the increased presence of the US military in Africa has been followed by an increase in terrorist incidents,[36] and essentially functions as a protection racket.[37] As an article in Peoples Dispatch points out, "the main cause behind the explosion of terrorist organizations in the region was the 2011 Libyan war in which AFRICOM itself was an aggressor."[38]
As was observed by Tunde Osazua of Black Alliance for Peace (BAP), the occupation of countries and bombings that the US has used to achieve its goals in Africa are acts of terror, along with the economic terrorism of murderous sanctions enforced by the US and austerity programs imposed via the IMF and World Bank.[39] The actual purpose of AFRICOM has been summarized by BAP as "to use U.S. military power to impose U.S. control of African land, resources and labor to service the needs of U.S. multi-national corporations and the wealthy in the United States".[40]
Niger[edit | edit source]

Niger has previously been a center for US operations in west and north Africa, as part of a chain of US bases and outposts across the Sahel region.[41][42] Prominent US bases in Niger are Air Base 101 in Niamey and Air Base 201 in Agadez, and a CIA-run base in Dirkou. Airbase 201 is the second largest US base in Africa (the largest being in Djibouti).[43]
In 2023, Niger's newly-formed National Council for the Safeguard of the Homeland (CNSP) terminated Niger's military agreements with France and ordered the withdrawal of French troops. France initially resisted this and attempted to mobilize the pro-western grouping of ECOWAS into a war against Niger,[44] but eventually stood down and withdrew its troops.[43] In March of 2024, CNSP suspended Niger's military cooperation with the US.[41]
Middle East[edit | edit source]
Europe[edit | edit source]
Indo-Pacific[edit | edit source]

The U.S. designates the area covering the Pacific Ocean, Indian Ocean, and much of Asia as USINDOPACOM. It is the oldest and largest of the U.S.'s unified commands, and it has been referred to by the DoD as its "priority theater". The DoD has identified competition with China as the organizing principle of the Indo-Pacific posture since the early 2010s.[45] Its area of responsibility covers more area than any of the other geographic commands and shares borders with all five of the other geographic commands.[46]

U.S. military presence in the Indo-Pacific is headquartered in the occupied nation of Hawaiʻi,[47] whose sovereign government the US Navy overthrew in an 1893 coup.[48] Some of the US's most significant overseas bases and forces are in the Indo-Pacific, with many positioned in south Korea and Japan, as US strategy in this area targets China, DPRK, and Russia. This area is the location of the world's largest maritime exercise, the US-led RIMPAC.[49]
In Oceania, the U.S. has significant air and naval bases on its occupied colony Guam, and operates the Ronald Reagan Ballistic Missile Defense Test Site at Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands. The Department of Defense is building a high-frequency radar system in Palau. Additionally, the U.S. military has ties with Fiji, Papua New Guinea, and Tonga.[47] Also significant is the Diego Garcia base in the Indian Ocean, built after the forced displacement of the island's inhabitants through a joint US-UK effort.[50][51] Diego Garcia's location is strategically significant, enabling the U.S. military to reach numerous locations in surrounding regions, for example having been used for launching U.S. bombings of Iraq and Afghanistan.[52][53]
Japan[edit | edit source]
Okinawa[edit | edit source]
Okinawa has more than half of the 54,000 U.S. troops based in Japan.[45] Okinawa was once the independent Ryukyu Kingdom which was then colonized by Japan, later falling under the rule of the United States for 27 years (until 1972),[54] and is currently regarded as a Japanese prefecture.[55] Protests against US occupation and land seizures in Okinawa began within months of the end of the Second World War.[1]
Sunagawa struggle[edit | edit source]
In the 1950s, a significant anti-base struggle emerged in the Tokyo suburb Sunagawa, in protest of the expansion of Tachikawa Air Base. The expansion was to occur via land expropriations on behalf of the U.S. Air Force,[1] slated to evict 140 families from their homes and farmland.[56] The local farmers began trying to prevent the work of land surveyors, such as by blocking the path of their vehicles and forming the Sunagawa Anti-Base Expansion Alliance. Over time, regional and national labor unions, student groups, Buddhist monks and nuns, lawmakers and other citizens became involved in the struggle as well.[56] A report in The Japan Times explains that by 1956, "2,000 police officers were ordered to evict the farmers from the land that they continued to occupy, only to be met with 6,000 protesters, resulting in a clash that left roughly 1,000 people injured, many seriously." The struggle against the base expansion continued, and by 1968, the U.S. military "quietly announced it had given up on the planned runway extension" and returned the base to the Japanese government in 1977.[56]
Dennis Banks, who would later be a co-founder of the American Indian Movement, was present during some of these events in 1956, while stationed in Japan at age 17. Banks described being ordered to "shoot to kill" if the demonstrators entered the base and did not respond to warning shots, and recounted feeling unable to comprehend the order: "We could not understand this. These people were nothing more than nonviolent demonstrators. This was their land that our Air Force was trying to take away." Banks then witnessed the Japanese police rushing the demonstrators "in a frenzy" and "cracking skulls with a terrible sound" and Banks saw "elderly nuns with blood streaming down their faces." Banks recounted, "I felt sick at what I had seen and ashamed of the uniform I was wearing. [...] That terrible scene has remained with me all of these years. I shall never forget those demonstrators were peaceful people literally being beaten to death. Since that time, during my struggles in the American Indian Movement, I have seen BIA police wield their clubs at Indians like that. Each time my memory flashed back to what I saw that day in Japan." Soon, following these and other experiences while "guarding the ramparts of the American Empire" in Japan, Banks went AWOL and "wanted nothing more to do with the military or the U.S. government."[57]
