More languages
More actions
"United States" redirects here. For other uses, see United States (disambiguation).
| United States of America ᏌᏊᎢᏳᎾᎵᏍᏔᏅᏍᎦᏚᎩ ᎾᎿ ᎠᎺᏰᏟ ʻAmelika Hui Pūʻia Tannapta Nunaat Amiarikami Mílahaŋska Tȟamákȟočhe Wááshindoon Bikéyah Ałhidadiidzooígíí Gichi-mookomaan-aki | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Capital | Washington, D.C. |
| Largest city | New York City |
| Official languages | None (de jure) English (de facto) |
| Demonym(s) | Statesian United Statesian US-American Yankee (pejorative) Gringo (pejorative) American (common)[a] |
| Dominant mode of production | Imperialist capitalism |
| Government | Federal corporatocratic republic |
| Donald Trump | |
• Speaker of the House | Mike Johnson |
• President of the Senate | JD Vance |
| History | |
| July 4, 1776 | |
• Current constitution | March 4, 1789 |
• Last state admitted | August 21, 1959 |
| Area | |
• Total | 9,833,520 km² |
| Population | |
• 2021 estimate | 331,893,745 |
| Currency | United States dollar |
The United States of America (USA), commonly referred to as just the United States (US) or America, is a settler colonial state[1] located primarily in North America. Consisting of 50 states, the District of Columbia, 14 internationally-recognised territories, and 326 Indian reservations, it is the second-largest country in North America and fourth-largest in the world. It borders Canada to the north, Mexico to the south, the Atlantic to the east, and the Pacific to the west. The country's system of governance is a liberal, federal presidential republic.
The United States is the most influential capitalist and imperialist state today, accounting for 15% of global GDP (PPP)[2] and more than 50% of global military spending.[3] With a population of more than 340 million,[4] it is the third-most populous country in the world; it constitutes 4.2% of the total human population, but is home to over 20% of the world's prisoners.[5]
A modern empire, the United States sits at the center of a group of imperialist Western regimes. The USA is the leading country of many international imperialist organizations, such as the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, Organization of American States, World Bank, International Monetary Fund, National Endowment for Democracy, Human Rights Watch, and others.
The pervasiveness of anti-communist ideology, the frequent relationship between government officials and corporate board of directors, the tendency for war, and the reach of nationalist, patriarchal and racial chauvinist ideas makes the USA a dictatorship of the bourgeoisie with traits of fascism.[6][7][8] Wealth distribution is extremely unequal, with the richest three Statesians owning more than the poorest 160 million combined.[9]
Beginning as a settler-colony of European maritime empires, the USA became an independent country in 1776. It has achieved remarkable economic, scientific and military development through the process of imperialism, where it uses military power to ensure access for its private industries to exploit the nations of the world. The United States deliberately killed over 11 million unarmed civilians in its imperialist wars and conquests before 2000[10] and another 4.5 million in the 21st century.[11]
Many of its methods of exploitation employed outwardly are also employed inwardly towards its own population with increasing intensity as its economy has been in steady decline since the 2008 financial crisis and the 2020–2022 COVID-19 pandemic.
Nomenclature[edit | edit source]
The official name of the country is the United States of America, but it is often shortened to US, America, or United States; however, these names are erroneous, as other countries, such as the Mexican United States, share the same wording "United States" in their name. Furthermore, the term "America" and "American" could refer to the geographic locations or inhabitants of North America, South America, or both.
Some of the indigenous names for the whole of North America include: Mishiike Minisi, Anowara:kowa, and Khéya Wíta.[b] "America" is often respelled as "AmeriKKKa" in reference to the pervasiveness of white supremacist ideology in the US.[12] In Iran, the US is referred to as Shaytân-e Bozorg,[c] which means "the great Satan."[13]
History[edit | edit source]
Pre-colonization[edit | edit source]
See main article: History of humanity


Human settlement in the Americas began between 12,500 to 27,000 years ago through different possible routes recognized by researchers. The most common and accepted theory is that humans crossed through land between Siberia and Alaska in the Beringia region at least 30,000 years ago,[14][15] when the sea levels were at a minimum, revealing a pathway which made possible to cross between the lands, and stayed there until at least 12,500 years ago,[16] when they went deep into American land.
Genetic evidence based on mitochondrial DNA suggests that the last common ancestor between central Asian and North American indigenous peoples was estimated to have diverged between 25,000 to 20,000 years ago,[17] during the time humans were located at the Beringian region, and sub-haplogroup analysis suggest that dispersion from Beringia may have occurred as early as 16,000 years ago.[18]
Around 10,500 years ago, the peoples of the eastern region of North America, developed agriculture based on corn, domestication of animals, along with hunting, fishing and gathering.[19] The development of agriculture in the region also required complex irrigation systems and developed through extensive trade between the peoples of Central and South America.[20] By the 15th century, the population of the whole continent of America was about 100 million people, and about 40 million lived in North America. In comparison, the European peoples at that time amounted to around 50 million.[21]
At the beginning of European colonization, most indigenous peoples lived in agricultural societies but others were hunters and gatherers.[22]
European colonization[edit | edit source]
In the 17th century, settlers from Britain and Holland began to arrive in North America. Of 10,000 settlers who left from Bristol between 1654 and 1685, most were farmers and artisans and less than 15% were proletarians. The settlers initially enslaved both Africans and natives.[23]
In 1675, Metacomet, also known as "King Philip," led an uprising against the settlers.[24]
In 1715, the settlers sold their native slaves abroad and focused on enslaving Africans. By the Revolutionary War, New Afrikans made up over 20% of the non-indigenous population, including more than half in Virginia and South Carolina.[23]
Bacon's Rebellion[edit | edit source]
Soon after King Philip's War, a conflict broke out in Virginia between settlers and the Susquehannock. A settler army of 1,100 surrounded the Susquehannock fort and executed five of their leaders, inspiring them to begin a guerrilla warfare campaign. In May 1676, plantation owner Nathaniel Bacon formed a vigilante group to attack the Susquehannock, against the orders of the British colonial governor. He went to an Occaneechee fort and persuaded the Occaneechee to attack the Susquehannock. After the Susquehannock were defeated, Bacon attacked the Occaneechee to steal their beaver furs, which were worth about £1,000.
After defeating the Occaneechee, Bacon turned against Governor William Berkeley, whom he accused of secretly selling guns to the indigenous peoples. On June 23, 1676, he marched to Jamestown with an army of over 500 and captured the city. Loyalist forces arrived in September but Bacon soon recaptured the city and burned it down.[24]
Seven Years' War[edit | edit source]
During the Seven Years' War, the British fought against France and their indigenous allies. The indigenous peoples supported the French because they traded with them but did not want to occupy their land. The British defeated the French in 1763 and France ceded the land west of the Appalachians to Britain. The natives continued a guerrilla warfare campaign against the British until they passed the Proclamation of 1763, which prevented colonists from settling west of the Appalachians.[25]
After 1765, a crisis began between British authorities and colonists and local newspapers were pressured to censor anti-secessionist material. The Sons of Liberty attacked and rioted against loyalists.[26]
Independence War[edit | edit source]
See main article: Statesian Revolution
Between 1775 and 1778, state governments passed laws making it illegal to criticize the Continental Congress, which was organizing a rebellion against the British. Eight states banished prominent loyalists and all states deprived their right to vote. Between 80,000 and 100,000 loyalists fled during the revolution, half of which moved to Canada. The percentage of colonists that fled from the Statesian Revolution (4% of the white population) was higher than those who fled the Russian Revolution (only 1.5% of the total population).[26]
During the Statesian Revolution, the British tried to form an alliance with the Cherokee Nation and provided them with weapons and funding. In 1776, over 5,000 settlers from Virginia, Georgia, and the Carolinas invaded the Cherokee Nation. Settlers attacked the Cherokee Nation again in 1780 and 1781.
In 1777, the British formed an alliance with the Shawnee in what is now Ohio. In 1780, settlers from Virginia attacked the Shawnee in what is now southern Ohio.
In the north, the six nations of the Haudenosaunee took different sides in the war. The Mohawk and Senecas sided with the British, the Oneidas sided with the settlers, and the Cayuga, Onondaga, and Tuscarora were neutral. George Washington gave orders to destroy the villages of the nations that did not side with the United States. The British surrendered in 1783 and allowed Statesian settlers to expand west into the territory between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi River.[27]
Early republic[edit | edit source]
Articles of Confederation[edit | edit source]
Shays' rebellion[edit | edit source]
In 1786, farmers in western Massachusetts rebelled because of debt and taxes, which were four times as high as they had been under the British. Washington opposed the uprising, and Samuel Adams passed the Riot Act to crush dissent.[28]
Federalist Era[edit | edit source]
The first decades after U.S. independence were characterized by conflict between the Federalist Party, which favored the wealthy, and the Democratic-Republican Party, which favored small farmers. John Adams, George Washington's Federalist successor, passed the Alien and Sedition Acts in 1798 to enforce censorship and ban criticism of the government. The law sentenced the radical labor leader David Brown to prison in October 1798 after he put up a pole saying "Downfall to the tyrants of America."[26]
Whiskey Rebellion[edit | edit source]
Invasion of Ohio[edit | edit source]
In 1784, the Continental Congress deployed Josiah Harmar to the Northwest Territory to survey the land so it could be sold to settlers. The USA built its first fort, Fort Harmar, in what is now Ohio in 1785, followed by Fort Washington in modern-day Cincinnati in 1789. From there, Harmar invaded the Miami and Shawnee nations and lost almost 200 troops in four days before retreating.[29]:103–6
Mohawk leader Thayendanegea had formed an alliance of the indigenous nations in the Ohio River valley in the 1780s and received weapons from the British. Secretary of War Henry Knox organized an army of settlers from Kentucky to invade the territory of the Miami and Shawnee nations.[30] Little Turtle and Blue Jacket ambushed the settler army, who destroyed 300 buildings and looted the two largest Miami towns. In 1791, they destroyed the invading army led by Arthur St. Clair at the Battle of Wabash, which was one of the largest defeats of the U.S. military in history.[31] 637 U.S. soldiers died, and less than half of St. Clair's forces returned unharmed to Fort Washington.[29]:106 Anthony Wayne, who led the settlers from 1792 to 1794, destroyed food supplies and murdered native civilians. After Blue Jacket refused an ultimatum at Fort Defiance, settler forces began an extermination campaign against civilians. They defeated the Shawnee at the Battle of Fallen Timbers in August 1794.
