Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (1922–1991): Difference between revisions
More languages
More actions
No edit summary Tag: Visual edit |
m (Added link for constitution) Tag: Visual edit |
||
| Line 322: | Line 322: | ||
== Human rights == | == Human rights == | ||
Article 123 of the 1936 Soviet Constitution guaranteed national equality and banned [[racism]].<ref>{{Citation|author=[[Joseph Stalin]]|year=1936|title=Constitution of the Soviet Union (1936)|title-url=https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/Constitution_of_the_Soviet_Union_(1936)|chapter=Fundamental Rights and Duties of Citizens|section=Article 123|city=Moscow}}</ref> | Article 123 of the 1936 [[Constitution of the Soviet Union|Soviet Constitution]] guaranteed national equality and banned [[racism]].<ref>{{Citation|author=[[Joseph Stalin]]|year=1936|title=Constitution of the Soviet Union (1936)|title-url=https://en.wikisource.org/wiki/Constitution_of_the_Soviet_Union_(1936)|chapter=Fundamental Rights and Duties of Citizens|section=Article 123|city=Moscow}}</ref> | ||
== Culture == | == Culture == | ||
Revision as of 17:43, 9 November 2022
| Union of Soviet Socialist Republics Союз Советских Социалистических Республик | |
|---|---|
| 1922–1991 | |
Flag
(1955-1991) | |
Motto: Пролетарии всех стран, соединяйтесь! Workers of the world, unite! | |
Anthem: Государственный гимн СССР | |
 | |
| Capital and largest city | Moscow |
| Dominant mode of production | Socialism |
| Government | Federal Marxist–Leninist socialist state |
• Notable leaderships | Vladimir Lenin (1922–1924) Joseph Stalin (1924–1953) |
| History | |
• October Revolution | 1917 November 7th |
| 1922 December 30th | |
• World War II victory | 1945 May 9th |
• Dissolution | 1991 December 26th |
| Population | |
• 1989 estimate | 285,742,511[1] |
| Labour | |
• Labour force | 152.3 million[2] |
• Occupation | 80% industry and other nonagricultural fields 20% agriculture[2] |
• Unemployment rate | 1–2%[3] |
| GDP (nominal) | 1989 estimate |
• Total | $2.66 trillion[2] (2nd) |
• Per capita | $9,211[4] |
| Exports | 1988 estimate |
• Value | $110.7 billion[2] |
• Commodities | Petroleum and petroleum products, natural gas, metals, wood, agricultural products, and a wide variety of manufactured goods (primarily capital goods and arms)[2] |
• Partners | Eastern Europe (49%), Western Europe (14%), Cuba (5%), United States[2] |
| Imports | 1988 estimate |
• Value | $107.3 billion[2] |
• Commodities | Grain and other agricultural products, machinery and equipment, steel products (including large-diameter pipe), consumer manufactures[2] |
• Partners | Eastern Europe (43%), Western Europe (18%), Cuba, China, United States[2] |
| Currency | Soviet ruble (РУБ) |
The Soviet Union, officially known as the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR),[note 1] was a Marxist-Leninist federal socialist state that existed in Eurasia from 1922 to 1991.
The USSR was established in 1922 as a union of four Soviet socialist republics formed after the October Revolution of 1917, the Russian SFSR, the Transcaucasian SFSR, the Ukrainian SSR and the Byelorussian SSR. From 1956 to 1991, the union had 15 member nations in total.
The Soviet Union developed under conditions of extreme pressure provoked by capitalist powers, from the Russian Civil War, the Nazi invasion, and espionage from the West. Besides the difficulties that it faced, the USSR managed to provide a positive political role for the working people, especially in a time when workers in the capitalist world were still struggling for basic union rights. The USSR also played an essential military role in the defeat of fascism in World War II.