Korea[edit | edit source]

The single nation of Korea has been divided by U.S. occupation since shortly after the Second World War, when the U.S. refused to withdraw its forces and helped orchestrate the holding of separate elections in the south, establishing the "Republic of Korea," a U.S. puppet state ruled by a series of right-wing dictatorships, which the U.S. continues to occupy and reserves control over the south Korean military during wartime. This puppet state is postured against the DPRK, which formed after the U.S.-sponsored separate elections in the south.[60] It is also positioned against China[61] and other targets of US imperialism, for example supplying thousands of soldiers on the imperialist side in the Vietnam war and Iraq war.[62]
Anti-US and anti-base movements in south Korea have existed since the beginning of U.S. occupation in Korea and continue to this day, both on the mainland of the Korean peninsula and on Jeju Island, where locals and their supporters (including activists from other occupied nations in the Pacific)[63] attempted to prevent the construction of a naval base for over a decade.[64]
Maehyang-ri Kooni Firing Range[edit | edit source]
Between 1954 and 2005, two small islets, accessible by foot at low tide, off the coast of the village of Maehyang-ri were used as a bombing range for the U.S. Air Force. Residents of Maehyang-ri suffered deaths and injuries from errant bombs, extreme noise exposure, psychological damage, a heightened suicide rate, and pollution of the land and sea. Media coverage of the firing range was forbidden until south Korea's democratization movement in 1988.[18]
An article from 2000, before the range's closure, describes the situation at the time, stating that overall management of the range had been contracted out to Lockheed Martin. The firing range's activities are described as follows:
The Kooni Range is composed of a bombing range for bomber planes on the Nong-do island (which can be reached on foot during low tide) off the coast and a strafing range on the edge of the village. U.S. Air Force fighter jets and bombers, such as F-16, A-10, and OV-10, not only from the U.S. Air Force based in Korea, but also in Okinawa, Thailand, Guam, and the Philippines swoop on Maehyang-ri to drop their bombs and spray their bullets on the targets in the range in bombing practice and gunnery drills. The bombing and firing take place throughout the daylight hours and even until late at night for 250 days a year, stopping only for weekends and holidays.[65]
Though persistent struggle against the firing range finally resulted in its 2005 closure, the U.S. Air Force made no known effort to clean up the bombs left over from practice drills, leaving used shells to disintegrate and bleed chemicals into the ground and water. Fishermen from the village have trouble selling their products as some buyers are concerned over the contamination. Meanwhile, residents who were not killed by errant bombs from the range live with physical and psychological damages and the remaining pollution of their village.[18]
Soseong-ri anti-THAAD struggle[edit | edit source]
Since the US's introduction of the Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD) system, residents of the village of Soseong-ri have conducted ongoing protests against it, regularly holding rallies on the road leading to the THAAD site and coming into conflict with the police who were tasked with clearing the protestors to make way for US military supply trucks.[66]
Hawaiʻi[edit | edit source]
The occupied nation of Hawaiʻi, whose sovereign government was overthrown by the US Navy in an 1893 coup d'etat, is the current location of the headquarters of the US military presence in the Indo-Pacific.[47][48] The percentage of military-controlled land in Hawaiʻi is higher than in any other US "state". On the island of O‘ahu, the US military controls about 25 per cent of the land.[67] There are at least 11 recognized military bases in Hawaiʻi.[67][68]
Kahoʻolawe struggle[edit | edit source]
The island of Kahoʻolawe was taken under U.S. military control during the Second World War, first by a 1941 sublease from Kahoʻolawe Ranch Company, where the U.S. Army acquired bombing rights for $1 per year. It was then sequestrated by the Army for use as a live ordinance training area and its southern and eastern cliffs used for torpedo bomb testing and its western beaches as rehearsal landing areas. Following the war, the island was placed under the jurisdiction of the secretary of the U.S. Navy and continued to be used as a bombing target.[69] During the Korean War, a mock airfield and vehicle convoys were set up on the island for practice bombing and strafing. During the Vietnam War, replicas of Vietnamese surface-to-air missile sites and radar stations were set up and bombed. In 1965, the Navy exploded 500 tons of TNT to simulate an atomic blast and observe its effects on target ships moored nearby. This left a massive crater on the island as well as cracked the island's freshwater aquifer, destroying the island's ability to hold freshwater.[70]