In 1794, John Jay signed a treaty with the British that made them leave their 13 forts in the Northwest.[29]:108 The USA annexed southern Ohio in 1795 with the Treaty of Greenville.[30] The British occupied some territory south of the Canadian border until 1796, when they withdrew and ended their support for the indigenous resistance.[29]:105–8
Quasi-War[edit | edit source]
Between 1798 and 1800, the USA fought undeclared naval battles with France in the Caribbean because it was seizing U.S. merchant ships. Congress was only two votes away from declaring war on France.[32]:135
Jeffersonian Era[edit | edit source]
In 1801, slave owner Thomas Jefferson came to power and replaced the Federalist government. He pardoned people convicted under the Alien and Sedition Acts but continued censorship and political repression against his own political opponents.[26]
In 1803, Congress approved $2,500 for Meriweather Lewis and William Clark's military expedition through the Louisiana Territory to plan the annexation of that area. Later, Zebulon Pike led expeditions in the Southwest and the Mississippi headwaters. In late 1803, the USA bought the Louisiana Territory from France, which had secretly taken it from Spain in 1800. In 1806, Statesian and Spanish soldiers had a skirmish on the border of Texas.[29]:113–8
Congress banned the international slave trade in 1808 without ending slavery within the country. In the early 19th century, the American Colonization Society emerged and attempted to persuade slave owners to sell their slaves and send them back to Africa to spread Christianity. It sought to make the United States into a white-only country without forcibly freeing the slaves. Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, and Oregon completely banned Black people (enslaved or free) from living in their territory.[33]
In 1807, the Shawnee brothers Tecumseh and Tenskwatawa began a movement for indigenous peoples to return to their pre-colonial culture. Tecumseh united the nations of the northwest and presented a program to prevent settlers from buying native land. The governor of Indiana, William Henry Harrison, bribed some Delaware, Miami, and Potawatomi to give up their land in 1809. In 1810, he moved south to bring the Muskogees, Choctaws, and Chickasaws into the alliance. In November 1811, Statesian troops attacked Tenskwatawa at Prophetstown and killed 200 natives. After the attack, Kickapoos, Winnebagos, Potawatomis, and Creeks obtained British weapons from Canada to fight the settlers.[30]
War of 1812[edit | edit source]
See main article: War of 1812
The United States declared war on Britain in 1812 because of its connections to Tecumseh's anticolonial movement. Indigenous forces liberated Michigan and forced thousands of settlers out of Illinois and Indiana, but the USA killed Tecumseh at the Battle of Thames in 1813, destroying the resistance.[30]
Barbary Wars[edit | edit source]
The Berber states of North Africa (Algiers, Tripoli, and Tunis) demanded taxes from ships traveling through their waters and captured ships if they refused to pay. Between 1801 and 1805, Jefferson sent the Navy to fight them and occupy Tripoli. In 1815, only ten days after the War of 1812 ended, James Madison told Congress to declare war again. The Navy quickly captured two warships from Algiers and forced them to end tribute payments.[32]:133–4
Era of Good Feelings[edit | edit source]
Jacksonian Era[edit | edit source]

After the war against the British Empire, the fledgling United States expanded westward with Thomas Jefferson (the third in a long line of Presidents) referring to the country as an "empire of liberty." As Nancy Isenberg elucidates in her book White Trash: The 400-Year Untold History of Class in America: "The Louisiana Territory, as he envisioned it, would encourage agriculture and forestall the growth of manufacturing and urban poverty—that was his formula for liberty. It was not Franklin's “happy mediocrity” (a compression of classes across an endless stretch of unsettled land), but a nation of farmers large and small. This difference is not nominal: Franklin and Paine used Pennsylvania as their model, while Jefferson saw America’s future—and the contours of its class system—through the prism of Virginia."[34]
Around 1800, as the lands further to the west were opened up to the fledgling United States, the young state saw the land as a way to appease its population and strengthen its power in the world. As Nancy Isenberg further explains: "By 1800, one-fifth of the American population had resettled on its 'frontier,' the territory between the Appalachian Mountains and the Mississippi. Effective regulation of this mass migration was well beyond the limited powers of the federal government. Even so, officials understood that the country’s future depended on controlling this vast territory. Financial matters were involved too. Government sale of these lands was needed to reduce the nation’s war debts. Besides, the lands were hardly empty, and the potential for violent conflicts with Native Americans was ever present, as white migrants settled on lands they did not own. National greatness depended as much as anything upon the class of settlers that was advancing into the new territories."[35]
After the Statesian Revolution, the United States began a genocidal policy of "Indian Removal" to clear the land between the Mississippi River and the Appalachians for settlers. In 1790, most of the settler population lived within 50 miles of the Atlantic Ocean. From 1800 to 1830, the number of white settlers west of the Appalachians grew from 700,000 to 4.5 million. Between 1820 and 1844, the number of Native Americans living east of the Mississippi dropped from 120,000 to under 30,000. President Thomas Jefferson bought the Louisiana Territory from France in 1803, doubling the size of the United States and extending the frontier to the Rocky Mountains.[36]
Through a series of treaties from 1814 to 1824, settlers took control of most of Alabama and Florida as well as parts of Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, North Carolina, and Tennessee. Future president Andrew Jackson relied on bribery and threats to make native leaders sign these treaties. In 1818, he began raids into Spanish Florida and destroyed Seminole villages until Spain surrendered the territory to the United States in 1819.[36]
Trail of Tears[edit | edit source]

Presidents Andrew Jackson and Martin Van Buren forced 70,000 Native Americans to move west across the Mississippi River. Secretary of War Lewis Cass promised in 1825 that the United States would never try to take indigenous land west of the Mississippi.[36]
Half of the 16,000 Cherokees died during the march. The Muskogees and Seminoles suffered similar death rates and about 15% of the Choctaws and Chickasaws died on the way to Oklahoma.[37]
Invasion of Mexico[edit | edit source]
See main article: Mexican–Statesian War

After the Mexican government banned slavery in 1829, US-backed settlers in Texas rebelled to form the Republic of Texas in 1836, which the United States annexed in 1845. The United States invaded Mexico in 1846, beginning in Veracruz. They occupied Mexico City in 1848 and did not leave until Mexico surrendered its northern territories to the USA. After the annexation, U.S. cavalry troops attacked the Apaches led by Mangas Coloradas, destroying crops and villages and murdering civilians.[38]
Slavery and the abolitionist movement[edit | edit source]
The extent to which average whites in slave states benefitted from and supported the institution of slavery has been minimised by American nationalists of the neo-Confederate and Unionist varieties alike. It is often claimed that only a very small elite of plantation-owners directly stood to benefit from slavery. According to the 1860 U.S. Census, there were 393,975 slavers out of a population of 31,183,582, or 1.26%. This figure is widely cited today as "proof" that few white Southerners directly benefitted from slavery.[39]
This picture is misleading however. Firstly, this is for the whole of the United States rather than just the states where slavery was practised. Secondly, it counts enslaved people themselves rather than just free people. Most importantly but least obviously, although slaves were typically only owned by one person (usually the head of a household), the rest of the slaver's family also directly profited from the institution. They shared in the wealth accumulated through the slave's exploitation and inherited slaves when the owner died. Thus, controlling for these factors, the percentage of free families that owned slaves in states which later seceded is 30.8%. At the state level, the percentage of free families which owned slaves in 1860 was:[39]
- 49% in Mississippi
- 46% in South Carolina
- 37% in Georgia
- 35% in Alabama
- 34% in Florida
- 29% in Georgia
- 28% in North Carolina
- 28% in Texas
- 26% in Virginia
- 25% in Tennessee
- 23% in Kentucky
- 20% in Arkansas
- 13% in Missouri
- 12% in Maryland
- 3% in Delaware
Thus, every third white had a direct interest in preserving slavery.
In 1805, South Carolina passed laws that allowed executing people who supported or encouraged slave rebellions. Georgia passed a similar law around the same time.[40]
By 1830, following the abolition of slavery in much of Latin America, the United States was effectively in a cold war with Haiti. South Carolina banned Africans from Haiti and other French colonies from entering the country in order to limit the spread of abolitionism.[41]:151
In 1836, Andrew Jackson allowed the postmaster general to censor any newspapers critical of slavery. The House of Representatives banned examining antislavery petitions.[40]
Slave rebellions and enslaved Africans[edit | edit source]
Yeoman farmers, who did not own slave labour, made up two-thirds of whites. They sometimes supported the institution of slavery but also occasionally challenged the goals of the planter elite where their interests came into conflict, especially on the western frontier (where there were fewer slavers to begin with due to the region's inhospitality to agriculture), advocating for the gradual abolition of slavery. Due to the dominance of cotton in the south, and yeoman farmers there saw, how detrimental it was to their own survival to compete with the slave owning elite, working from dawn until dusk on with their own hands on their own lands. Poor white farms gained more voting rights in the 1830s and 1840s and sought to influence state legislatures about their political and economic concerns. Even then, trouble arose for elite slave owners with nations around the world from Europe to South America abolishing slavery, as the abolition movement picked up steam, an example of which, Britain's emancipation of ''all slaves'' in 1834, so elite white farmers came up with a system that was to ensure the institution of slavery was to be intact forever. With the three-fifths compromise, giving elite whites political power in congress, white elite planters also consolidated power, by making loans to those in need, hiring poor whites for work, as well as using resources to transport crops of yeoman farmers to the market. Even if some yeoman farmers didn't participate in the institution of slavery, they had major incentives not to end it because white settler colonial elites had made white society dependent upon themselves. White settler-colonialism, and its justification for the institution for slavery, was a political and economic move, to coerce, and influence those in slavery, and those who didn't contribute to slavery as much as actual slave owners, to disprove the evils, and horrors of slavery and to justify its evil to end it. The white settler elite created the idea of white supremacy to uphold white society together under elitist control. The idea that all whites were equal and superior towards black African slaves, was not in question due to the lower, and poor white farmers, who either did or did not support the idea of white supremacy, not having any benefits to opposing the idea of it, since the elite white farmers did in fact keep the yeoman poor farmers alive, and sustainable. Two justifying phrases include those that explain slavery, as a ''necessary evil'' or a ''positive good''. John C. Calhoun noted that:
''I hold that in the present state of civilization, where two races of different origin, and distinguished by color, and other physical differences, as well as intellectual, are brought together, the relation now existing in the slaveholding States between the two, is, instead of an evil, a good - positive good... There never has yet existed a wealthy and civilized society in which one portion of the community did not, in point of fact, live on the labor of the other. Broad and general as is this assertion, it is fully borne out by history... I fearlessly assert that the existing relation between the two races in the South, against which these blind fanatics are waging war, forms the most solid and durable foundation on which to rear free and stable political institutions.''
Explaining the ''inherent'', and ''moral'', as well as, ''necessary'', domination of the white race over the black, race bound southern society together. The planter elite and forged a unbreakable tie with the lower white classes and established a stronghold on southern culture.[citation needed]
Nat Turner's rebellion[edit | edit source]
The largest slave rebellion in the United States happened near New Orleans in 1811. 400 or 500 armed slaves overthrew the plantation owner and began liberating slaves from other plantations. The U.S. army crushed the uprising, immediately killing 66 rebels and executing 16 later.
In 1822, Denmark Vesey planned to start a large rebellion in Charleston, South Carolina, which was the sixth largest city in the USA. When authorities found out, they hanged Vesey and 34 others. The trial record was destroyed soon after.