The Soviet Union was the subject of some of the most impressive economical achievements in modern history. The socialist system transformed a nation of illiterate and starving peasants into an industrial superpower, with one of the fastest growing economies on Earth, one of the world's best-educated and healthiest populations, and some of the most impressive industrial and technological achievements to date. It provided a very influential model for other socialist nations of the world, such as China, Cuba and Vietnam.
From 1988, many Soviet Socialist Republics seceded from the USSR before its dissolution in 1991. Its past territory is now occupied by the states of Russia, Latvia, Lithuania, Estonia, Belarus, Ukraine, Pridnestrovie, Moldova, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Tajikistan, and Kyrgyzstan.
History
Background
In early 20th century, the Russian Empire was a semi-feudal country ruled by an absolute monarchy. The average life expectancy in Russia was about 35 years. Literacy rates were only about 20%. The workers and peasants lived horrible lives without minimum wage laws or basic work safety regulations and worked 60 or 70 hours per week.[5]
Despite the size of the country, there was a constant shortage of farm land and famines were common. Most of the land belonged to the wealthy landlords and rich peasants. Because of technological backwardness, only the softest and most fertile soil could be used, which severely limited the amount of available farm land. There were many large strikes and protests but it was not uncommon that the police would be deployed and break the strike, often by firing at the strikers.
In 1898 the Russian Social Democratic Labor Party (RSDLP) was created, uniting the several communist study groups scattered around Russia. Among its founders were people like Vladimir Lenin and Julius Martov. It established itself as a Marxist party that had the task of overthrowing the monarchy and bring about socialism. However during the course of the struggle there was a lot of disagreement about when this goal was to be implemented and how. In 1903 emerged a de facto split in the party, and two factions were formed: the Mensheviks led by Martov and the Bolsheviks led by Lenin.
Through the leadership of the RSDLP, and against the worsening life conditions, the Russian workers attempted a democratic revolution in 1905. Massive protests erupted all over the country, mutinies were widespread in the army and the people organized public meetings, called “soviets” or councils, which would get together and discuss what to do in an early form of organisation. The revolution eventually failed however. It won some democratic liberties from the Tsar, but those liberties would be constantly under attack by the monarchy afterwards. This revolution would be seen as a rehearsal for the later revolution.
In 1914 the First World War began and launched Russia into chaos. The economy was ruined by the war, there was a shortage of food and large amounts of the population were drafted to fight in the war. The war is seen by many people, especially the socialist, as an unjust imperialist conquest, where millions of poor and working class people from different countries had to die for the profits and wealth of the capitalist and monarchist governments of their countries.
The attitude towards the war ended up splitting the international socialist movement, the so-called Second international working men’s association. Many parties initially opposed the war, but then chose to support their own government in it, so as to protect their country from the other imperialist powers. Lenin, Rosa Luxemburg and other revolutionaries saw this as treachery. In their opinion, if everyone only supported their own imperialist government in an imperialist war, it wouldn't do anything to stop the war. They called for “turning the imperialist war to a class war”, friendship between the workers of the various countries, and unity against the capitalist governments of all warring countries. This led to the splitting of the International.
February Revolution
In February 1917 the Russian monarchy was overthrown. This led to the creation of the Russian Provisional Government, consisting of the capitalist Cadet party, the Socialist-Revolutionary party (or SR) and the Mensheviks.
The Bolsheviks initially gave “conditional support” for the Provisional Government, meaning they supported it to the degree that it carried out the democratic reforms and other policies demanded by the population. However it soon became very evident the Provisional Government was a failure.
The Provisional government refused to carry out land reforms. This was necessary to prevent famine and reduce the land shortage, but it would have meant going against the landlords.
The Provisional government also refused to impose stricter regulations on trading and the economy. This would have been necessary to prevent economic disaster, but it would have meant going against the capitalists who greatly profited from the war and chaos.
Lastly, the Provisional government supported the war. They advocated a “war to a finish”, meaning until they won. It became evident that Russia was losing the war, however the Provisional government was still committed to fulfil the treaties and agreements with their allies in World War 1.