Though efforts to return the island to the people of Hawaiʻi had begun since 1941,[71] it was in the 1970s that a series of protest occupations of the island escalated and brought increased attention to the movement. Members of Aboriginal Lands of Hawaiian Ancestry, or ALOHA, had been seeking recognition for Native Hawaiian rights and reparations, "inspired by recognition given to Native Americans at Wounded Knee, and to Native Alaskans," as one activist later described.[72] However, as legal methods stalled, they wanted to call attention to the condition of Native Hawaiians by occupying federal land, and organizing began to occupy Kahoʻolawe.[72]
The first successful landing on the island occurred on January 4, 1976 when nine individuals in one boat managed to get past the Coast Guard which was blocking most of the other people who came to join the occupation. Two of the nine individuals managed to remain on the island for two days, surveying the land. Witnessing the devastation of the bombings and acting out of Aloha ʻAina, love of the land, a movement to stop the bombing also formed, notably coalescing into the organization Protect Kahoʻolawe ʻOhana (PKO).[72]
Bombing on Kahoʻolawe was finally halted in 1990. The Navy finally transferred Kahoʻolawe to the state of Hawaiʻi in 2003, halting its clean up efforts, including the clean up of unexploded ordinance, in 2004, with approximately 25% of the island remaining uncleared.[72][69] As noted on PKO's website, "Selected areas were cleared for specific uses including revegetation with native species, trails and roads, cultural sites, camping areas, and educational facilities. However, the island and its surrounding waters remain dangerous. Therefore, access continues to be restricted."[71]
Regarding the significance of Kahoʻolawe and the struggle for its return and rehabilitation, PKO's website says "In working for the return of Kaho‘olawe, many of the current generation rediscovered what it means to be Hawaiian. Restoring the island will provide a place and a purpose for a new generation of Hawaiians to be trained in the rights and responsibilities of 'kahu o ka ‘āina,' or stewards of the land."[71] One member of PKO was quoted in a 2011 Honolulu Civil Beat article as saying, "Coming out of a very conservative Cold War era to challenge the military industrial complex was to set yourself outside of the dominant norm. It wasn’t easy."[73] The struggle for Kahoʻolawe has also been described as a significant landmark in the Hawaiian Renaissance of the 1970s.[73][74]
Pōhakuloa Training Area[edit | edit source]

Mākua Valley struggle[edit | edit source]
Parts of Mākua valley have been used for live-fire training since the 1920s. After the attack on Pearl Harbor during the Second World War, martial law was imposed in Hawaii and the US military took control of Mākua and Kahoʻolawe. Local families who were displaced by this land seizure were told at the time that it was temporary and that most would be able to return after the war. However, in 1945 the War Department sought the transfer of 6,608 acres at Mākua for training, and in 1964, the Army paid $1 for a 65-year lease to continue training on Mākua and other areas.[75] The current lease on Mākua expires in 2029.[76]
Mālama Mākua is an organization formed in 1996 which strives for the return of Mākua Valley from US military occupation and states its solidarity with "other Indigenous Peoples throughout the world whose lands are threatened by all manner of settler-colonialism, whether it be through militarism or settler-colonial land grabs."[77] They state on their homepage that "Sacred Mākua is a place where Papa (Earth mother) and Wākea (sky father) created human life, a place of healing and refuge, not a place for bombs and bullets or military training by the US military."[76]
Shut Down Red Hill[edit | edit source]

A fuel storage facility built during the Second World War and located on Kapūkaki, also known as Red Hill, has been leaking since 1943, releasing a conservative estimate of 200,000 gallons of fuel into the surrounding environment. It is located just 100 feet (30.48 meters) above Oʻahu’s primary drinking water supply. A 2021 fuel leak from the facility poisoned the water system for nearly 100,000 residents, sending thousands of people into acute reactions due to petroleum exposure.[78] Following the incident, more than 70 organizations joined in the cause for closing Red Hill, including organizations such as Oʻahu Water Protectors and the Sierra Club. The military initially denied the problems, but finally suspended operation of the facility, though still fought against citizens' demands to close the facility completely. In the face of continued pressure, the Department of Defense eventually agreed to shut down the facility.[9]
Though the DoD agreed to shut down the facility, the medical repercussions for citizens harmed by the past leaks are ongoing, and residual fuel remains in the facility and the soil which poses a danger of contaminating Oʻahu's sole source aquifer. Speaking on the state of affairs in a 2024 interview with The Red Nation, activist Mikey Inouye commented "At this point, we are going to have to organize around Red Hill for, probably, the rest of our lives."[79] Inouye observed that the facility was not "defueled" so much as it was "dispersed [...] into our drinking water, into our sole source aquifer that provides water to nearly half a million people on the this island, it was dispersed into our bloodstreams, into the blood of children, including civilian children, including Kānaka Maoli children--Native Hawaiians, into our ecosystem, into our other-than-human relatives, and until that is removed from Hawaiʻi, Red Hill, to me, has not been shut down yet. And so, it's going to be the work of, possibly, generations."[79]
Guam[edit | edit source]