Nat Turner's Rebellion, was an organized slave revolt in Virginia, led by an enslaved worker named Nat Turner. Being a spiritual individual he believed that god had chosen him for a mission. In obedience to that vision, Turner and his followers began by killing his masters in Southhampton county and then headed to other plantations to do the same. In the end Turner and his followers had killed 57 white people and the next day the Virginia Militia encountered the rebels and squashed the rebellion. Turner and 55 others believed to be his conspirators were hanged. And as a result of this, Virginia planters panicked, and unleashed terror on an estimated 200 of their enslaved workers, beating all of them and killing many.[42]
John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry[edit | edit source]
John Brown tried to start a slave rebellion in Virginia in 1859. He failed and was executed by hanging.[41]
Civil War era[edit | edit source]
See main article: Statesian Civil War
In January 1861, several slave states seceded from the USA to form the Confederate States of America. They seized an army base at Fort Sumter in April, beginning a war against the United States. In addition the the Union Army, the Confederacy also fought against guerrilla units of indigenous peoples and former slaves in Kansas.[43]:133–6
Reconstruction[edit | edit source]
After the defeat of the Confederacy, Congress passed a series of laws putting the south under military rule. The army prevented former Confederates from voting and organized an anti-secessionist electorate. They elected delegates to create new state constitutions so their states could rejoin the USA. The army enfranchised almost 700,000 Black people and prevented 200,000 Confederates from voting. Most Confederate leaders were only jailed for short periods or not at all, and only one, Henry Wirz, was executed.
President Ulysses S. Grant declared martial law in nine counties of South Carolina to combat the Ku Klux Klan and arrested 500 to 600 people. In 1872, an amnesty act restored voting rights to most Confederates and only kept the top 300 or 400 disenfranchised. Many former slave owners fled to Brazil or Cuba.[44] Reconstruction ended in 1877, leading to the creation of a white supremacist dictatorship in the south.[45]
Westward expansion[edit | edit source]

The US passed the first of several Homestead Acts in 1862, establishing a homesteading system for westward expansion by settlers, resulting in 270 million acres of land being "claimed" and "settled." The Homestead Act would remain in effect until 1976, with additional provisions for homesteading in Alaska until 1986.[46][47]
The U.S. Army fought 943 battles and skirmishes against native peoples between 1865 and 1898. Settlers reduced the native population in California from 150,000 in 1845 to 18,000 in 1890.[48]
The Arapaho, Arikara, Assiniboine, Cheyenne, Crow, Gros Ventre, Mandan, and Sioux signed a treaty with the United States that reserved them to certain areas of land in exchange for the government paying them goods for ten years. It allowed the government to build roads and forts on their reservations. Despite the promise of goods, many natives were starving by 1853.
The Dakota people of Minnesota were starving by 1862 and began a revolt against the settlers. The Union crushed them and hanged 38 in the largest mass execution in U.S. history. John Chivington's volunteers killed 133 Cheyennes and Arapahos on the Sand Creek reservation. Colonel Patrick Connor massacred the Shoshone, Bannock, and Ute in Nevada and Utah. James Carleton fought against Cochise, the leader of the Apaches, in Arizona. He enlisted Kit Carson, who forced 8,000 Navajo people to march 300 miles to a concentration camp in the New Mexico desert. A quarter of them starved to death.[43]:136–9
In 1871, the Indian Appropriation Act unilaterally ended US recognition of indigenous nationhood and ended treaty-making with indigenous nations.[46][49]
Black Kettle (Mo'ôhtavetoo'o) of the Cheyenne survived the Sand Creek massacre and was forced into Indian Territory (now Oklahoma). The Army killed civilians in response to a guerrilla resistance. Black Kettle rode out unarmed to meet with George Custer, and Custer ordered his soldiers to shoot him even though he was flying a white flag.[43]:145–6 In 1874, the Army attacked Arapahos, Cheyennes, Comanches, and Kiowas in northern Texas and destroyed their supplies, forcing them onto reservations.[48]
In 1877, Chief Joseph (Hinmatóowyalahtq̓it) of the Nez Perce led 800 civilians out of Idaho and towards the Canadian border. They held out for four months while 2,000 soldiers pursued them. In 1878, Little Wolf (Ó'kôhómôxháahketa) and Dull Knife (Vóóhéhéve) led more than 3,000 Cheyenne out of Oklahoma and back to their homeland in Montana and Wyoming. The military caught them and put them on a reservation that included only part of their homeland.[43]:149–50
The Lakota and Cheyenne, led by Crazy Horse (Tȟašúŋke Witkó) and Sitting Bull (Tȟatȟáŋka Íyotake), killed Custer and defeated his entire Seventh Cavalry at Little Bighorn in 1876. A year later, the USA captured Crazy Horse and killed him when he tried to escape.[43]:151–2 In response, the Army began a ruthless campaign that ended with the Wounded Knee massacre of 1890, killing up to 300 unarmed and starving people. With the decline of the resistance, the number of forts dropped from 187 to 118.[48]
By 1879, dozens of native nations were confined to Indian Territory.[48] Geronimo (Goyaałé) of the Apache nation led a resistance war against the U.S. colonizers from 1850 to 1886.[31] He surrendered as a prisoner of war, and the Army sent him and his nation to Fort Sill in Indian Territory.[43]:150–51
With the General Allotment Act (or Dawes Act) of 1887, the US federal government authorized itself to unilaterally abrogate past treaties and divide tribal lands into individually owned parcels and "assign" allotments even to tribal members who refused to participate. Land would be assigned to individuals and then any land that the US deemed "surplus" was then taken and made available for settlers. Tribes generally opposed these transfers and litigation over them is ongoing.[46] In 1903, the US Supreme Court ruling of the Lone Wolf v. Hitchcock case decided that the US Congress could abrogate existing treaties with indigenous nations.[49]
The bulk of homesteading by settlers which occurred under the Homestead Acts (first enacted in 1862) took place from 1900 to 1930.[46] A 2024 research paper asserts that physical occupation by settlers provided a strategic attempt by the US to solidify indigenous land dispossession regardless of legal battles which may ensue following the "enormous and questionable" land transfers which occurred in the latter half of the nineteenth century. As the paper states, "Settler occupation disrupted tribal land uses, physical development, and infrastructure; it also created vested political interests in maintaining non-native settlement. These irreversible effects of settlement meant that even a future legal loss could only result in a payment to tribes, not the return of the land. [...] Thus, the federal state strategically allowed homesteading to continue in order to solidify the transfer of lands away from tribes. This strategy complemented the various political forces that wanted lands to remain in the hands of non-native settlers."[46] Despite these various maneuvers by the US settler colonial entity to entrench its grip over land, indigenous nations have continued their ongoing resistance to assert and preserve their sovereignty and resist land dispossession by a variety of methods.
Rise as global empire[edit | edit source]
Between the end of the Civil War and the invasion of Cuba in 1898, the United States expanded its army from 25,000 to almost 300,000 troops.[50]
The USA began an attack against the workers' movement following the Haymarket affair of 1886 and executed four anarchists, including two who had not been involved in the incident. Soon after, the police raided the houses of dissidents throughout Chicago and destroyed foreign language newspapers. Leaders of the Knights of Labor from multiple states were also arrested.
Starting in 1892, states began to declare martial law in order to suppress strikes. In 1903, 1,000 troops invaded the town of Cripple Creek, Colorado, arrested 600 strikers, and held them in prison for weeks without trial.[51]
Austronesian genocide[edit | edit source]
By the end of the 19th century, the United States would find itself as a predominant imperialist power in the world, invading countries such as the Philippines in a brutal war for control. J. Sakai recounts that, "U.S. Brig. Gen. James Bell, upon returning to the U.S. in 1901, said that his men had killed one out of every six Filipinos on the main island of Luzon (that would be some one million deaths just there). It is certain that at least 200,000 Filipinos died in the genocidal conquest. In Samar province, where the patriotic resistance to the U.S. invaders was extremely persistent, U.S. Gen. Jacob Smith ordered his troops to shoot every Filipino man, woman or child they could find 'over ten' (years of age)."[52]
The United States would expand beyond its continental borders with the colonialist acquisition of lands such as Hawaii, the Philippines, Guam, etc. With the attack on several of these territories by the Japanese empire, most notably at Pearl Harbor, President Roosevelt would downplay the colonialist additions to the American empire, such as the Philippines, and give more emphasis to the U.S. territory of Hawaii (which was not yet a state during this time). From Daniel Immerwahr's How To Hide An Empire: A History of the Greater United States:
"Why did Roosevelt demote the Philippines? We don't know, but it's not hard to guess. Roosevelt was trying to tell a clear story: Japan had attacked the United States. But he faced a problem. Were Japan's targets considered 'the United States'? Legally, yes, they were indisputably U.S. territory. But would the public see them that way? What if Roosevelt's audience didn't care that Japan had attacked the Philippines or Guam? Polls taken slightly before the attack show that few in the continental United States supported a military defense of those remote territories. Consider how similar events played out more recently. On August 7, 1998, al-Qaeda launched simultaneous attacks on U.S. embassies in Nairobi, Kenya, and Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Hundreds died (mostly Africans), and thousands were wounded. But though those embassies were outposts of the United States, there was little public sense that the country itself had been harmed. It would take another set of simultaneous attacks three years later, on New York City and Washington, D.C., to provoke an all-out war."[53]
While an embassy is different from a territory, as the book concedes, a similar logic was at play. And as Immerwahr says, Hawaii had more Americans and was closer to statehood. However, as Immerwahr explains, even Roosevelt felt the need to say that the "American island of Oahu" was attacked and that "very many American lives" had been lost. As Immerwahr says in explaining the nationalism implicit in Roosevelt's speech after Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor: "An American island, where American lives were lost - that was the point he was trying to make. If the Philippines was being rounded down to foreign, Hawai'i was being rounded up to 'American.'"[54]
First World War[edit | edit source]
See main article: First World War
The Socialist Party of America and Industrial Workers of the World opposed U.S. involvement in the First World War. In May 1918, the USA passed the Sedition Act, banning opposition to the war, and arrested New York SPA leader Benjamin Gitlow. Arizona, California, Montana, New York, and West Virginia passed laws banning left-wing activism. 27 farmers from South Dakota were sent to prison for petitioning against the war. Between 1917 and 1923, 33 states banned the use of red flags. In April 1918, 113 IWW members were convicted of over 10,000 offenses. Big Bill Haywood, who was sentenced to 20 years in prison, escaped to the Soviet Union. In addition to socialists, the United States suppressed pro-Irish publications that criticized the British Empire. Eugene Debs, who was imprisoned following an anti-war speech in June 1918, ran for president in 1920 and received over a million votes.[51]:161–70
Invasion of Russia[edit | edit source]
In December 1917, the United States authorized aid to anti-communist forces in southern Russia and the Caucasus.[55] At the end of the First World War, Woodrow Wilson sent 15,000 troops to western and eastern Russia to fight the Bolsheviks and limit the power of Japan. The USA occupied Vladivostok from August 1918 to April 1920.[56]
Palmer Raids[edit | edit source]
On January 2, 1920, federal agents led by A. Mitchell Palmer arrested over 4,000 dissidents in 33 cities across 23 states. Between 1917 and 1921, they deported 900 leftists. During this same period, the KKK and American Legion attacked leftists and trade unionists. Membership of the newly founded CPUSA dropped from 70,000 to 12,000, the SPA from 110,000 to 10,000, and the IWW from over 100,000 to under 10,000.[51]:169–72
Great Depression[edit | edit source]
See main article: Great Depression