The Bolsheviks were quick to point out that the Provisional government acted exactly like the Tsarist government, which also sided with the landlords, capitalists and started the imperialist war. In their view, the Provisional government was continuing the Tsarist policy.
In April 1917, Vladimir Lenin returned to Russia from exile and puts forward his April theses, political proposals which call for the overthrow of the Provisional government.
The Bolsheviks put forward their slogans:
Down with the provisional government!
Down with the capitalist ministers!
Factories for the workers, land to the peasants, end to the imperialist war!
Peace, Bread & Land
In June of that year, the capital city Petrograd (today called St. Petersburg) held municipal elections. Bolsheviks achieved a massive victory, growing from essentially nothing to one of the biggest parties in Russia. The so-called “defencist bloc” still held the majority of seats however. This bloc consisted of the SR-party and Mensheviks. Defencism meant that they supported the war effort. The biggest loser of the election was the Cadet party, which achieved only 15% of the votes and lost its power as the biggest party.
On July 1, Russia launched an offensive on the front, which was known as the “Kerensky offensive” or the “July offensive.” The war was going badly and casualties were mounting for Russia, the thirst for blood from the imperialists and the Provisional government were very evident.
On July 3 and 4, there was a massive demonstration in Petrograd, of hundreds of thousands of people. Among the demonstrators were armed soldiers who came from the front to demand change and revolution. The Bolsheviks urged caution and said that the demonstration should be peaceful and organized. They opposed bringing weapons to the demonstration and said that they were not yet strong enough for a revolution. The workers and soldiers decided to bring weapons despite the advice of the Bolsheviks but the Bolsheviks still took part in the demonstrations to lend support to the workers.
The workers and soldiers carried the Bolshevik slogans of "End the war”, "Peace, bread and land". There was a government crack down against the demonstrators. Machine guns were turned towards the crowd, leaving countless dead. The Bolsheviks were now seen as a serious threat by the government. A warrant was issued for Lenin’s arrest, which forced him into hiding. Bolshevik newspaper Pravda was banned, their printing plant and party offices were destroyed. This period of repression is known as the “July Days”. The Provisional government restored the death penalty on the front, against soldiers who disobeyed orders.
The Bolsheviks lost a lot of their forces, and many of their important resources. They began publishing their newspapers under new names to avoid censorship. Despite all their difficulties the workers supported them more than ever, the Provisional government was exposed as a supporter of the capitalist elite and the imperialists. The Provisional government started forming stronger ties with the old capitalist party, the Cadets, to make up for the support they lost from the workers.
In August, there was an attempted coup against the Provisional government, called the “Kornilov Affair”. Kornilov was a general of the White Guard in the Russian army, who wanted to institute military dictatorship and strong rule of law, to stop the chaos in Russia. In other words, complete counter-revolution, end to the demonstrations, end to democracy, end to the working class movement.
The railway workers started a strike and refused to transport his troops while the workers and soldiers of Petrograd formed the armed Red Guard units and took up the defence of Petrograd against Kornilov. Kornilov’s coup ended in failure.
After the overthrow of the monarchy, the formation of soviets had begun again in all large cities, but at the time their leadership would be predominantly Menshevik.
In September the Bolsheviks gained the majority in the Petrograd Soviet and soon after in the soviets of Moscow and other large cities. The Soviets already carried out many important functions in the cities as the Russian government was incapable of doing so. The Soviets even organized the defence of Petrograd. As the economy was in ruins and the war effort was failing, more people turned towards the Soviets' leadership.
Great October Socialist Revolution
The 6th Bolshevik party congress had agreed that they should carry out an armed revolution. In October, the Petrograd Soviet created a Military Revolutionary Committee. These special bodies were formed all over the country connected with each soviet in each city. The Menshevik and SR minorities in the soviets opposed revolution, but the SR party split. The “left-SR” group sided with the Bolsheviks.