Guåhan, also called Guam, is a heavily militarized US colony with 27% of its land occupied by the US military. Guam is sometimes referred to as the "tip of the spear" of US military presence in the Pacific.[80]
Prutehi Guåhan, formerly Prutehi Litekyan: Save Ritidian, is a direct action group which promotes the protection of natural and cultural resources in all sites identified for DoD live-fire training on Guam and opposes the establishment of any firing range.[81] Additionally, the organization "promotes the continued pursuit for return of ancestral lands."[81] The organization's previous name refers to Litekyan, or Ritidian, an area on the northern part of Guam which was taken over by the DoD in 1963, then transferred to the US Fish and Wildlife Service.[82] It is the location of a number of archeologically and ecologically significant sites.[83] The nearby Anderson Air Force Base and Marine Corps Camp Blaz pose threats to the natural environment and to peoples' health and safety, on top of the ongoing dispossession of their land.[84] On their webpage, Prutehi Guåhan writes:
When the survival of our CHamoru culture is continually threatened by outside forces, we must take action. Without our free, prior and informed consent, our cultural sites are being cleared for U.S. Military buildup construction. Many sites have already been cleared for the new Marine base, Camp Blaz. Our indigenous rights are being violated every single day the buildup construction continues. This must stop.[85]
Prutehi Guåhan also called for the cancellation of the "Resolute Force Pacific" (REFORPAC) 2025 military exercise and for the US to get out of the Mariånas, in a joint social media post with Resist US-Led War. The statement also denounced "all training with lethal weapons in these lands and waters used to slaughter Palestinians and other civilians."[86]
The US Air Force in Guam has also applied for a permit to openly burn and openly detonate (OB/OD) 35,000 pounds of bombs and other munitions on Tarague Beach in Litekyan. Some CHamoru community members have entered into a lawsuit against the US Air Force, citing that the Air Force failed to conduct a proper analysis of the environmental impacts of OB/OD, which poses a threat to numerous sensitive animal habitats, to traditional medicinal plants, and to the water of Guam's aquifer which supplies 80% of Guam's drinking water to residents.[84]
Philippines[edit | edit source]
Subic Bay[edit | edit source]
Clark Air Base[edit | edit source]
Diego Garcia[edit | edit source]
Diego Garcia is part of the Chagos Islands in the Indian Ocean, where a U.S. base is sustained on a British land lease. Over a ten year period beginning in 1965, a joint US-UK effort expelled the population in order to build a US military base.[50][51] John Pilger, writing in Al Jazeera, explained: "People were herded into the hold of a rusting ship, the women and children forced to sleep on a cargo of bird fertiliser. They were dumped in the Seychelles, where they were held in prison cells, and then shipped onto Mauritius, where they were taken to a derelict housing estate with no water or electricity. Twenty-six families died there in brutal poverty, nine individuals committed suicide, and girls were forced into prostitution to survive."[52]
The strategically significant location of Diego Garcia enables the U.S. military to reach numerous locations, for example helping to launch the U.S. bombings of Iraq and Afghanistan.[52][53]
Though not strictly an anti-base movement, there is a movement for the survivors of the forced expulsion to be able to return to their home. However, this has been blocked by various political maneuvers by the West, including by the establishment of a marine nature reserve in the area, which would prevent them from engaging in necessary subsistence fishing if they were able to return.[52][51]
North America[edit | edit source]
United States of America[edit | edit source]

School of the Americas[edit | edit source]
The Western Hemisphere Institute for Security Cooperation, often (and formerly) called the School of the Americas, is infamous for its training of officers in tactics used for violent suppression, torture, and massacres throughout Latin America. It was originally founded in 1948 in Panama, but was expelled in 1984 and relocated to the US, and is currently located in Fort Moore (formerly Fort Benning), Georgia, USA.[87]
Fort Lawton occupation[edit | edit source]
Fort Lawton was a 1,100-acre Army post in Seattle, Washington, USA. It was located on land from which the local indigenous peoples had been forcibly removed in the wake of the 1855 Treaty of Point Elliot. By the 1960s, the U.S. government began a process of declaring the fort as surplus,[88] and amid various proposals for the land's future use, an organization called the United Indians People's Council (later, United Indians of All Tribes)[89] made a claim on Fort Lawton, citing rights under 1865 US-Indian treaties which had promised "the reversion of surplus military land to their original landowners."[88]
In 1970, when the base was in the process of being decommissioned, Native leaders met with Senator Henry M. Jackson and presented him with a detailed plan for turning the base into a center for indigenous arts, culture, and social services, intending to create a facility that could help Native people who had been displaced into the city by federal relocation policies. However, the senator was not receptive, and as Sid Mills, who participated in the events recounted, "After that, we realized if we were going to get any land back, we were going to have to take it."[90]