Political repression weakened after 1923 but resumed following the economic collapse of 1929. Ben Boloff, a Russian immigrant and CPUSA member, was arrested in 1930 and sentenced to ten years in prison. Dirk De Jonge, leader of the Oregon Communist Party, was sentenced to seven years in prison in 1934. Patterson, New Jersey, banned all labour meetings and pro-worker protests.[51]:172–73
New Deal[edit | edit source]
Second World War[edit | edit source]
See main article: Second World War
Because the CPUSA initially stayed neutral in the Second World War, the United States arrested some of its members, including General Secretary Earl Browder. The Smith Act, passed in 1940, criminalized opposition to the U.S. government or war effort and was used against Trotskyists as well as Nazis. After the entry of the USSR into the war, the CPUSA changed its line, and Roosevelt pardoned Browder.[51]
In September 1940, the USA gave 50 old destroyers to the UK in exchange for taking control of British bases in the Americas. The bases were located in eight British colonies: Antigua, the Bahamas, Bermuda, Guiana, Jamaica, Newfoundland, and Saint Lucia, and Trinidad.[57]:223–4 Only nine of the destroyers actually worked. The USA also used the Lend-Lease program to give military aid to at least thirty countries, starting with the UK. China, Greece, Norway, and the Soviet Union later joined the program.[57]:235–7
The U.S. government forced 112,000 Japanese people living west of the Mississippi River into concentration camps in remote areas, giving them only two days to two weeks of warning. The camps were surrounded by barbed wire and guard towers and did not allow Japanese culture and language. The army confined and isolated strikers.[51]:173–75
After the defeat of Japan, the United States resurrected its former enemy to be used as a satellite state against socialism.[58] The USA became the most powerful empire in history and controlled both ends of Eurasia from Japan to the Britain.[59]
Cold War[edit | edit source]
Red Scare[edit | edit source]
See main article: Second Red Scare
Invasion of Korea[edit | edit source]
See main article: Fatherland Liberation War
Civil Rights movement and counterculture[edit | edit source]
By 1972, more than 500 municipalities had created political police squads to target radicals. Los Angeles had 167 political agents (1970), New York had 361 (1972), and Chicago had over 1,000 (1969). The New York police had files on 1.2 million political dissidents. The government actively spied on over 250,000 Statesians in the late 1960s and early 1970s. The FBI created a list of dissidents who would immediately be arrested or investigated in the event of a national emergency. This list included black nationalists, anarchists, and SDS members. The FBI sabotaged Marxist and black nationalist movements by planting information claiming their members were informants and infiltrated the SDS with agent provocateurs.[51]:187–88
Invasion of Vietnam[edit | edit source]
See main article: Vietnam War
War on Drugs[edit | edit source]
21st century[edit | edit source]
Internal crises[edit | edit source]
The US is embroiled in crisis as its middle class (the petit bourgeoisie) is increasingly impoverished.[60][61] This is due to the capitalist class deciding to offshore well-paying industrial jobs to lower-income countries,[62] as well expansionary monetary policy[63] which enriches the bourgeoisie through asset price inflation,[64] and deepens the crisis among the poor by weakening their purchasing power.
As a result of this ongoing crisis of capitalism, populist movements have risen to challenge the rule of "the elites." Occupy Wall Street was a popular movement against the financial elites in 2011. During the 2016 presidential election, the corporate-owned media attacked both the left-wing populist Bernie Sanders, as well as the right-wing populist Donald Trump. The Democratic Party's strategy to "elevate Trump" to make the Republican ticket look unsavory ended up backfiring and resulting in Trump's victory.
With the economic hardships of the 2020's, a growing number of Americans, often of younger ages, have begun to lose faith in capitalism.[65] While many of these discontent people have achieved consciousness in how many problems (constant wars, homelessness, global warming, etc.) in society can ultimately be traced back to capitalism, and have therefore aligned themselves with Marxist or otherwise socialist ideologies, there are many other malcontent people who have taken to the far-right. A trend that is present especially among the middle-class, there has been an increase in the popularity of populist and xenophobic groups, as well as an increasing fascistization of the Republican Party (one of the two ruling parties in the Statesian government).[66][67][68]
Mass shootings and racism[edit | edit source]
External losses[edit | edit source]
The American empire has been on the decline since the 21st century and possibly earlier. This is a slow process that will take years to complete however. One major factor of this decline is the United States' incapacity to respond to the People's Republic of China's Belt and Road Initiative, as more countries are moving towards the PRC and away from the USA for trade and loans.
If a superpower is measured through objective metrics such as scientific output (number of research papers per year),[69] exports & other trade metrics,[70] GDP,[71] then these metrics show the US is on the decline and has been for several years. In subjective metrics, a superpower's hegemony is measured in its soft power (putting compradors in power abroad to ensure collaboration), its cultural exports (media, entertainment, software), and generally its respect in the world. In these trends too we see the USA declining. They have been unable for some time to ensure compradors in other countries, and are becoming less respected in the eyes of the international community (see list below). The United States' cultural export is still high, but even at home people are increasingly moving away from domestic entertainment, though it remains to be seen if this will be a lasting trend.
Other losses that the American empire has had to endure in the 21st century include, in chronological order:
- The September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks completely blindsided intelligence and security agencies and showed a very big weakness in the imperial apparatus; it was not as invincible as it thought.
- A smear campaign originated in the US media in January 2019 when Venezuelan president Nicolás Maduro was reelected. US News organisations started reporting about a supposed humanitarian crisis in the country, owing to Maduro's allegedly "disastrous" policies. Two weeks later, president of the Assembly Juan Guaido proclaimed himself president of Venezuela as he contested Maduro's results under the guise that he was not allowed to run for office a third time as per the constitution. Juan Guaido, who enjoyed very little support at home and was a nobody, was nonetheless instantly recognized as the legitimate president of Venezuela by the United States and other countries and organisations (Canada, European Union...). An attempted color revolution then was planned in Venezuela, but went nowhere. Guaido was then slowly phased out of the public eye in the international community, though he continues to make noise in Venezuela. Maduro remains the president of Venezuela.
- In late 2019, Bolivian president Evo Morales was reelected at his position. The election results were immediately contested by the Organisation of American States, a US-led organisation for the purpose of securing imperialism on the American continent. While these allegations proved to be false, Morales went in exile for over six months while Jeanine Añez, a far-right comprador politician, was placed as an interim. After delaying new elections twice, Añez finally relented and took a huge blow when Luis Arce, from the same party as Morales was elected. Añez is now in prison awaiting trial on various charges including terrorism, sedition, and leading a coup against the government.
- In January 2020, the United States ordered the assassination of Iranian general Qasem Soleimani while on visit in Baghdad, Iraq. Later that month, Iran retaliated by launching an attack on a US military base in Iraq on a scale never seen before. The US did not retaliate against this attack in any way.
- In August 2021, the United States, after 20 years of occupation in Afghanistan to prevent the Taliban from controlling the state, did exactly the opposite and let the Taliban seize the Afghan state.
It is important to compare this list to earlier imperialist ventures of the United States who, for example, considered South America their "backyard" for most of the 20th century and successfully pulled-off coups and regime changes unimpeded in the region. While the Empire also took losses in the 20th century (the invasion of Vietnam, the Bay of Pigs invasion, etc.), it must only contextualised by looking at the general trends and how these losses are rapidly adding up.
Genocide of indigenous peoples[edit | edit source]
Over 90% of the indigenous population of North America was killed due to colonization, and some have estimated that no more than 2% of the pre-Columbian population survived and settlers killed over 18 million indigenous people. From 1641 to the late 18th century, legislation existed that rewarded settlers for killing indigenous peoples, with extra rewards for the scalps of boys.[10]
In 1871, Congress banned native nations from creating treaties and put them under the control of the federal government. Settlers and the Army killed tens of millions of buffalo, the economic base of the Plains, leaving only a few hundred alive by the 1880s.[43]:142
By the late 19th century, the native population had been decimated and the survivors were forced into concentration camps. Native children were forced into boarding schools and prevented from speaking their native languages.[72] Several hundred children died in these schools.[73] The federal government also set up an educational system to "kill the Indian and save the man" by eliminating Native American religious and cultural traditions.[74] These policies were deliberately designed to bring about the extinction of Native American people and their customs.[74] By 1900, only 190,000 Native Americans in the United States remained alive compared to five million at the beginning of colonization.[72]
Congress passed House Concurrent Resolution 108 in 1953, terminating tribes in California, Florida, New York, and Texas. Over 100 nations were terminated between 1953 and 1964 and 1.3 million acres of native land were privatized. In 1955, the Bureau of Indian Affairs created offices to relocate natives to cities to be assimilated. They relocated 750,000 natives into cities, where they often experienced severe poverty. By 2010, 78% of natives lived off of reservations.[31]
Many Native Americans are restricted to reservations in remote areas and live in poverty.[75] Overall, Native Americans are twice as likely to be in poverty.[76] They do not have access to the natural resources of the reservations, which are owned by corporations and mining companies. Indigenous peoples have the worst health and educational outcomes and the highest level of suicide[75] and indigenous women are 2.5 times more likely to be sexually assaulted.[76] During the COVID-19 pandemic, Native American communities were disproportionately affected, with the highest rate of infection and death.[72]
Government[edit | edit source]
See main article: Government of the United States of America



The US political system is a de facto plutocracy, a government entirely controlled by the wealthy.[77] The richest three Statesians have more money than the poorest 160 million combined.[78] Public support for the U.S. government is very low, with only 2% of Statesians believing the government almost always does what is right and only 19% believing it mostly does the right thing. 7% of Statesians have confidence in Congress, 23% have confidence in the presidency, and 25% have confidence in the Supreme Court.[79] Protests are illegal without permits from the government, and police often attack protestors with clubs and chemical weapons. It is illegal for protestors to wear helmets or gas masks to protect themselves.[80]
The US is also a de facto one-party state,[81] with aesthetical differences between its two main parties, the Republicans and the Democrats, but both parties follow common policies, especially abroad. The ruling capitalist oligarchy has two factions: the Democratic Party which is center-right[82] and is controlled by the monopolistic managerial bourgeoisie who seeks to maintain the stability of the imperialist system by being less reactionary on inconsequential social issues, and the Republican Party, which is more reactionary and backwards when it comes to social issues[83] and tends to pander to the petit bourgeoisie in their effort to deepen the exploitation of labor.
The election system further solidifies this duopoly with its "First Past the Post" system, resulting in citizens having to choose "the lesser of two evils." The two political parties stir up public debate around their small disagreements to create a facade of democracy, but bipartisan agreement reigns on questions of foreign policy (imperialism, war, attacking socialist countries) as well as domestic policies such as prioritizing funding for police repression over social programs such as free housing, higher education, healthcare, etc.