The Bolshevik soldiers organization took over the garrison. On 24 October the Military Revolutionary Committee occupied the telegraph, telephone offices and other important buildings. The cruiser Aurora, which was controlled by Bolshevik sailors, fired a shot to signal the beginning of the revolution. The workers and soldiers stormed the winter palace. The same evening there was a congress of Soviets, where delegates arrived from all over the country. This congress elected the new Russian government, elected by the soviets of workers and soldiers, the Soviet Government. The October Revolution had taken power.
The October Revolution showed that a revolution by the ordinary people was possible. It showed that capitalism is ultimately incapable of solving its internal contradictions. Despite getting moderate leftists into the government, the policy was as imperialist, profit-driven and anti-popular as during the Tsarist era. The moderate leftists didn’t improve capitalism, they were used by capitalism. Only revolution stopped Russia’s involvement in the World War, carried out land reform and dealt with the crisis of unregulated capitalism, and began the process of building a new economic model which would serve the needs and interests of the people, not profits.[6]
Civil War
The October Revolution led to a civil war where the capitalists tried to seize back the state. 14 capitalist governments including the USA, Great Britain, France, Japan, Poland and many others invaded Soviet Russia to destroy the Soviet government, but they failed, and the Soviet Union was created.[6]
Treaty on formation of the USSR
See main article: Declaration and Treaty on the Formation of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
New Economic Policy
Lenin proposed the New Economic Policy at the 10th Party Congress in March 1921. The NEP allowed peasants to keep their grain and sell their surplus. By 1924, the Soviet Union had defeated foreign invaders and the counterrevolutionary Whites and nationalized key industries. Trotsky and the Left Opposition believed that the Soviet Union could only survive if there was a socialist revolution in the imperial core. The 14th Party Congress in 1925 rejected the Left Opposition and adopted a course of rapid industrialization for the Soviet economy to catch up to the West.
The Right Opposition, led by Bukharin and Rykov, strongly supported the NEP and encouraged private enterprise. They opposed collectivization and rapid industralization.[7]
Industrialization
From 1928 to 1940, industrial production grew by an average of 11% every year. Literacy rates increased from 46% to 80%.[7]
First Five Year Plan (1928–1932)
During the First Five Year Plan, crop area increased from 118 million hectares to 129.7 million. In 1929, only 3.9% of farms had been collectivized, but by 1933 75% of farmland was in collective farms (kolkhozy), 10.8% was in state farms (sovkhozy), and 15.7% was farmed by individual peasants. Over 167,000 collective farms were established during this period. The number of livestock decreased dramatically due to kulaks killing their animals to sabotage the Soviet Union. The number of tractors increased from 34,900 to 204,100 during the First Five Year Plan, and the number of combine harvesters increased from 1,700 to 13,500. The industrial output of the Soviet Union doubled between 1929 and 1933.[8]
Second Five Year Plan (1933–1938)
During the Second Five Year Plan, livestock recovered from the kulak sabotage. By 1938, there were more than twice as many sheep, goats, and hogs as there had been in 1933. The number of cattle increased by 64.6% during the Second Five Year Plan and the number of horses increased by 5.4%. The amount of mechanical farm equipment continued to increase, and the number of tractors grew from 210,900 to 483,500. During this same time period, the economies of capitalist countries were shrinking because of the Great Depression, which did not affect the Soviet Union.[8]
Great Patriotic War
See main article: Second World War
Postwar period
By 1952, industrial production reached 2.5 times the amount from before the Second World War.[7]
Khrushchev period
Brezhnev period
Counterrevolution
See main article: Dissolution of the USSR
The overthrow of the Soviet Union was the process of bourgeois counter-revolution which culminated in the disintegration of the USSR into independent states in December of 1991. Among the various causes for dissolution was the organization of a bourgeois class inside the USSR under a 'shadow economy' which effectively guaranteed their interests through corrupt officials of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU). It's generally accepted that the political and economic policies of Khrushchev, Brezhnev and ultimately Gorbachev paved the way for counter-revolution in the USSR.