A week later,[90] on March 8, 1970, a protest occupation by over 100 Native Americans and supporters occurred at the fort, which had been "virtually empty and dormant for months" and used only intermittently.[88] The occupation began first with a breach of the base's perimeter, after which "about 30 Native American men, women, and children were setting up camp and had managed to erect a teepee when they were discovered by a patrol."[89] Military police attacked the occupiers with nightsticks and chased them with Jeeps and arrested them,[90] though some people managed to escape and roam the base for some time.[89] Two more takeover attempts occurred over the next three weeks. Meanwhile, outside the front gate, a 24-hour occupation camp was maintained. After a third takeover attempt on April 2, negotiations began with city, state, and federal officials to get at least some of the land back, eventually resulting in a 99-year agreement in which the city would receive the land, but would lease 17 acres to the United Indians of All Tribes Foundation. The Daybreak Star Indian Cultural Center was built on the land and opened in 1977 while other parts of the area were turned into a park.[90]
Vieques, Puerto Rico[edit | edit source]

The U.S. military used the island of Vieques as a bombing range and as a location for training exercises from 1941 until 2003. Over the course of its activity there, the U.S. military forcibly displaced people from their homes; seized 77% of the island;[91] caused injury, illness and deaths[92][19] among the local population and committed acts of sexual violence and harassment; polluted the land and water with lead, depleted uranium, napalm, and other toxic substances; and left behind unexploded ordinance.[93]
Vieques has been reported to have higher cancer rates than any other municipality of Puerto Rico, with one study showing a 27% higher cancer rate than the rest of Puerto Rico.[94] As a result of the extreme health and environmental damages caused in Vieques, it was declared a Superfund cleanup site, meaning it requires a special protocol for decontamination due to its toxicity. The military and its contractors cleanup methods have included open-air bombing of found munitions and open-air burning of vegetation, both of which have been criticized as exacerbating the health and environmental damage.[95]

The U.S. began forced removals of the population and land theft of the island of Vieques in 1941, with people being removed from their homes with as little as 24-hour notice, losing access to their subsistence farm plots and their homes getting bulldozed. Another wave of forced removals began in 1947, with the U.S. Department of Defense seizing 17,500 acres of agricultural land; by 1948, the U.S. Navy had forcibly taken 77% of the island of Vieques away from the local population, with the displaced people either having to leave entirely or be crowded into the remaining 23% of the island.[91]
Among the protests of the people against the Navy's activity in Vieques were the actions in the wake of the death of Davis Sanes in 1999, a local who was killed when the Navy misidentified a target and dropped a bomb on the security guard post where he worked, as well as wounding others. Activists engaged in acts of civil disobedience as well as instances of breaking into the base[93] and occupying the base, with their activities preventing naval exercises for a year until the military forcibly cleared their encampments in 2000.[96] Also in 2000, a march was conducted in San Juan with approximately 150,000 marchers to protest the Navy's presence in Puerto Rico.[97]
[edit | edit source]
South America[edit | edit source]
See also[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
- USA’s Military Empire: A Visual Database by World Beyond War. A database of the USA's network of military bases around the world, with an interactive map.
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 David Vine (2019). No Bases? Assessing the Impact of Social Movements Challenging US Foreign Military Bases, vol. Volume 60, Number S19. [PDF] Current Anthropology.
- ↑ Yeo, Andrew. "Not in Anyone's Backyard: The Emergence and Identity of a Transnational Anti-Base Network." International Studies Quarterly, Vol. 53, No. 3 (Sep., 2009), pp. 571-594. Oxford University Press.
- ↑ David Vine, Patterson Deppen and Leah Bolger. "Drawdown: Improving U.S. and Global Security Through Military Base Closures Abroad." Quincy Institute for Responsible Statecraft, September 20, 2021. Archived 2024-03-12.
- ↑ Jawad, Ashar. "5 Countries With the Most Overseas Military Bases." Insider Monkey, December 15, 2023.
- ↑ "Why 90% Of Foreign Military Bases Are American." AJ+ on YouTube, Jan 13, 2022.
- ↑ “The Feminist Response to RIMPAC and the US War against China.” Friends of Socialist China, July 27, 2022. Archived 2023-09-22.
- ↑ Mohammed Hussein and Mohammed Haddad. "Infographic: US military presence around the world." Al Jazeera, 10 September 2021. Archived 2024-03-28.
- ↑ Chris Gelardi and Sophia Perez. “‘Biba Guåhan!’: How Guam’s Indigenous Activists Are Confronting Military Colonialism.” The Nation, October 21, 2019.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Jedra, Christina. “How Hawaii Activists Helped Force the Military’s Hand on Red Hill.” Honolulu Civil Beat, March 14, 2022. Archived 2022-02-22.
- ↑ “Hyper-Imperialism: A Dangerous Decadent New Stage.” Tricontinental: Institute for Social Research, January 23, 2024. Archived 2024-05-21.
- ↑ David Vine (2012-07-16). "The Military’s New Lily-Pad Strategy" The Nation. Archived from the original on 2025-04-23.
- ↑ “American Nuclear Submarine Enters Jeju Naval Base.” Hankyoreh, 2017. Archived 2023-03-25.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Prashad, Vijay. “Why Does the United States Have a Military Base in Ghana?” Peoples Dispatch, June 15, 2022. Archived 2024-03-18.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 “Defending Our Sovereignty: US Military Bases in Africa and the Future of African Unity.” Tricontinental: Institute for Social Research, July 5, 2021. Archived 2023-03-04.