Given the presence of campaign donations and lobbying (legalized corruption), the billionaires who buy off politicians to serve their will are sometimes referred to as the "donor class".[84]
In his autobiographical account of taking on monopolistic corporations as president, President Theodore Roosevelt recounted:
…we had come to the stage where for our people what was needed was a real democracy; and of all forms of tyranny the least attractive and the most vulgar is the tyranny of mere wealth, the tyranny of a plutocracy.[85]
Despite various anti-monopoly countermeasures (anti-trust legislation, etc.) the underlying system of capitalism and the desire to accumulate more surplus value and increase profitability continues to result in monopolistic formations within the US economy. These monopolies are more powerful than the public state apparatus, and by most approximations can be considered the same object. According to fascist dictator Mussolini, the merging of corporate power and state power is the definition of fascism.[86]
Foreign policy[edit | edit source]

The United States has long seen itself as a very special nation, playing a uniquely noble role on the world stage. While other nations are said to be guided by vulgar self-interest, the United States is supposedly different; the primary goal of American foreign policy is, according to the State Department’s website, to “promote and demonstrate democratic values and advance a free, peaceful, and prosperous world.” Despite these imperialist lies, the United States has been at war for more than 90% of its existence[87] and has over 800 military bases in foreign countries, compared to 30 for the rest of the world combined.[88]
Foreign aid and human rights[edit | edit source]
The US has a horrific foreign aid record. It seems that American aid is quite a good predictor of human rights abuses, and that this trend goes back decades; according to a 1981 study in the journal Comparative Politics, US aid is “clearly distributed disproportionately to countries with repressive governments… this distribution represented a pattern and not merely one or a few isolated cases.” Indeed, it is quite easy to find examples of the United States supporting vicious repressive regimes (such as Pinochet's Chile, the Shah of Iran, and the military junta of El Salvador).
Similarly, a 1984 study in the Journal of Peace Research looked at human rights and US aid under Nixon, Ford, and Carter. The authors found that “under Presidents Nixon and Ford foreign assistance was directly related to levels of human rights violations, i.e. more aid flowed to regimes with higher levels of violation, while under President Carter no clear statistical pattern emerged.” They therefore conclude that “the Carter administration did not implement a policy of human rights which actually guided the disposition of military and economic assistance.” In other words, the US attitude towards human rights seems to vary from outright hostility (under more conservative administrations) to mere indifference (under more liberal ones).[89]
More recent studies have painted a similarly bleak picture. A 2008 book by Rhonda Callaway and Elizabeth Matthews found that “both United States economic and military aid have detrimental effects on security rights of the citizens in recipient states.” They note that these results “provide support for those critical of the US foreign assistance program.” The most recent research has continued to back up these conclusions. A 2016 study in the Quarterly Journal of Political Science sampled 150 countries from 1972 to 2008, finding that “US aid harms political rights, fosters other forms of state repression (measured along multiple dimensions), and strengthens authoritarian governance. [...] These findings counter the publicly stated objectives of the US government to foster political liberalization abroad via bilateral economic assistance.”
All-in-all, it seems that aid from the United States has a deleterious impact on the human rights situation in recipient nations. It provides military and economic aid to repressive regimes, arming and propping up some of the most vicious dictators on the planet, all in service of its own interests.
Alan MacLeod of MintPress News has compiled a thread of times the US military has deliberately bombed hospitals.[90]
War on Terror[edit | edit source]
Lest we think that the harm of US foreign policy stops at providing aid to dictators, the United States has also carried out a great deal of violence all on its own. To demonstrate the enormous death toll of US military intervention and invasion, let's take a look at the post-9/11 "War on Terror," including the invasions of Iraq and Afghanistan (among others).
According to a 2019 report from Brown University's Costs of War project, "between 770,000 and 801,000 people have died" in what the report refers to as "America's post-9/11 wars." This tally does not include so-called "indirect deaths," such as those resulting from displacement and the destruction of crucial infrastructure (e.g. water and sanitation systems). In a 2019 article for the Hill, David Vine (Professor of Anthropology at American University) writes that "total deaths during the post-2001 U.S. wars in Afghanistan, Iraq, Syria, Pakistan and Yemen [are] likely to reach 3.1 million or more — around 200 times the number of U.S. dead."[91] Others have come to similar conclusions. According to a 2018 report from the Intercept:
In addition to those killed by direct acts [of] violence, the number of indirect deaths — those resulting from disease, displacement, and the loss of critical infrastructure — is believed to be several times higher, running into the millions.[92]
These death tolls are backed up by earlier research. A 2009 article from the MIT Center for International Studies, which looked only at Iraq, found that "we have, at present, between 800,000 and 1.3 million 'excess deaths' in this war as we approach its six-year anniversary." Keep in mind that this is only one of the invaded countries, and that this article was authored in 2009 (more than a decade ago). The current death tolls, when factoring in all nations (as well as the decade of subsequent warfare), are likely many times higher.
The United States government has engaged in a concerted effort to hide the civilian cost of its Middle Eastern wars. According to a 2017 report from the New York Times, the actual rate of civilian causalities inflicted by coalition forces in the Middle East is "more than 31 times that acknowledged by the coalition. It is at such a distance from official claims that, in terms of civilian deaths, this may be the least transparent war in recent American history."
In point of fact, US forces often kill more people than the terrorists they are supposedly there to fight; a 2019 article in the New York Times reports that "more civilians are being killed by Afghan government and American forces than by the Taliban and other insurgents, according to a [United Nations] report on Wednesday."[93] This is not even mentioning the US drone program, which was detailed in a 2013 report from the Intercept. To make matters worse, civilian casualties from US wars have been increasing dramatically since Donald Trump took office, according to a 2018 article from the Washington Post.
While it must be noted that the United States did not personally kill all of the millions of people mentioned above, it still bears a heavy burden for these deaths, having initiated the invasions, and started the entire conflict. In the same way that we hold Hitler responsible for the deaths of WWII (since he was the one who started it), so too should we hold the United States responsible for the deaths listed above. For more information on the civilian cost of US intervention, I recommend The Deaths of Others: The Fate of Civilians in America's Wars, a study authored by John Tirman, director of the MIT Center for International Studies.
Regime change[edit | edit source]
The United States has a long history of overthrowing governments it doesn't like, typically then replacing them with brutal dictatorships. There are many, many examples of this, ranging from Jacobo Arbenz in Guatemala, to Mohammad Mosaddegh in Iran (a coup for which the CIA actually admitted responsibility in 2013).
Chile[edit | edit source]
In 1973 the United States helped to overthrow the elected socialist government of Salvador Allende in Chile, replacing it with the right-wing dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet. Peter Kornbluh, the director of the National Security Archive's Chile Documentation Project, said the following of Chile:
“To see on a piece of paper, for example, the president of the United States ordering the C.I.A. to preemptively overthrow a democratically elected president in Chile is stunning,” Mr. Kornbluh said. “The importance of having these documents in the museum is for the new generations of Chileans to actually see them.”[94]
As if this were not enough, in a 2014 interview with the Atlantic, Jack Devine (a former CIA agent who was in Chile at the time of the coup) confirmed that the Nixon administration was directly instructing the CIA to support the coup. According to declassified documents, Nixon had previously ordered Henry Kissinger to "make the economy scream," in an effort to rally support for the right-wing forces. The United States also attempted to prevent Allende from being inaugurated after his election, and provided support for state-terrorist campaigns after the coup. Now that the US role has been established, let's look at what Pinochet did once in power.
To begin with, Pinochet killed, tortured, and "disappeared" tens of thousands of people. According to a 2011 article from the BBC, the "total of recognized victims" numbers over 40,000, including more than 3,000 who were killed or forcibly disappeared. The rest were kidnapped, tortured, exiled, or some combination of the above. Pinochet was one of the most vicious dictators in the history of Latin America, and the United States played a direct role in propping up his regime.[95]
In addition, Pinochet introduced hard-line neoliberal reforms, which did immense damage to Chile's economy. A good study on this was published in 1990 in the journal Critical Sociology. The authors note that growth rates under Pinochet were remarkably unimpressive:
The Pinochet model produced growth rates well below the Chilean average established over the 1950-72 period. The average yearly GDP rate of growth in the latter period was 3.9 percent, while the Pinochet regime averaged 1.4 percent over the 1974-83 period... overall growth throughout the 1980s has been far from miraculous: GDP per capita grew at a 1.2 percent average rate between 1980 and 1989, below the 1.7 percent average yearly rate for 1950-72.[96]
In addition, the authors charge Pinochet with "creating a great deal of poverty," noting that unemployment "rose dramatically after the coup," while real wages fell. At the same time, social expenditures were reduced, and "infectious diseases readily associated with poverty, overcrowding, poor hygiene, and inadequate sanitation underwent explosive growth." This assessment is echoed by a study in the International Development Planning Review, which found that "the radical neoliberal policies and structural adjustment of the 1970s and 1980s during the Pinochet regime had severe negative effects on the poor and middle class."[97] The poverty rate itself increased dramatically; according to a report from the North American Congress on Latin America:
The number of poor Chileans doubled during the Pinochet regime. By 1989, 44% of Chileans lived in poverty.[98]
In addition, it seems that Pinochet's privatizations also helped to create enormous corruption. According to a study in the Journal of Economic History, "firms were sold underpriced to politically connected buyers." This had predictable consequences:
These newly private firms benefited financially from the Pinochet regime. Once democracy arrived, they formed connections with the new government, financed political campaigns, and were more likely to appear in the Panama Papers. These findings reveal how dictatorships can influence young democracies using privatization reforms.[99]
Neocolonialism[edit | edit source]
The United States has begun the process of looting Ukraine by forcing the country into enormous debt in exchange for weapons. The USA is once again applying the same lend-lease program it used to facilitate the transfer of the British Empire to Statesian hands in the aftermath of World War II.[100]
Domestic policy[edit | edit source]
Education[edit | edit source]
The U.S. education system promotes anti-communism and racism and denies or apologizes for U.S. war crimes. By law, teachers are not allowed to go against Western capitalist ideology.[101] Due to extreme inequality in educational funding, about 130 million Statesians, or 50% of the adult population, have low literacy and are unable to read above 6th grade level.[102]
Poverty[edit | edit source]
According to a study from the Brookings Institute:
53 million Americans between the ages of 18 to 64—accounting for 44% of all workers—qualify as “low-wage.” Their median hourly wages are $10.22, and median annual earnings are about $18,000.[103]
Almost half of the American workforce is officially "low-wage," and that's only if we use an extremely low standard (below minimum wage, in some states). This is especially horrifying when we remember how many deaths can be directly linked to poverty and deprivation in the United States. According to a study from Columbia University:
Overall, 4.5% of U.S. deaths were found to be attributable to poverty... the number of deaths the researchers calculated as attributable to low education (245,000) is comparable to the number caused by heart attacks (192,898), which was the leading cause of U.S. deaths in 2000. The number of deaths attributable to racial segregation (176,000) is comparable to the number from cerebrovascular disease (167,661), the third leading cause of death in 2000, and the number attributable to low social support (162,000) compares to deaths from lung cancer (155,521).[104]
Hundreds of thousands of people are dying every year because of poverty, deprivation, and lack of access to social services. Almost half of people 55 or older have no retirement savings.[105]
Healthcare[edit | edit source]
The U.S. healthcare system is among the most dysfunctional institutions imaginable, with the highest costs in the world, and some of the worst outcomes of any advanced country.[106] That being said, there are still those who deny the necessity of completely overhauling the system, and as such, it is useful to take some time and go over the essential facts of the matter. As always, all sources will be listed at the end.