Government
Elections
Before 1936, priests, landlords, capitalists, and former Whites had not been allowed to vote. The 1936 Soviet constitution removed these restrictions so all citizens aged 18 or older could vote, with the exception of insane people and convicted criminals disenfranchised by a court. Under the 1924 constitution, the people elected the lowest level of representatives and higher soviets were elected indirectly. The 1936 constitution made all soviets from the local to all-union level directly elected.[9]
Supreme Soviet
The Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union was the legislature of the USSR and was elected every four years. It consisted of two branches: the Soviet of the Union, which was elected based on population, and the Soviet of Nationalities, which was elected according to the republics, ASSRs, autonomous oblasts, and autonomous okrugs of the Soviet Union. Either house could initiate legislation and it had to be passed by a majority vote of both houses to become law. Each house elected a chairman and two vice-chairmen to preside over their sessions, which occurred twice every year. The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet could also convene special sessions.[10] Before 1936, the Supreme Soviet was known as the Congress of Soviets and the Soviet of the Union was known as the Federal Soviet.[11]
The Federal Soviet was elected with one deputy per 25,000 urban inhabitants or 125,000 rural inhabitants.[11] After 1936, the Soviet of the Union had one deputy for every 300,000 inhabitants.[10]
From 1924 to 1936, the Soviet of Nationalities had five deputies for every union republic and one for every autonomous republic and autonomous oblast.[11] In 1936, this was changed to 25 for every union republic, ten for each ASSR, five for each autonomous oblast, and one for each autonomous okrug.[10] In 1977, it was changed again so that every SSR would have 32 deputies and every ASSR would have 11.[12]
Presidium
The Presidium of the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union was elected at a combined session of the Soviet of the Union and the Soviet of Nationalities. It consisted of a President, Secretary, one vice president from every union republic, and 24 members.[11]
Council of People's Commissars
The Council of People's Commissars (Sovnarkom) was the executive branch of the USSR and was elected at a joint session of the Soviet of the Union and Soviet of Nationalities.[11]
Supreme Court
The Supreme Court was the highest court in the Soviet Union and was elected by the Supreme Soviet once every five years.[11]
Administrative divisions
See main articles: Soviet republic (system of government) and Republics of the Soviet Union
Constitutionally, the USSR was a federation of constituent Union Republics, which were either unitary states, such as Ukraine or Byelorussia (SSRs), or federations, such as Russia or Transcaucasia (SFSRs), all four being the founding republics who signed the Declaration and Treaty on the Formation of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics in December 1922. In 1924, during the national delimitation in Central Asia, Uzbekistan and Turkmenistan were formed from parts of Russia's Turkestan ASSR and two Soviet dependencies, the Khorezm and Bukharan SSRs. In 1929, Tajikistan was split off from the Uzbekistan SSR. With the constitution of 1936, the Transcaucasian SFSR was dissolved, resulting in its constituent republics of Armenia, Georgia and Azerbaijan being elevated to Union Republics, while Kazakhstan and Kirghizia were split off from Russian SFSR, resulting in the same status.[13] In August 1940, Moldavia was formed from parts of Ukraine and Bessarabia and Ukrainian SSR. Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania (SSRs) were also admitted into the union. Karelia was split off from Russia as a Union Republic in March 1940 and was reabsorbed in 1956. Between July 1956 and September 1991, there were 15 union republics (see map below).[14]
While nominally a union of equals, in practice the Soviet Union was dominated by Russians. The domination was so absolute that for most of its existence, the country was commonly (but incorrectly) referred to as "Russia". While the RSFSR was technically only one republic within the larger union, it was by far the largest (both in terms of population and area), most powerful, and most highly developed. The RSFSR was also the industrial center of the Soviet Union.
