North Atlantic Treaty Organization: Difference between revisions
Jucheguevara (talk | contribs) (added new information) Tag: Visual edit |
(Infobox) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Infobox settlement|image_map=Member states of NATO.png|conventional_long_name=North Atlantic Treaty Organization|official_languages=English<br>French|native_name=Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord|capital_type=Headquarters|capital=Brussels, [[Belgium]]|established_event1=Formation|established_date1=4 April 1949}} | |||
The '''North Atlantic Treaty Organisation''', more often called '''NATO''', is an anticommunist international military treaty created in the [[imperial core]] following [[World War II]].<ref>{{News citation|author=[[Ben Norton]]|newspaper=[[Multipolarista]]|title=NATO is a tool of US imperialism that has backed Nazis for decades|date=2022-06-14|url=https://youtu.be/Maqkl4fEQfs}}</ref> | The '''North Atlantic Treaty Organisation''', more often called '''NATO''', is an anticommunist international military treaty created in the [[imperial core]] following [[World War II]].<ref>{{News citation|author=[[Ben Norton]]|newspaper=[[Multipolarista]]|title=NATO is a tool of US imperialism that has backed Nazis for decades|date=2022-06-14|url=https://youtu.be/Maqkl4fEQfs}}</ref> | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
== Members == | == Members == | ||
The 12 founding members of NATO were [[Belgium]], [[Canada]], [[Denmark]], [[France]], [[Iceland]], [[Italy]], [[Luxembourg]], the [[Netherlands]], Norway, [[Portugal]], the [[United Kingdom]] and the [[United States]].<ref name=":0">https://archive.vn/wip/ogQgV</ref> | The 12 founding members of NATO were [[Belgium]], [[Canada]], [[Denmark]], [[France]], [[Iceland]], [[Italy]], [[Luxembourg]], the [[Netherlands]], Norway, [[Portugal]], the [[United Kingdom]] and the [[United States]].<ref name=":0">https://archive.vn/wip/ogQgV</ref> Since that time, other countries have joined the alliance: [[Greece]] and [[Turkey]] (1952), [[Germany]] (1955), [[Spain]] (1982), [[Czech Republic|the Czech Republic]], [[Hungary]] and [[Poland]] (1999), [[Bulgaria]], [[Estonia]], [[Latvia]], [[Lithuania]], [[Romania]], [[Slovakia]] and [[Slovenia]] (2004), [[Albania]] and [[Croatia]] (2009), [[Montenegro]] (2017) and [[North Macedonia]] (2020).<ref name=":0" /> | ||
In 1990, U.S. Secretary of State [[James Baker]] claimed NATO would not expand into [[Eastern Europe]], although this proved to be a lie,<ref>{{News citation|newspaper=National Security Archive|title=NATO Expansion: What Gorbachev Heard|url=https://nsarchive.gwu.edu/briefing-book/russia-programs/2017-12-12/nato-expansion-what-gorbachev-heard-western-leaders-early}}</ref> and 14 countries in Central and Eastern Europe joined NATO after the [[overthrow of the Soviet Union]].<ref name=":1">{{News citation|author=[[Chris Hedges]]|newspaper=[[MintPress News]]|title=Chris Hedges: NATO—The Most Dangerous Military Alliance on the Planet|date=2022-07-12|url=https://www.mintpressnews.com/chris-hedges-nato-most-dangerous-military-alliance/281304/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220721133324/https://www.mintpressnews.com/chris-hedges-nato-most-dangerous-military-alliance/281304/|archive-date=2022-07-21|retrieved=2022-07-26}}</ref> | |||