The United States ranks at the very bottom of the developed world in terms of preventable deaths. Annual deaths could be reduced by 101,000 if the U.S. had a health care system as good as other comparable countries.[107]
Health outcomes[edit | edit source]
The USA ranks near the bottom of the developed world in most essential health outcomes. A 2020 paper from the American College of Physicians (published in the Annals of Internal Medicine) reports that "despite higher spending, the United States generally has less favorable outcomes than other countries." Let's take infant mortality, for example. According to a 2016 study from the American Economic Association:
The United States has higher infant mortality than peer countries... The US disadvantage persists after adjusting for potential differential reporting of births near the threshold of viability.
The ACP paper confirms that the United States' poor infant mortality ranking persists "even after adjustment for reporting differences." According to the AEA, this subpar performance "is driven by poor birth outcomes among lower socioeconomic status individuals." As if this wasn't bad enough, maternal mortality is also shockingly high in the USA. According to an article from NPR (reporting on data from the CDC):
More American women are dying of pregnancy-related complications than any other developed country. Only in the U.S. has the rate of women who die been rising.[108]
To make matters worse, there is evidence that the official statistics actually leave out a great number of deaths, meaning that the actual rate is probably much higher. According to an article from ProPublica, "the new rate, while capturing just how poorly the U.S. ranks among other countries, is actually a significant underestimate of the problem."[109] This only makes the issue even more horrifying. In addition, healthcare-amenable mortality is generally higher in the United States than in peer countries. According to the American College of Physicians:
The United States has a higher mortality rate for medical conditions for which there are recognized health care interventions than Germany, the Netherlands, Japan, France, and Australia.
A 2017 study in the Lancet looked at global amendable mortality, finding that the United States ranked 35th in the world in overall performance. In a press release following the publication of the paper, Dr. Christopher Murray (the study's lead author) said the following:
What we have found about health care access and quality is disturbing. Having a strong economy does not guarantee good health care. Having great medical technology doesn’t either. We know this because people are not getting the care that should be expected for diseases with established treatment. [...] America’s ranking is an embarrassment, especially considering the US spends more than $9,000 per person on health care annually, more than any other country. Anyone with a stake in the current health care debate, including elected officials at the federal, state, and local levels, should take a look at where the US is falling short.[110]
While many people acclaim the US health system for its advanced technology, it is clear that this does no good if people cannot actually access the care they need. All-in-all, it clear that outcomes in the American healthcare system are extremely subpar, especially when one takes into account the ludicrously high cost. On that note, let's discuss cost and expenditures.
Cost and expenditures[edit | edit source]
The United States spends more per-capita on healthcare than any other country on Earth. According to the aforementioned study from the American College of Physicians:
The United States spends far more per capita on health care than other wealthy countries, and spending is increasing at an unsustainable rate. [...] The pricing of health care goods and services is substantially higher in the United States than in other developed nations. A 2003 analysis of OECD data showed that health care utilization in the United States did not exceed that of other countries, and price was the key driver of spending differences.
Much of this excessive cost is due to the enormous inefficiency and bureaucracy of the Statesian system. There is a massive amount of administrative spending in the US, which is due primarily to the fragmented multi-payer nature of the healthcare system. According to the ACP:
In large part owing to its pluralistic financing system, the United States spends more on administration of health care than peer countries. One study estimated that in 2012, the United States spent $471 billion on billing and insurance-related costs—$375 billion (80%) more than in a “simplified financing system,” such as Canada's single-payer model. Another study concluded that administrative costs were 31% of total U.S. health care expenditures, nearly double those of Canada.
These findings are validated by a study in the Journal of the American Medical Association, which said the following:
The fragmented financing system is one of the principal explanations for the high cost of medical care in the United States. A careful consolidation of financing into some form of single-payer system is probably the only feasible solution.[111]
Another study from the same journal says the following:
The United States spent approximately twice as much as other high-income countries on medical care, yet utilization rates in the United States were largely similar to those in other nations. Prices of labor and goods, including pharmaceuticals, and administrative costs appeared to be the major drivers of the difference in overall cost between the United States and other high-income countries.
According to a 2020 study in the Lancet (conducted at Yale Medical School), a single-payer system would save an enormous amount of money and (more importantly) lives:
Taking into account both the costs of coverage expansion and the savings that would be achieved through the Medicare for All Act, we calculate that a single-payer, universal health-care system is likely to lead to a 13% savings in national health-care expenditure, equivalent to more than US $450 billion annually (based on the value of the US$ in 2017). [...] Furthermore, we estimate that ensuring health-care access for all Americans would save more than 68 000 lives and 1.73 million life-years every year compared with the status quo.[112]
Claims that a single-payer system would be unaffordable are entirely baseless, and contradicted by the overwhelming mass of evidence. A 2020 meta-analysis in PLOS Medicine found "a high degree of analytic consensus for the fiscal feasibility of a single-payer approach in the US." As they put it:
There is near-consensus in these analyses that single-payer would reduce health expenditures while providing high-quality insurance to all US residents. To achieve net savings, single-payer plans rely on simplified billing and negotiated drug price reductions, as well as global budgets to control spending growth over time. Replacing private insurers with a public system is expected to achieve lower net healthcare costs.[113]
Access to care and lack of insurance[edit | edit source]
To make matters worse, a large chunk of the Statesian population is uninsured, and many are forced to go without the care that they need. According to the ACP:
The United States is the only wealthy industrialized nation without universal health coverage, a crucial component to ensuring quality health care for all without financial burden that causes delay or avoidance of necessary medical care... nearly 30 million remain uninsured, millions more are underinsured, and the number of uninsured persons is expected to grow.
The high rate of uninsured people is extremely troubling, especially seeing as a lack of insurance is associated with increased risk of mortality. A 2009 study in the American Journal of Public Health said the following on the matter:
Uninsurance is associated with mortality. [...] Lack of health insurance is associated with as many as 44 789 deaths per year in the United States, more than those caused by kidney disease.
A 2017 study in the Annals of Internal Medicine validated these findings, saying:
The evidence strengthens confidence in the Institute of Medicine's conclusion that health insurance saves lives: The odds of dying among the insured relative to the uninsured is 0.71 to 0.97.[114]
The high costs of US medical care cause a great deal of financial strain for patients. According to a 2019 study in the Journal of General Internal Medicine (carried out by the American Cancer Society), "medical financial hardship is common among adults in the USA, with nearly 140 million adults reporting hardship in the past year. Among those aged 18–64 years, more than half report problems with medical bills or medical debt; stress or worry; or forgoing or delaying health care due to cost." A 2019 Gallup poll found that 25% of Americans say that they or a family member have put off treatment for a "serious illness" in the past year because of cost, with a further 8% saying they or a family member has put off treatment for a "less serious illness" in the past year.[115] Overall, there is strong evidence that the United States' lack of universal healthcare causes tens of thousands of deaths every year, and financial ruin for many more.

Incarceration[edit | edit source]
According to the Prison Policy Initiative (PPI), not only does the U.S. have the highest incarceration rate in the world; every single U.S. state incarcerates more people per capita than virtually any country on earth. States like New York and Massachusetts "appear progressive in their incarceration rates compared to states like Louisiana, but compared to the rest of the world, every U.S. state relies too heavily on prisons and jails to respond to crime." PPI adds in their 2021 report that "incarceration has become the nation’s default response to crime, with 70 percent of convictions resulting in confinement — far more than other developed nations with comparable crime rates."[116]
Beyond the millions of people in the U.S. who are incarcerated, tens of millions more are dealing with the "collateral consequences" of punishment. Many cannot vote or get a driver's license, face barriers to employment, and are prohibited from living with the families who want them back because they have a criminal record.[117]
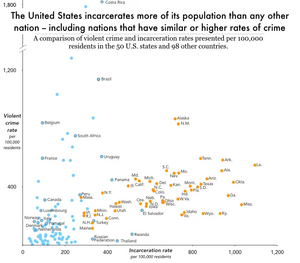
The U.S. doesn’t have one singular criminal justice system. Instead, it has thousands of federal, state, local, and tribal systems. Together, these systems hold almost 2 million people (as of 2022) in 1,566 state prisons, 102 federal prisons, 2,850 local jails, 1,510 juvenile correctional facilities, 186 immigration detention facilities, and 82 Indian country jails, as well as in military prisons, civil commitment centers, state psychiatric hospitals, and prisons in the U.S. territories.[118]
The PPI notes that "local jails often receive short shrift in larger discussions about criminal justice, but they play a critical role as 'incarceration's front door' and have a far greater impact than the daily population suggests. [...] In a typical year, about 600,000 people enter prison gates, but people go to jail over 10 million times each year. Jail churn is particularly high because most people in jails have not been convicted. Some have just been arrested and will make bail within hours or days, while many others are too poor to make bail and remain behind bars until their trial." The PPI further notes that at least 1 in 4 people who go to jail will be arrested again within the same year, often those dealing with poverty, mental illness, and substance use disorders, whose problems only worsen with incarceration.[118]
See also[edit | edit source]
Further reading[edit | edit source]
History[edit | edit source]
- Endless Holocausts: Mass Death in the History of the United States Empire
- Killing Hope: U.S. Military and CIA Interventions since World War II
Communist movement[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ “To begin with, the U.S. definitely was founded as a settler colonial state as well as a capitalist state.”
Albert Bender (2022-05-12). "What’s at stake in the settler colonial debate" Communist Party USA. Archived from the original on 2022-05-13. Retrieved 2025-08-22. - ↑ "United States' share of global gross domestic product (GDP) adjusted for purchasing power parity (PPP) from 2019 to 2029". Statista. Archived from the original on 2025-07-16. Retrieved 2025-08-22.
- ↑ Sara Flounders (2023-01). "Congressional chaos – deals and trades" Workers World. Archived from the original on 2023-01-10. Retrieved 2023-01-22.
- ↑ "Population, total - United States". World Bank Group. Archived from the original on 2025-07-26. Retrieved 2025-08-22.
- ↑ Roy Walmsley. "World Prison Population List, twelfth edition" World Prison Brief. Archived from the original on 2025-08-22. Retrieved 2025-08-22.
- ↑ Michael Cetewayo Tabor. Capitalism Plus Dope Equals Genocide. [PDF] [MIA]
- ↑ Fred Hampton (1969). It’s a Class Struggle, Godamnit!. [MIA]
- ↑ "Minju Joson on Final Doom of U.S.". KCNAWatch. Archived from the original on 2021-05-28. Retrieved 2025-08-22.