| Republic | Map of the Union Republics between 1956 and 1991 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | [[|]] | 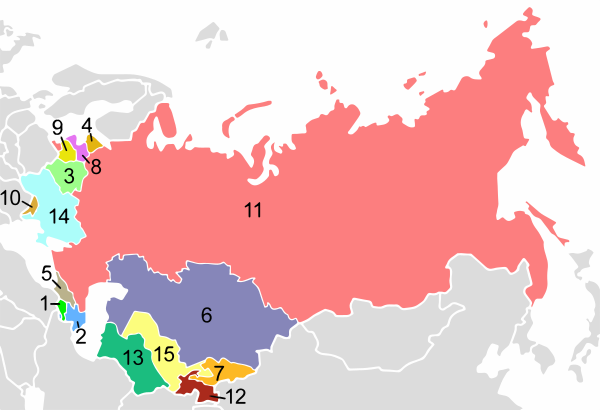
|
| 2 | [[|]] | |
| 3 | [[|]] | |
| 4 | [[|]] | |
| 5 | [[|]] | |
| 6 | [[|]] | |
| 7 | [[|]] | |
| 8 | [[|]] | |
| 9 | [[|]] | |
| 10 | [[|]] | |
| 11 | [[|]] | |
| 12 | [[|]] | |
| 13 | [[|]] | |
| 14 | [[|]] | |
| 15 | [[|]] | |
Economy
In the Soviet Union, the richest people earned about five times as much money as the poorest. The income gap was tiny compared to the United States, where billionaires have many thousands of times more money than the poorest workers.[15]
Planning
The soviet economy was a planned economy, in which much of the economic planning was aided by teams of mathematicians and economists. These plans were enacted in the form of five year plans.
These five year plans used production quotas to encourage growth of the soviet economy. contrary to popular belief, these quotas were based on previous production records, available technology, amid many other factors
Agriculture
Farms and farm equipment in the USSR were collectively owned.
Housing and construction
After the October Revolution, hundreds of thousands of workers moved from slums to nationalized houses. In 1919, a decree was passed setting a minimum of at least 8.25 square meters of living space per person, 30 cubic meters of air space for every adult, and 20 cubic meters for every child. This space only included living and bed rooms, not bathrooms or entrances. Rent in the Soviet Union was kept at under 4% of workers' total incomes.[16]
In 1920, 254 residential buildings were built and 2,347 were repaired. From 1923 to 1927, 12.5 million square meters of living space were built. From 1927 to 1931, another 28.85 million were built. The average living space for each worker greatly increased from the revolution to 1938: there was a 94% increase in Moscow, 100% in Leningrad, 176% in the Donbass, and 195% in the Urals.[16]
Industry and manufacturing
Services
Environment
Infrastructure
Transportation
Energy
Science and technology
Demographics
Living standards
In 1917, the Bolsheviks reduced the working day to 8 hours. Workers had 12 to 48 guaranteed vacation days per year. The average person in the Soviet Union ate over 3,000 kilocalories per day and had a better diet than in the United States. By the 1980s, the Soviet Union had the seventh best diet in the world.[5]
Soviet life expectancy was 59.4 years in 1953. By 1965, it had increased to 68.4 years, more than twice as long as before the revolution and 15 years more than the world average at the time.[5] Infant mortality decreased from 25% before the revolution to lower than Italy or Austria by 1960,[17] and child mortality decreased by half from 1917 to 1928.[18] Literacy increased from under 30% before the revolution to 87.4% in 1939 and reached 100% by 1970.[5]
Education
Education in the Soviet Union was free[19] and was mandatory between the ages of 8 and 15. There were also ten-year schools that went to the age of 18, but the last three years were not mandatory. The curriculum included nature study, art, music, social science, and foreign languages.[20] School days lasted between 4.5 and 6 hours, depending on age.[20] Schools were taught in 52 different languages.[21]
| 1913 | 1929 | 1933 | 1942 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7-year schools | 6,800,000 | 11,700,000 | 21,300,000 | 23,000,000 |
| 10-year schools | 1,000,000 | 2,700,000 | 5,500,000 | 17,000,000 |
| Total | 7,800,000 | 14,400,000 | 33,400,000 | 40,000,000 |
Between 1932 and 1937, 20,000 schools were built in the Soviet Union. Between 1938 and 1941, 20,000 more schools were built and 500,000 new teachers were trained. Between 1913 and 1940, the number of libraries in the USSR increased by 57,400. 12% of the USSR's national budget was spent on education.