- ↑ Stewart, Richard W. "American Military History." Chapter: "Winning the West: The Army in the Indian Wars, 1865-1890." Volume 1: The United States Army and the Forging of a Nation, 1775-1917. Second Edition. Center of Military History, United States Army. Washington, D.C., 2009. Archived 2024-04-22.
- ↑ David Vine. The United States of War, University of California Press, 2020.
- ↑ Mitchell, Jon. “NCIS Case Files Reveal Undisclosed U.S. Military Sex Crimes in Okinawa.” The Intercept. October 3, 2021. Archived 2022-08-06.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 "Bombing ends, but village still not free from past." Yonhap News Agency. September 12, 2012. Archived 2022-09-27.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 “On April 19,1999, two F-18 jets mistook the navy's red-and-white checked observation post on the island of Vieques, Puerto Rico for a target, and dropped 500 pound bombs on it. Vieques resident David Sanes was working at the observation post as a security guard for the navy. He was killed almost instantly. Three other men from Vieques were seriously injured.”
Linda Backiel (2003). The People of Vieques, Puerto Rico vs. the United States Navy, vol. Vol. 54, No. 9 February 2003. Monthly Review. doi: 10.14452/MR-054-09-2003-02_1 [HUB] - ↑ Shorrock, Tim. “Welcome to the Monkey House.” The New Republic. December 2, 2019. Archived 2022-09-26.
- ↑ "For People, Land, Air and Sea: Stop RIMPAC Military Exercises." Petition to Governor of Hawaii David Ige, started by World Can't Wait-Hawai`i. Change.org, May 17, 2018. Archived 2024-04-03.
- ↑ Yeo, Andrew. "Security, Sovereignty, and Justice in U.S. Overseas Military Presence." International Journal of Peace Studies, Volume 19, Number 2, Winter 2014. Archived 2023-04-13.
- ↑ "Status of Forces Agreement (SOFA): What Is It, and How Has It Been Utilized?" Congressional Research Service, March 15, 2012. (PDF). Archived 2024-04-15.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 "Agreement Between the UNITED STATES OF AMERICA and GHANA." May 9, 2018. United States Department of State.
- ↑ Maxwell Boamah Amofa. “The Sandhurst Colonial Mentality and the Rule of Law.” Modern Ghana. March 13, 2023. Archived 2023-02-14.
- ↑ Katie Bo Williams. “AFRICOM Adds Logistics Hub in West Africa, Hinting at an Enduring US Presence.” Defense One, February 20, 2019. Archived 2024-04-02.
- ↑ Joseph Gerson and Michael Klare. "Statement on Averting a New Cold War Between the United States and China." Committee for a SANE U.S.-China Policy, October 2020. Archived 2022-01-19.
- ↑ Michael Lujan Bevacqua. “In Wake of Trump’s Win, Let’s Consider Independence for Guåhan.” The Guam Daily Post, November 19, 2016.
- ↑ Kenneth Gofigan Kuper. "Living at the tip of the spear: Guam and restraint." Responsible Statecraft, July 21, 2020. Archived 2023-09-27.
- ↑ "Militarization and Resistance in the Pacific, In the Age of Trump." University of Hawai'i at Manoa, March 13, 2017. APECEpic on YouTube, Apr 1, 2017. Archived 2024-04-18.
- ↑ “USAFA Library Guides: Combatant Commands: Combatant Command Overview.” U.S. Air Force Academy.
- ↑ "Combatant Commands." U.S. Department of Defense. Archived 2023-04-15.
- ↑ 33.0 33.1 "About the Command." Africom.mil. Archived 2024-05-16.
- ↑ "China and Sub-Saharan Africa." Congressional Research Service, January 8, 2024.
- ↑ Mohammed Abunahel (2024-03-22). "The United States Has Built a Network of Drone Bases Across Africa" World BEYOND War. Archived from the original on 2025-01-04.
- ↑ Turse, Nick. “Violence Has Spiked in Africa since the Military Founded AFRICOM, Pentagon Study Finds.” The Intercept, July 29, 2019. Archived 2024-04-09.
- ↑ Dan Glazebrook. “Recolonisation of Africa by Endless War.” The Herald, November 7, 2017. Archived 2022-07-05.
- ↑ Kulkarni, Pavan. “AFRICOM Military’s Exercise: The Art of Creating New Pretexts for Propagating US Interests.” Peoples Dispatch, June 2021. Archived 2023-12-02.
- ↑ Tunde Osazua. “AFRICOM and the Guise of Terrorism.” Black Agenda Report, July 15, 2020. Archived 2023-04-02.
- ↑ “U.S. Out of Africa! Shut Down AFRICOM.” The Black Alliance for Peace. Archived 2024-05-19.
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 “Niger Suspends Military Cooperation with US: Spokesman.” Al Jazeera, March 17, 2024. Archived 2024-05-21.
- ↑ Banks, Chris. “Niger Declares American Military Presence ‘Illegal,’ Kicks out U.S. Troops.” Liberation News, March 28, 2024. Archived 2024-05-15.