[[Republic of Finland|Finland]] and [[Kingdom of Sweden|Sweden]] will likely join NATO soon. Turkish president [[Recep Tayyip Erdoğan]] gave permission for them to join NATO after they expanded domestic terror laws and lifted restrictions on selling weapons to Turkey.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
== Anticommunist projects == | == Anticommunist projects == | ||
NATO took over anti-Soviet subversive activities from their predecessors when they started operating Nazi general Richard Gehlen's network of spies in the [[Union of Soviet Socialist Republics|Soviet Union]]. | NATO took over anti-Soviet subversive activities from their predecessors when they started operating Nazi general Richard Gehlen's network of spies in the [[Union of Soviet Socialist Republics|Soviet Union]]. | ||
NATO is perhaps best known among European communists for [[Operation Gladio]], which is a name given to a series of operations that consisted of funding fascist groups in Europe to assassinate and destabilize communists in the 20th century. | NATO is perhaps best known among European communists for [[Operation Gladio]], which is a name given to a series of operations that consisted of funding fascist groups in Europe to assassinate and destabilize communists in the 20th century. In 2022, a Spanish lawmaker [[Gerado Pisarello]] criticized NATO for promoting a [[New Cold War]] on [[People's Republic of China|China]].<ref>{{News citation|author=[[Ben Norton]]|newspaper=[[Multipolarista]]|title=Spanish lawmaker: NATO subordinates Europe to US, pushes war on China, enriches weapons companies|date=2022-07-05|url=https://youtu.be/F4C6MKbhuZQ}}</ref> | ||
== Imperialist acts == | == Imperialist acts == | ||
The Coalition fighting in [[Afghanistan]], in a [[Afghanistan War|conflict]] that started in 1979 when the Afghan government asked the USSR to help fight against the [[Mujahideen]], was sent on the request of NATO. | |||
When the USA was attacked on [[9/11|September 11, 2001]] and followed with a declaration of [[Iraq War|war against Iraq]] for imperialist interests, NATO -- by their own admission -- put their principle of collective defence to practice: if one member country is attacked, then all must join the war in defense. It is important to note that the government of [[Iraq]] never claimed responsibility or was ever tied to the terrorist attacks. Notably, president Bush admitted in 2006 that Saddam Hussein, president of Iraq in 2001, was not responsible for the attack<ref>https://www.theguardian.com/world/2006/sep/12/september11.usa2</ref>. | When the USA was attacked on [[9/11|September 11, 2001]] and followed with a declaration of [[Iraq War|war against Iraq]] for imperialist interests, NATO -- by their own admission -- put their principle of collective defence to practice: if one member country is attacked, then all must join the war in defense. It is important to note that the government of [[Iraq]] never claimed responsibility or was ever tied to the terrorist attacks. Notably, president Bush admitted in 2006 that Saddam Hussein, president of Iraq in 2001, was not responsible for the attack<ref>https://www.theguardian.com/world/2006/sep/12/september11.usa2</ref>. | ||
NATO backed Turkey's occupation of parts of [[Syrian Arab Republic|Syria]] and Iraq. Turkey has the second largest military of any NATO member.<ref name=":1" /> | |||