Children aged 12 and older formed committees to care for school property and help other students. Corporal punishment was illegal.[20]
Literacy rates
Before the October Revolution, most people in Central Asia were illiterate. By the late 1930s, most people throughout the Soviet Union could read and literacy was nearly universal by the late 1950s.[15]
Preschool
Optional preschool and kindergarten were available in the Soviet Union from birth to the age of 8. In 1932, there were 600,000 children in daycares; this number increased to three million by 1937.[20]
Universities
In 1940, there were 700 universities in the USSR with 650,000 students enrolled. There were 22 universities in Belarus, 13 in Azerbaijan, and 30 in Uzbekistan.[20]
Health

Nikolai Semashko, the People's Commissar for Public Health from 1918 to 1930, proposed a health system based on the following principles:
- Unified principles of organization and centralization of the health care system
- Equal accessibility of healthcare for all citizens
- Priority attention to childhood and maternity
- Unity of preventive healthcare and treatment
- Elimination of social bases of diseases
- Involvement of the society in the cause of healthcare
The public health budget of the USSR increased by 75 times from the Russian Empire's budget in 1913. From the Civil War to 1928, the number of physicians increased from 19,785 to 63,219,[18] and it reached 334,000 doctors (including dentists) by 1955.[17] By the late 1950's, the life expectancy of the Soviet Union had increased to 68.7 years, which was as high as the United States at the time.[22] Production of pharmaceutical chemicals increased by five times from 1940 to 1950 and 3.1 times from 1950 to 1955 and there were 1,290,000 hospital beds in 1955.[17]
In 1978, the World Health Organization recognized the Soviet principles of healthcare as some of the best in the world.[17]
By republic
By 1941, Azerbaijan had 2,500 doctors compared to 291 before the revolution. The number of physicians in Tajikistan increased from 13 to 372 over the same time period.[18]
Infectious diseases
During the Russian Civil War, there were outbreaks of cholera, typhus, and smallpox. The prevalence of typhus decreased by more than twice from 1919 to 1922 and by 80 times by 1927 and the prevalence of malaria decreased by more than three times from 1917 to 1930. Compulsory vaccination for smallpox was introduced in 1919 and it was eradicated by 1937.[17]
Human rights
Article 123 of the 1936 Soviet Constitution guaranteed national equality and banned racism.[23]
Culture

Sports
The USSR put a lot of emphasis on sports, as evidenced by the material they produced (such as posters). They were also a participant in the Olympic Games and created their own competing event, the Spartakiads (named after Spartacus, the slave rebel).
Weightlifting
Moreover, the USSR produced many record-setting athletes, mainly in weightlifting, which was a very popular sport in the USSR and remains one to this day in existing socialist countries such as China or the DPRK.
The Soviets pioneered their own system, which is today mostly saved and translated by Pavel Tsatsouline. While most weightlifters today reach their peak around 26 and retire around the age of 35, a few Soviet weightlifters produced world records well past their 30s. This is because their method focused on preserving longevity in their athletes, developed with the scientific method. Athletes were followed by scientists who analysed their data and produced a routine adapted to their level.[24]
The most famous Soviet weightlifter is arguably Vasily Alekseyev, who set 80 world records in an eight-year period. He retired at the age of 38 after failing to register a total at the Moscow Olympics, following an injury he sustained in 1978.[25]
Film
References
- ↑ Демоскоп Weekly. Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года. Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР [The 1989 All-Union Population Census. National composition of the population by republics of the USSR].