- ↑ Noah Kirsch (2017-11-09). "The 3 Richest Americans Hold More Wealth Than Bottom 50% Of The Country, Study Finds" Forbes. Archived from the original on 2023-01-21. Retrieved 2023-01-23.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Austin Murphy (2000). The Triumph of Evil: 'Introduction' (pp. 22–24, 34). [PDF] European Press Academic Publishing. ISBN 8883980026 [Anna's Archive]
- ↑ Patrick Martin (2023-05-19). "US wars since 2001 have killed 4.5 million people" WSWS. Archived from the original on 2023-05-19.
- ↑ “The spelling Amerikkka has sometimes been used, especially in graffiti, to suggest that the Ku Klux Klan has great influence over how the US is governed. The usage is both imaginative and striking, but to many Americans it is very far from pleasing.”
"FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE". Encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on August 13th, 2025. Retrieved September 9th, 2025. - ↑ Ruhollah Khomeini (1979-11-05). "America the Great Satan" Emam.com. Archived from the original on 2016-05-22. Retrieved 2021-12-29.
- ↑ “The port of entry for America’s first peoples was the Bering Sea region. They could, and likely did, walk across from Siberia to Alaska when expanding continental ice sheets dropped sea levels worldwide and Beringia surfaced. Crossing its Mammoth Steppe, blanketed by parkland and grazed by mammoth, horse, and bison, was possible anytime between 27,000 and 10,000 years ago. The recent genetic evidence of a possible Beringian standstill suggests the first peoples may have been relatively isolated in this region for much of that time.”
David J. Meltzer (2009). First peoples in a New World: colonizing Ice Age America (p. 329). University of California Press. - ↑ “The new data suggest that the initial founders of the Americas emerged from a single source ancestral population that evolved in isolation, likely in Beringia. This scenario is consistent with the unique pattern of diversity from autosomal locus D9S1120 of a private allele in high frequency and ubiquitous in the Americas. The finding that humans were present at the Yana Rhinoceros Horn Site dated to 30,000 ybp suggests that the isolation in Beringia might have lasted up to 15,000 years. Following this isolation, the initial founders of the Americas began rapidly populating the New World from North to South America.”
Erika Tamm, et al (2007). Beringian Standstill and spread of Native American founders. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000829 [HUB] - ↑ “In any case, it appears from the evidence at Monte Verde that the first Americans were here by at least 12,500 BP and possibly earlier still. Certainly by 11,500 BP, Clovis Paleoindians were widespread, possibly representing a second migratory pulse to the New World, one that may have spread across the continent in less than a thousand years.”
David J. Meltzer (2009). First peoples in a New World: colonizing Ice Age America (p. 329). University of California Press. - ↑ “Establishing when central Asian and Native American haplogroup lineages last shared a common ancestor has proven to be difficult. Current coalescent estimates based on variation in extant mtDNA lineages set the event at 25 to 20 ka or less than 20 ka, after the last glacial maximum (LGM), and estimates based on Y- chromosome variability suggest that divergence occurred after 22.5 ka, possibly as late as 20 to 15 ka.”
Goebel, Waters & O’Rourke (2008). The Late Pleistocene dispersal of Modern Humans in the Americas. doi: 10.1126/science.1153569 [HUB] - ↑ “New analyses of haplogroup subclades help to resolve when modern humans subsequently spread from Beringia to the rest of the Americas. Three subclades of mtDNA subhaplogroup C1 are widely distributed among North, Central, and South Americans but absent in Asian populations, which suggests that they evolved after the central Asian–Native American split, as the first Americans were dispersing from Beringia. The estimated date of coalescence for these subclades is 16.6 to 11.2 ka, which suggests that the colonization of the Americas south of the continental ice sheets may have occurred some time during the late-glacial period, thousands of years after the initial splitting of Asian and Native American lineages.”
Goebel, Waters & O’Rourke (2008). The Late Pleistocene dispersal of Modern Humans in the Americas.. doi: 10.1126/science.1153569 [HUB] - ↑ “Domestication of plants took place around the globe in seven locales during approximately the same period, around 8500 BC. Three of the seven were in the Americas, all based on corn: the Valley of Mexico and Central America (Mesoamerica); the South-Central Andes in South America; and eastern North America. [...] During this time, many of the same human societies began domesticating animals. Only in the American continents was the parallel domestication of animals eschewed in favor of game management, a kind of animal husbandry different from that developed in Africa and Asia. In these seven areas, agriculture based "civilized" societies developed in symbiosis with hunting, fishing, and gathering peoples on their peripheries, gradually enveloping many of the latter into the realms of their civilizations, except for those in regions inhospitable to agriculture.”
Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An indigenous peoples' history of the United States (pp. 15-16). [PDF] ISBN 978-0-8070-0040-3 [LG] [Anna's Archive] - ↑ “Corn, being a summer crop, can tolerate no more than twenty to thirty days without water and even less time in high temperatures. Many of the areas where corn was the staple were arid or semiarid, so its cultivation required the design and construction of complex irrigation systems-in place at least two thousand years be fore Europeans knew the Americas existed. The proliferation of agriculture and cultigens could not have occurred without centuries of cultural and commercial interchange among the peoples of North, Central, and South America, whose traders carried seeds as well as other goods and cultural practices.”
Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An indigenous peoples' history of the United States (p. 16). ISBN 978-0-8070-0040-3 [LG] - ↑ “The total population of the hemisphere was about one hundred million at the end of the fifteenth century, with about two-fifths in North America, including Mexico. Central Mexico alone supported some thirty million people. At the same time, the population of Europe as far east as the Ural Mountains was around fifty million.”
Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An indigenous peoples' history of the United States (p. 17). ISBN 978-0-8070-0040-3 [LG] - ↑ “Most were agriculturalists living in settled communities, some were hunters and gatherers.”
Dennis Etler (2021-03-29). "U.S. treatment of Native Americans is a gross human rights violation" CGTN. Archived from the original on 2021-03-29. Retrieved 2025-08-22. - ↑ 23.0 23.1 J. Sakai (1983). Settlers: The Mythology of the White Proletariat: 'The Heart of Whiteness'. [PDF] ISBN 9781629630762 [Anna's Archive]
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 J. Sakai (1983). Settlers: The Mythology of the White Proletariat: 'Struggles & Alliances'. ISBN 9781629630762
- ↑ Howard Zinn (1980). A People's History of the United States: 'A Kind of Revolution' (pp. 89–90). [PDF] HarperCollins. ISBN 0060194480 [Anna's Archive]
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 26.3 Albert Szymanski (1984). Human Rights in the Soviet Union: 'The Land of the Free' (pp. 152–156). [PDF] London: Zed Books Ltd. ISBN 0862320186 [LG]
- ↑ Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States: 'Bloody Footprints' (pp. 72–78). ReVisioning American History. [PDF] Boston: Beacon Press Books.
- ↑ Chad Pearson (2023-07-12). "Sober Up Liberals: The U.S. Constitution Sucks" MR Online. Archived from the original on 2023-07-12.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 29.3 29.4 David Vine (2020). The United States of War: 'Why Are So Many Places Named Fort?'. Oakland: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520972070 [LG]
- ↑ 30.0 30.1 30.2 30.3 Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States: 'The Birth of a Nation' (pp. 81–87). ReVisioning American History. [PDF] Boston: Beacon Press Books.
- ↑ 31.0 31.1 31.2 Nick Estes, et al. (2021). Red Nation Rising: 'Anti-Indianism' (pp. 22–27). [PDF]
- ↑ 32.0 32.1 David Vine (2020). The United States of War: 'Invading Your Neighbors'. Oakland: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520972070 [LG]
- ↑ Domenico Losurdo (2011). Liberalism: A Counter-History: 'Liberalism and Racial Slavery: A Unique Twin Birth' (pp. 52–57). [PDF] Verso. ISBN 9781844676934 [LG]
- ↑ Nancy Isenberg (2016). White trash: the 400-year untold history of class in America (p. 92). Viking. ISBN 9780670785971 [LG]
- ↑ Nancy Isenberg (2016). White trash: the 400-year untold history of class in America (p. 110). Viking. ISBN 9780670785971 [LG]
- ↑ 36.0 36.1 36.2 Howard Zinn (1980). A People's History of the United States: 'As Long as Grass Grows or Water Runs' (pp. 124–129). [PDF]
- ↑ Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States: 'Andrew Jackson's White Republic' (pp. 112–113). ReVisioning American History. [PDF] Boston: Beacon Press Books.
- ↑ Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States: 'Sea to Shining Sea' (pp. 123–132). ReVisioning American History. [PDF] Boston: Beacon Press Books.
- ↑ 39.0 39.1 Al Mackey (2017-04-18).: "The Extent of Slave Ownership in the United States in 1860". Student of the American Civil War. Retrieved 2025-09-10.
- ↑ 40.0 40.1 Domenico Losurdo (2011). Liberalism: A Counter-History: 'Were Eighteenth and Nineteenth Century England and America Liberal?' (p. 102). [PDF] Verso. ISBN 9781844676934 [LG]
- ↑ 41.0 41.1 Domenico Losurdo (2011). Liberalism: A Counter-History: 'Crisis of the English and American Models'. [PDF] Verso. ISBN 9781844676934 [LG]
- ↑ Howard Zinn (1980). A People's History of the United States: 'Slavery without Submission, Emancipation without Freedom' (pp. 165–166). [PDF] HarperCollins. ISBN 0060194480
- ↑ 43.0 43.1 43.2 43.3 43.4 43.5 43.6 Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States: '"Indian Country"'. [PDF] Boston, Massachusetts: Beacon Press. ISBN 9780807000403
- ↑ Albert Szymanski (1984). Human Rights in the Soviet Union: 'The Land of the Free' (pp. 160–161). [PDF] London: Zed Books Ltd. ISBN 0862320186 [LG]
- ↑ Domenico Losurdo (2011). Liberalism: A Counter-History: 'The West and the Barbarians' (p. 222). [PDF] Verso. ISBN 9781844676934 [LG]
- ↑ 46.0 46.1 46.2 46.3 46.4 Douglas W. Allen and Bryan Leonard (2024). Late Homesteading: Native Land Dispossession through Strategic Occupation, vol. 119. American Political Science Review. doi: 10.1017/S0003055423001466 [HUB]
- ↑ "About the Homestead Act". National Park Service.
- ↑ 48.0 48.1 48.2 48.3 David Vine (2020). The United States of War: 'The Permanent Indian Frontier' (pp. 157–66). Oakland: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520972070 [LG]
- ↑ 49.0 49.1 Mark Hirsch (2014). "1871: The End of Indian Treaty-Making" American Indian Magazine.
- ↑ Roxanne Dunbar-Ortiz (2014). An Indigenous Peoples' History of the United States: 'US Triumphalism and Peacetime Colonialism' (p. 164). ReVisioning American History. [PDF] Boston: Beacon Press Books.