In June 2022, NATO announced it would increase its standing army in Europe from 40,000 to 300,000 troops, including over 3,000 troops in the [[Baltics|Baltic]] states on the border with [[Russian Federation|Russia]].<ref>{{News citation|author=Andre Damon|newspaper=[[World Socialist Web Site]]|title=NATO announces plan for massive European land army|date=2022-06-27|url=https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2022/06/28/sosw-j28.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220630011006/https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2022/06/28/sosw-j28.html|archive-date=2022-06-30|retrieved=2022-06-30}}</ref> NATO also added [[People's Republic of China|China]] to its list of enemies and labeled it a "systemic challenge."<ref>{{News citation|author=Sameena Rahman|newspaper=[[Liberation News]]|title=NATO officially adds China to its list of enemies|date=2022-06-30|url=https://www.liberationnews.org/nato-officially-adds-china-to-its-list-of-enemies/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220630223716/https://www.liberationnews.org/nato-officially-adds-china-to-its-list-of-enemies/|archive-date=2022-06-30|retrieved=2022-07-02}}</ref> | In June 2022, NATO announced it would increase its standing army in Europe from 40,000 to 300,000 troops, including over 3,000 troops in the [[Baltics|Baltic]] states on the border with [[Russian Federation|Russia]].<ref>{{News citation|author=Andre Damon|newspaper=[[World Socialist Web Site]]|title=NATO announces plan for massive European land army|date=2022-06-27|url=https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2022/06/28/sosw-j28.html|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220630011006/https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/2022/06/28/sosw-j28.html|archive-date=2022-06-30|retrieved=2022-06-30}}</ref> NATO also added [[People's Republic of China|China]] to its list of enemies and labeled it a "systemic challenge."<ref>{{News citation|author=Sameena Rahman|newspaper=[[Liberation News]]|title=NATO officially adds China to its list of enemies|date=2022-06-30|url=https://www.liberationnews.org/nato-officially-adds-china-to-its-list-of-enemies/|archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220630223716/https://www.liberationnews.org/nato-officially-adds-china-to-its-list-of-enemies/|archive-date=2022-06-30|retrieved=2022-07-02}}</ref> | ||
Revision as of 16:46, 26 July 2022
North Atlantic Treaty Organization Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Headquarters | Brussels, Belgium |
| Official languages | English French |
| Establishment | |
• Formation | 4 April 1949 |
The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, more often called NATO, is an anticommunist international military treaty created in the imperial core following World War II.[1]
Its original aim was to defend bourgeois republics against a possible Soviet liberation of Europe. When this reality never materialized, NATO moved to funding anticommunist (more often fascist) acts in Europe and abroad.
Members
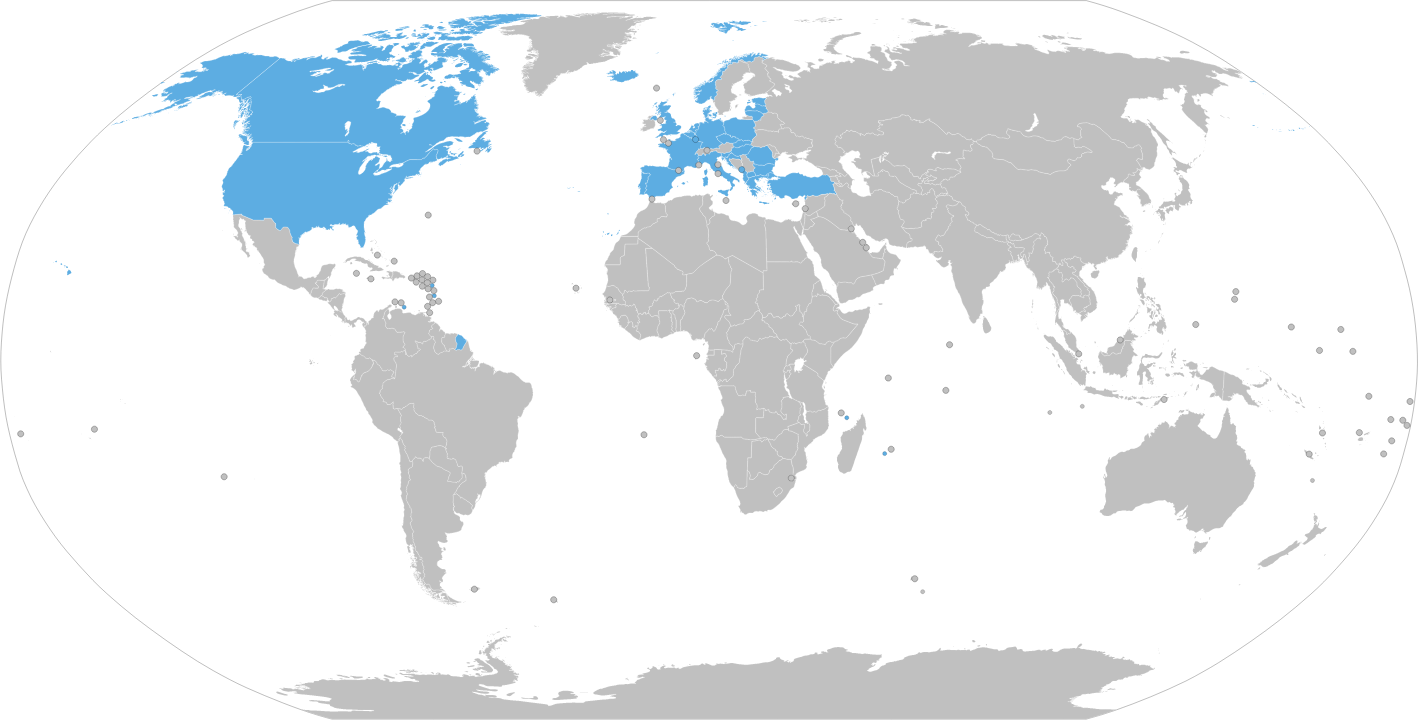
The 12 founding members of NATO were Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom and the United States.[2] Since that time, other countries have joined the alliance: Greece and Turkey (1952), Germany (1955), Spain (1982), the Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland (1999), Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia (2004), Albania and Croatia (2009), Montenegro (2017) and North Macedonia (2020).[2]