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 2.8 CIA World Factbook (1990). Soviet Union – World Factbook (Wikisource)
- ↑ CIA World Factbook (1991). Soviet Union Economy
- ↑ CIA World Factbook (1990). GDP per Capita 1990
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Standard of living in the Soviet Union" (2021-08-23). Oktaybr. Archived from the original on 2021-08-24. Retrieved 2022-09-11.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 TheFinnishBolshevik (2017-11-08). "Brief History of the October Revolution" Retrieved 2022-03-25.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 Roger Keeran, Thomas Kenny (2010). Socialism Betrayed: Behind the Collapse of the Soviet Union: 'Two Trends in Soviet Politics' (pp. 18–25). [PDF] iUniverse.com. ISBN 9781450241717
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 TheFinnishBolshevik (2016-08-07). "The results of the 1st & 2nd Five-Year Plans: Soviet industrial revolution." ML-Theory. Archived from the original on 2022-06-22. Retrieved 2022-08-07.
- ↑ Joseph Stalin (1939). History of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (Bolsheviks): 'The Bolshevik Party in the Struggle to Complete the Building of the Socialist Society. Introduction of the New Constitution'. [MIA]
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Joseph Stalin (1936). Constitution of the Soviet Union: 'The Highest Organs of State Authority of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics'.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 Second All-Union Congress of Soviets (1924). Constitution of the Soviet Union.
- ↑ Government of the Soviet Union (1977). Constitution of the Soviet Union: 'Higher Bodies of State Authority and Administration of the USSR'.
- ↑ Russian Republics (2005) (p. 21). Black Rabbit Books. ISBN 978-1-58340-606-9
- ↑ Russian Law: The Rnd of the Soviet system and the Role of Law (1993) (p. 94). Martinus Nijhoff Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7923-2358-7
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 Carlos Martinez (2017-11-19). "Why doesn’t the Soviet Union exist any more? Part 1: Introduction" Invent the Future. Archived from the original on 2022-02-11. Retrieved 2022-10-08.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 "Housing in the USSR" (2017-01-13). Stalin Society. Archived from the original on 2022-03-30. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 17.4 "Healthcare Under Socialism: The History of the Soviet Healthcare System" (2021-09-07). Politsturm. Archived from the original on 2021-11-12. Retrieved 2022-05-20.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 Carlos Rule (2017-01-18). "Health in the USSR" Stalin Society. Archived from the original on 2022-02-16. Retrieved 2022-06-27.
- ↑ Joseph Stalin (1936). Constitution of the Soviet Union: 'Fundamental Rights and Duties of Citizens; Article 121'. Moscow.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 Anglo-Soviet Youth Friendship Alliance (1942). "Education in the U.S.S.R." Revolutionary Democracy. Retrieved 2022-04-17.
- ↑ Eugene Puryear (2022-06-12). "Nations and Soviets: The National Question in the USSR" Liberation School. Archived from the original on 2022-06-13. Retrieved 2022-08-31.
- ↑ Reiner Dinkel (1986). Paradoxical Effects of Social Behavior: 'Declining Life Expectancy in a Highly Developed Nation: Paradox or Statistical Artifact?' (pp. 311–321). Munich: Department of Economics, University of Munich.
- ↑ Joseph Stalin (1936). Constitution of the Soviet Union (1936): 'Fundamental Rights and Duties of Citizens; Article 123'. Moscow.
- ↑ Craig Marker (2014-11-14). "4 secrets of Soviet weightlifting as revealed by Pavel Tsatsouline" Breaking Muscle.
- ↑ "Vasily Ivanovich Alekseyev Soviet weightlifter". Britannica.
Notes
- ↑ Russian: Союз Советских Социалистических Республик (СССР)