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 Kulkarni, Pavan. “Why Has Niger Declared US Military Presence in Its Territory Illegal?” Peoples Dispatch, March 19, 2024. Archived 2024-04-14.
- ↑ Marie, Kayla. “Niger’s New Government Defies Imperialist-Backed ECOWAS War Threats.” Liberation News, August 11, 2023. Archived 2024-05-23.
- ↑ 45.0 45.1 45.2 "U.S. Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM)." Congressional Research Service, March 5, 2024.
- ↑ "USPACOM Area of Responsibility." U.S. Indo-Pacific Command.
- ↑ 47.0 47.1 47.2 "The Pacific Islands." Congressional Research Service, January 25, 2024. Archived 2024-02-11.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 Jon Olsen (2022-11-15). "Hawai’i—The Very First U.S. Regime Change." CovertAction Magazine. Archived from the original on 2022-11-16.
- ↑ Takahashi Kosuke. “US-Led RIMPAC, World’s Largest Maritime Exercise, Starts without China or Taiwan.” The Diplomat, July 01 2022. Archived 2024-02-26.
- ↑ 50.0 50.1 Asoka Bandarage. “U.S. Military Presence and Popular Resistance in Sri Lanka.” CovertAction Magazine, August 12, 2019. Archived 2023-10-03.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 David Vine. “The Truth about the U.S. Military Base at Diego Garcia.” Truthdig, June 15, 2015. Archived 2023-01-29.
- ↑ 52.0 52.1 52.2 52.3 Pilger, John. “How Britain Forcefully Depopulated a Whole Archipelago.” Al Jazeera, February 25, 2019. Archived 2023-03-31.
- ↑ 53.0 53.1 Marsh, Jenni. “Is the United States about to Lose Control of Its Secretive Diego Garcia Military Base?” CNN, March 9, 2019.
- ↑ Sayo Saruta. “Okinawa’s Peace Movement Carves Its Own Path.” The Japan Times, March 4, 2024. Archived 2024-04-06.
- ↑ Moé Yonamine. “Fighting for Okinawa.” MR Online, July 28, 2017. Archived 2023-09-28.
- ↑ 56.0 56.1 56.2 Dustin Wright. "‘Sunagawa Struggle’ ignited anti-U.S. base resistance across Japan." The Japan Times, May 3, 2015. Archived 2015-05-05.
- ↑ Dennis Banks, Richard Erdoes. "Ojibwa Warrior: Dennis Banks and the Rise of the American Indian Movement." University of Oklahoma Press, 2004.
- ↑ 김준. (Kim Jun). "쌍용훈련 재개 예고에 23기 중앙통선대, 포항 한미연합상륙훈련장 지휘소 기습점거투쟁" ("23rd Central Telecommunication Battalion, Pohang ROK-U.S. Combined Amphibious Training Center Command Post, Surprise Occupation Struggle to Announce Resumption of Ssangyong Training"). 노동과세계. 2022.08.12. Archived 2022-08-28.
- ↑ "23기 민주노총 중앙통일선봉대 활동영상" ("23rd KCTU Central Unification Vanguard Activity Video"). 민주노총 (Confederation of Trade Unions). Aug 14, 2022. YouTube.
- ↑ People's Democracy Party and Liberation School. “70 Years Too Long: The Struggle to End the Korean War.” 25 June 2020. Archived 2023-09-26.
- ↑ “THAAD Missile System Agitates South Korea-China Ties.” Nikkei Asia, June 22, 2023.
- ↑ “Voices from Iraq: Why Is South Korea There?” Hankyoreh, 2006-09-09. Archived 2024-05-22.
- ↑ “With RIMPAC, South Korea Expands Its Military Footprint.” Friends of Socialist China, August 2022. Archived 2023-09-27.
- ↑ Benjamin, Medea. “Korea’s Jeju Island: A Model for Opposing Militarism.” Telesurenglish.net. teleSUR. 2015. Archived 2020-01-19.
- ↑ "Maehyang-ri: From a Firing Range to a Test Ground for Human Rights and International Justice." National Action Committee for the Closure of the Maehyang-ri U.S. Armed Forces International Bombing Range (August 15, 2000).
- ↑ Elich, Gregory. "The Fight Over THAAD in Korea." Counter Punch, May 1, 2024. Archived 2024-05-03.
- ↑ 67.0 67.1 Teuila Fuatai (2025-03-26). "From Hawai’i: To the U.S., we’re a giant military station" MR Online. Archived from the original on 2025-04-01.
- ↑ Buddy Blouin. "What are the military bases in Hawaii?" MyBaseGuide.
- ↑ 69.0 69.1 "History." Protect Kaho'olawe 'Ohana.
- ↑ Graff, Cory. "Kaho’olawe: The Pacific’s Battered Bullseye." The National WWII Museum, New Orleans, November 20, 2021. Archived 2024-04-15.
- ↑ 71.0 71.1 71.2 "moʻolelo ʻāina." Protect Kaho'olawe 'Ohana.
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 72.3 Noe Tanigawa. "Navy bombs and the rescue of Kahoʻolawe in the 1970s." Hawaiʻi Public Radio, February 18, 2022. Archived 2024-05-02.