In 1990, U.S. Secretary of State James Baker claimed NATO would not expand into Eastern Europe, although this proved to be a lie,[3] and 14 countries in Central and Eastern Europe joined NATO after the overthrow of the Soviet Union.[4]
Finland and Sweden will likely join NATO soon. Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan gave permission for them to join NATO after they expanded domestic terror laws and lifted restrictions on selling weapons to Turkey.[4]
Anticommunist projects
NATO took over anti-Soviet subversive activities from their predecessors when they started operating Nazi general Richard Gehlen's network of spies in the Soviet Union.
NATO is perhaps best known among European communists for Operation Gladio, which is a name given to a series of operations that consisted of funding fascist groups in Europe to assassinate and destabilize communists in the 20th century. In 2022, a Spanish lawmaker Gerado Pisarello criticized NATO for promoting a New Cold War on China.[5]
Imperialist acts
The Coalition fighting in Afghanistan, in a conflict that started in 1979 when the Afghan government asked the USSR to help fight against the Mujahideen, was sent on the request of NATO.
When the USA was attacked on September 11, 2001 and followed with a declaration of war against Iraq for imperialist interests, NATO -- by their own admission -- put their principle of collective defence to practice: if one member country is attacked, then all must join the war in defense. It is important to note that the government of Iraq never claimed responsibility or was ever tied to the terrorist attacks. Notably, president Bush admitted in 2006 that Saddam Hussein, president of Iraq in 2001, was not responsible for the attack[6].
NATO backed Turkey's occupation of parts of Syria and Iraq. Turkey has the second largest military of any NATO member.[4]
In June 2022, NATO announced it would increase its standing army in Europe from 40,000 to 300,000 troops, including over 3,000 troops in the Baltic states on the border with Russia.[7] NATO also added China to its list of enemies and labeled it a "systemic challenge."[8]
References
- ↑ Ben Norton (2022-06-14). "NATO is a tool of US imperialism that has backed Nazis for decades" Multipolarista.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 https://archive.vn/wip/ogQgV
- ↑ "NATO Expansion: What Gorbachev Heard". National Security Archive.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Chris Hedges (2022-07-12). "Chris Hedges: NATO—The Most Dangerous Military Alliance on the Planet" MintPress News. Archived from the original on 2022-07-21. Retrieved 2022-07-26.
- ↑ Ben Norton (2022-07-05). "Spanish lawmaker: NATO subordinates Europe to US, pushes war on China, enriches weapons companies" Multipolarista.
- ↑ https://www.theguardian.com/world/2006/sep/12/september11.usa2
- ↑ Andre Damon (2022-06-27). "NATO announces plan for massive European land army" World Socialist Web Site. Archived from the original on 2022-06-30. Retrieved 2022-06-30.
- ↑ Sameena Rahman (2022-06-30). "NATO officially adds China to its list of enemies" Liberation News. Archived from the original on 2022-06-30. Retrieved 2022-07-02.