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 51.2 51.3 51.4 51.5 51.6 Albert Szymanski (1984). Human Rights in the Soviet Union: 'The Land of the Free'. [PDF] London: Zed Books Ltd. ISBN 0862320186 [LG]
- ↑ Sakai 2014, p. 111
- ↑ Daniel Immerwahr (2019). How to hide an empire: a history of the greater United States (p. 6). Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 9780374172145 [LG]
- ↑ Daniel Immerwahr (2019). How to hide an empire: a history of the greater United States (p. 7). Farrar, Straus and Giroux. ISBN 9780374172145 [LG]
- ↑ David S. Foglesong (1995). America's Secret War against Bolshevism: 'The British Connection' (p. 76). University of North Carolina Press. [Anna's Archive]
- ↑ David Vine (2020). The United States of War: 'The Military Opens Doors' (p. 218). Oakland: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520972070 [LG]
- ↑ 57.0 57.1 David Vine (2020). The United States of War: 'Reopening the Frontier'. Oakland: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520972070 [LG]
- ↑ Stephen Gowans (2018). Patriots, Traitors and Empires: The Story of Korea’s Struggle for Freedom: 'Suppressing a Worldwide Movement for Liberty' (pp. 105–107). [PDF] Montreal: Baraka Books. ISBN 9781771861427 [LG]
- ↑ David Vine (2020). The United States of War: 'Normalizing Occupation' (p. 301). Oakland: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520972070 [LG]
- ↑ The State of America’s Middle Class in Eight Charts PBS Frontline by Jason M. Breslow and Evan Wexler on July 9th, 2013
- ↑ Deindustrialization is Killing America
- ↑ A New Assessment of the Role of Offshoring in the Decline in US Manufacturing Employment on Naked Capitalism by Yves Smith on Aug 16, 2019
- ↑ US’ excessive money-printing prompts de-dollarization on Global Times by Ma Jingjing published on April 6th, 2021
- ↑ The Cantillon Effect: Because of Inflation, We’re Financing the Financiers on Fee.org by Jessica Schultz on Oct 28, 2018
- ↑ Laura Wronski (2021-6-11). "Axios|Momentive Poll: Capitalism and Socialism" SurveyMoney. Retrieved 2022-6-11.
- ↑ Marc-André Argentino, Blyth Crawford, Florence Keen, Hannah Rose (2021). Far-From-Gone:The Evolutionof Extremism in the First 100 Daysof the Biden Administration: '3. The 6 January Insurrectionists: Narratives and Motivations; Discontent with Presidential Election Results' (pp. 63-72). [PDF] London: International Centre for the Study of Radicalisation.
- ↑ Alison Durkee (2021-4-5). "More Than Half Of Republicans Believe Voter Fraud Claims And Most Still Support Trump, Poll Finds" Forbes. Retrieved 2022-6-10.
- ↑ Dr. Robert A. Pape (2021). UNDERSTANDING AMERICAN DOMESTIC TERRORISM: 'STUDY 1:WHO ARE THE INSURRECTIONISTS AND WHERE DID THEY COME FROM; MANY BUSINESS OWNERS/WHITECOLLAR' (pp. 6-9). [PDF] The University of Chicago: Chicago Project on Security and Threats.
- ↑ https://ncses.nsf.gov/pubs/nsb20206/
- ↑ https://www.statista.com/statistics/264623/leading-export-countries-worldwide/archive: https://archive.ph/dKloW
- ↑ https://www.indexmundi.com/g/r.aspx?t=10&v=65 - GDP adapted to purchasing power parity (PPP)
- ↑ 72.0 72.1 72.2 Dennis Etler (2021-03-29). "U.S. treatment of Native Americans is a gross human rights violation" CGTN. Archived from the original on 2022-02-19. Retrieved 2022-07-01.
- ↑ "U.S. govt finds burial sites at 53 Native American boarding schools" (2022-05-13). CGTN. Archived from the original on 2022-05-13. Retrieved 2022-07-01.
- ↑ 74.0 74.1 Jeffrey Ostler (2015). Empire’s Twin: U.S. Anti-Imperialism from the Founding Era to the Age of Terrorism: '“Native Americans against Empire and Colonial Rule,”' (p. 53). Ithaca, New York: Cornell University Press.
- ↑ 75.0 75.1 "Native Americans: The invisible minority in the U.S." (2021-05-19). CGTN. Archived from the original on 2021-05-20. Retrieved 2022-07-01.
- ↑ 76.0 76.1 Xin Ping (2022-01-06). "Surviving in oblivion: Who cast a miserable shadow over the Native Americans?" CGTN. Archived from the original on 2022-01-07. Retrieved 2022-07-01.
- ↑ TOM MCKAY (2016-4-16). "Princeton Concludes What Kind of Government America Really Has, and It's Not a Democracy" MIC. Retrieved 2022-8-30.
- ↑ Tom Kertscher (2019-07-03). "'The wealthiest three families now own more wealth than the bottom half of the country.'" PolitiFact. Archived from the original on 2022-01-26. Retrieved 2022-05-01.
- ↑ Ben Norton (2022-07-30). "Polls show almost no one trusts US media, after decades of war propaganda and lies" Multipolarista. Archived from the original on 2022-08-06. Retrieved 2022-08-07.
- ↑ Austin Murphy (2000). The Triumph of Evil: 'A Detailed Autopsy of the Collapse of the Superior System in the Divided Germany' (p. 141). [PDF] Fucecchio: European Press Academic Publishing. ISBN 8883980026
- ↑ “'Yes, we have one party here. But so does America. Except, with typical extravagance, they have two of them!'”
Mark J. Green (1982). Winning Back America. Bantam Books. ISBN 9780553226300 - ↑ Like it or Not, the Democratic Party is a Right-Wing Party
- ↑ How did the Republican Party become so conservative?
- ↑ Bob Herbert (1998-07-19). "The Donor Class" The New York Times.
- ↑ "Roosevelt, Theodore. 1913. An Autobiography: XII. The Big Stick and the Square Deal".
- ↑ "Fascism should more appropriately be called corporatism because it is a merger of state and corporate power." --Benito Mussolini. (from Encyclopedia Italiana, Giovanni Gentile, editor)
- ↑ Sabir Shah (2020-01-09). "The US Has Been at war 225 out of 243 years since 1776" The News. Retrieved 2022-03-11.
- ↑ David Vine. "Where in the World Is the U.S. Military?" Politico. Retrieved 2022-03-11.
- ↑ Michael Stohl, David Carleton, Steven E. Johnson (1984). Human Rights and U.S. Foreign Assistance From Nixon to Carter. [PDF] doi: 10.1177/002234338402100302 [HUB]
- ↑ @AlanRMacLeod on Twitter: "A short history of the United States deliberately bombing hospitals [Thread]" (Archived)
- ↑ The Hill | Reckoning With the Costs of War: It's Time to Take Responsibility
- ↑ The Intercept | The Assassination Complex: The Drone Papers
- ↑ The New York Times | U.S. and Afghan Forces Killed More Civilians Than Taliban Did, Report Finds
- ↑ The New York Times (2017) Documenting U.S. Role in Democracy’s Fall and Dictator’s Rise in Chile
- ↑ BBC | Chile Recognizes 9,800 More Victims of Pinochet's Rule
- ↑ Critical Sociology | The Chilean "Economic Miracle": An Empirical Critique
- ↑ International Development Planning Review | Land of Miracles? A Critical Analysis of Poverty Reduction Strategies in Chile, 1975-2005
- ↑ NACLA | In Pursuit of "Growth With Equity": The Limits of Chile's Free-Market Social Reforms
- ↑ Journal of Economic History | The Privatization Origins of Political Corporations: Evidence from the Pinochet Regime
- ↑ “for fiscal years 2022 and 2023, the President may authorize the United States Government to lend or lease defense articles to the Government of Ukraine or to governments of Eastern European countries impacted by the Russian Federation's invasion of Ukraine to help bolster those countries' defense capabilities and protect their civilian populations from potential invasion or ongoing aggression by the armed forces of the Government of the Russian Federation.”
United States Congress (2022-05-09). "Ukraine Democracy Defense Lend-Lease Act of 2022" Congress.gov. Retrieved 2023-01-25. - ↑ "Anti-Communism in the American Classroom" (2022-06-28). Red Patriot. Archived from the original on 2022-06-28. Retrieved 2022-08-27.
- ↑ Emily Schmidt (2022-03-16). "Reading the Numbers: 130 Million American Adults Have Low Literacy Skills, But Funding Differs Drastically By State" APM Research Lab. Retrieved 2023-03-28.
- ↑ Brookings Institute | Low-Wage Work is More Prevalent Than You Think, and There Aren't Enough Good Jobs to Go Around
- ↑ Columbia University | How Many US Deaths Are Caused by Poverty, Lack of Education, and Other Social Factors?
- ↑ "Retirement Security: Most Households Approaching Retirement Have Low Savings, an Update" (2019-05-26). Gao. Archived from the original on 2022-04-14. Retrieved 2022-07-01.
- ↑ Roosa Tikkanen, Melinda K. Abrams (2020-01-30). "U.S. Health Care from a Global Perspective, 2019: Higher Spending, Worse Outcomes?" The Commonwealth Fund. Archived from the original on 2022-04-24. Retrieved 2022-05-01.
- ↑ Reuters | US Worst in Preventable Death Ranking of Industrialized Countries
- ↑ NPR | U.S. Has the Worst Rate of Maternal Deaths in the Developed World
- ↑ ProPublica | The New U.S. Maternal Mortality Rate Fails to Capture Many Deaths
- ↑ The Lancet | Healthcare Access and Quality Index Based on Mortality from Causes Amenable to Personal Health Care
- ↑ Journal of the American Medical Association | Health Care Spending in the United States and Other High-Income Countries
- ↑ The Lancet | Improving the Prognosis of Health Care in the USA
- ↑ PLOS Medicine | Projected Costs of Single-Payer Healthcare Financing in the United States: A Systematic Review of Economic Analyses
- ↑ Annals of Internal Medicine | The Relationship of Health Insurance and Mortality: Is Lack of Insurance Deadly?
- ↑ Gallup Poll | More Americans Delaying Medical Treatment Due to Cost
- ↑ Emily Widra and Tiana Herring. September 2021. “States of Incarceration: The Global Context 2021.” Prison Policy Initiative. Archived 2022-08-26.
- ↑ “Collateral Consequences.” Prison Policy Initiative.
- ↑ 118.0 118.1 Wendy Sawyer and Peter Wagner. "Mass Incarceration: The Whole Pie 2022." Prison Policy Initiative. March 14, 2022. Archived 2022-08-31.
Notes[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Inhabitants of the USA are sometimes called simply "Americans," which can cause confusion because there are many other countries in the Americas. The terms "Statesian" and "United Statesian" are based on words in other languages, notably including the Spanish estadounidense, that refer specifically to the USA. The term "US-American" has precedent in the German term US-amerikanisch, though that term is not universally accepted in German.
- ↑ Respectively in Anishinaabe, Kanien'kéha and Lakota. All mean "Turtle Island".
- ↑ Persian: شيطان بزرگ