- ↑ 73.0 73.1 LaFrance, Adrienne. “Who Remembers the Hawaiian Renaissance?” Honolulu Civil Beat, October 7, 2011. Archived 2023-12-02.
- ↑ “5 Major Events of the 1970s Hawaiian Renaissance Movement.” ʻĀina Momona, September 27, 2021. Archived 2024-05-05.
- ↑ Kevin Knodell (2021-08-15). "A Shaky Truce: The Army And Native Hawaiians Both Want Oahu’s Makua Valley" Honolulu Civil Beat. Archived from the original on 2025-04-01.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 "Homepage". Mālama Mākua. Archived from the original on 2025-04-01.
- ↑ Mālama Mākua. "About Us" Mālama Mākua.
- ↑ "Shut Down Red Hill." Sierra Club of Hawaiʻi.
- ↑ 79.0 79.1 Mikey Inouye, Jen Marley. "From Hawai’i to Palestine, occupation is a crime w/ Mikey." Episode 348, The Red Nation Podcast, March 5, 2024. Archived 2024-05-03. (YouTube version).
- ↑ Kenneth Gofigan Kuper. “Guam: The Sharpening of the Spear’s Tip.” Foreign Policy In Focus, July 20, 2022. Archived 2024-01-28.
- ↑ 81.0 81.1 “Prutehi Guåhan is a direct action group dedicated to the protection of natural and cultural resources in all sites identified for DOD live-fire firing training on Guam. We oppose the establishment of any military firing range and align our efforts with other regional movements working to prevent environmental degradation and destruction on sacred and native lands. Our work promotes the continued pursuit for return of ancestral lands.”
"About". Retrieved 2025-08-19. - ↑ Sara Mar (2022-08-18). "Guam: Love and Loss at Litekyan" Pulitzer Center.
- ↑ Mike Carson. "Ritidian (Litekyan)" Guampedia.
- ↑ 84.0 84.1 Sara Mar (2024-05-31). "Indigenous People of Guam Are Fighting US Militarism and Environmental Ruin" TruthOut. Archived from the original on 2025-07-17.
- ↑ "Prutehi Guåhan". Prutehi Guåhan. Archived from the original on 2025-06-12. Retrieved 2025-08-19.
- ↑ @resistusledwar and @prutehi_gu (2025-06-22). "Cancel REFORPAC! No consent for war games in the Mariånas, Asia and the Pacific!" Instagram.
- ↑ 87.0 87.1 MacLeod, Alan. “How a Notorious Georgia Army School Became America’s Training Ground for Global Torture.” MintPress News, July 5, 2023. Archived 2024-04-18.
- ↑ 88.0 88.1 88.2 "Discovery Park History." Seattle.gov. Archived 2024-05-09.
- ↑ 89.0 89.1 89.2 Patrick McRoberts and Kit Oldham. “Fort Lawton military police clash with Native American and other protesters in the future Discovery Park on March 8, 1970.” Essay 5513, HistoryLink.org, 2003-08-15. Archived 2023-04-06.
- ↑ 90.0 90.1 90.2 90.3 Hopper, Frank. “The Day the Indians Took over Seattle’s Fort Lawton—and Won Land Back.” YES! Magazine, August 31, 2023. Archived 2024-05-09.
- ↑ 91.0 91.1 Monisha Rios (2023-04-23). "The Toxic Legacy of U.S. Foreign Policy in Vieques, Puerto Rico" Foreign Policy in Focus. Archived from the original on 2023-09-26.
- ↑ “With as little as a 24-hour notice, their belongings were tossed into uncleared resettlement plots that “lacked any previous conditioning, water, or basic sanitary provisions,” and their family homes were bulldozed. Some, including pregnant women and children, were given only tarps to live under for three months until the Navy brought materials for them to build a new home. Under these conditions, several people became severely ill, and a pregnant woman died.”
Monisha Rios (2023-04-23). "The Toxic Legacy of U.S. Foreign Policy in Vieques, Puerto Rico" Foreign Policy in Focus. Archived from the original on 2023-09-26. - ↑ 93.0 93.1 Wilfred Chan (2023-05-01). "‘I thought they’d kill us’: how the US navy devastated a tiny Puerto Rican island" The Guardian. Archived from the original on 2024-09-02.
- ↑ Valeria Pelet (2016-09-03). "Puerto Rico’s Invisible Health Crisis" The Atlantic. Archived from the original on 2024-10-11.
- ↑ Denise Oliver Velez (2018-03-11). "Women in Vieques, Puerto Rico, lead the fight against U.S. Navy contamination of their island" Daily Kos. Archived from the original on 2023-01-27.
- ↑ AJ+ (2019-06-12). "The US Navy's Toxic Playground: Vieques, Puerto Rico | AJ+". YouTube.
- ↑ Ronald Ávila-Claudio. "Vieques: el oscuro episodio de los bombardeos sobre Puerto Rico que el ejército de EE.UU. realizó durante décadas." BBC News Mundo. Archived 2024-11-23.
