More languages
More actions
| Democratic People's Republic of Korea 조선민주주의인민공화국 | |
|---|---|
Anthem: 애국가 Aegukka ("The Patriotic Song") | |
 Territories of Korea presently occupied by the United States are shown in light green. | |
| Capital and largest city | Pyongyang |
| Dominant mode of production | Socialism |
| Government | Unitary Juche people's republic |
• General Secretary of the Workers' Party | Kim Jong-un |
• President of the Presidium | Choe Ryong-hae |
• First Vice Chairman of the State Affairs Commission | Choe Ryong-hae |
• Premier of the Cabinet | Kim Tok-hun |
• Chairman of the Supreme People's Assembly | Pak Thae-song |
| History | |
• Start of partial US occupation | 8 September 1945 |
• Founding of the DPRK | 9 September 1948 |
| Area | |
• Total | 120,540 km² |
| Population | |
• 2020 estimate | 25,845,400 (77,048,000 including Koreans under neocolonial occupation) |
| Labour | |
• Unemployment rate | 2.8%[1] |
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
• Total | $16.3 billion[1] |
• Per capita | $639.6[1] |
| Exports | 2020 estimate |
• Value | $1.1 billion[1] |
| Imports | 2020 estimate |
• Value | $3.46 billion[1] |
| Currency | Korean People's Won (KPW) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +850 |
| ISO 3166 code | KP |
| Internet TLD | .kp |
The Democratic People's Republic of Korea (DPRK; Korean: 조선민주주의인민공화국, Chosŏn Minjujuŭi Inmin Konghwaguk), also known as People's Korea and incorrectly referred to as North Korea by bourgeois media, is a socialist country in East Asia. Korea is one nation, but the southern half of Korea is occupied by the US-backed anti-communist Republic of Korea, also known as Capitalist Korea. DPRK's capital city is Pyongyang.
The DPRK is led by the Workers' Party of Korea (WPK) and the Democratic Front for the Reunification of Korea. According to its constitution, the DPRK is an "independent socialist state", guided by the ideology of Juche which is a derivative of Marxism–Leninism originally codified by Kim Il-Sung.[2]
While the DPRK distanced itself from USSR's ideological leadership in the 1960s, some authors still consider it a Marxist–Leninist socialist state.[3]
In 2017, DPRK's Minister of Foreign affairs, Ri Yong Ho, stated at the United Nations General Assembly that "The U.S. had put sanctions against our country from the very first day of its foundation, and the over 70-year long history of the DPRK can be said in a sense a history of struggle, persevering along the road of self-development under the harshest sanctions in the world." Ri also stated that the essence of the situation of the Korean peninsula is a confrontation between the DPRK and the US, where the DPRK tries to defend its national dignity and sovereignty against the hostile policy and nuclear threats of the US, and points out that it was the US who first introduced nuclear weapons to the Korean peninsula. Ri stated that "The very reason the DPRK had to possess nuclear weapons is because of the U.S., and it had to strengthen and develop its nuclear force onto the current level to cope with the U.S. [...] Our national nuclear force is, to all intents and purposes, a war deterrent for putting an end to nuclear threat of the U.S. and for preventing its military invasion".[4]
Minister Ri also clarified DPRK's nuclear policy by quoting Kim Jong-un as saying that international justice can only be achieved when the anti-imperialist independent countries are strong enough, and that possession of nuclear deterrence by the DPRK is a righteous self-defensive measure taken as an ultimate option, pursuant to this principle, and further clarified that the DPRK "do[es] not have any intention at all to use or threaten to use nuclear weapons against the countries that do not join in the U.S. military actions against the DPRK."[4]
DPRK representative Kim Song stated at the 2021 UN General Assembly, "If the U.S. wants to see the Korean war, the most prolonged and long-lasting war in the world, come to an end, and if it is really desirous of peace and reconciliation on the Korean peninsula, it should take the first step towards giving up its hostile policy against the DPRK by stopping permanently the joint military exercises and the deployment of all kinds of strategic weapons which are levelled at the DPRK in and around the Korean peninsula."[5]
In 1965 Che Guevara said that the DPRK "was a model to which revolutionary Cuba should aspire".[6][7]
History[edit | edit source]
Early history and Japanese occupation[edit | edit source]
See main article: Korea
Division of Korea[edit | edit source]
Following the defeat of Japan and the end of the Second World War, Japan lost control of its colonies, including what was formerly the Korean Empire. As a result of negotiations between the Soviet Union and the United States, the Korean Peninsula was divided into occupation zones along the 38th Parallel North. Although there was an attempt at establishing the People's Republic of Korea, the nascent state was outlawed by U.S. forces. In the northern zone, the Soviets allowed Koreans to govern themselves, and a system of people's committees developed into a full provisional government.[8] Originally, the division of Korea was not intended to be an actual dividing line nor a border to split the country, but simply meant as designated areas where Soviet and U.S. forces would be temporarily assisting Korea as it stabilized after liberation from Japan and formed an independent Korean state. However, the U.S. sought to prolong Korea's division in order to form Korea into a state subordinate to U.S. interests, pushing for separate elections in the south despite opposition from the masses and despite attempts among the Korean populace to form a unified nation.[9]
Under conditions in which the U.S. imperialists were occupying south Korea and foreign and domestic reactionaries were gathered together in the occupied zone and opposing the founding of a unified independent Korean state, the policy of constructing a powerful democratic base in the northern half of Korea was adopted. The formation of a broad united front to rally the masses of people in all walks of life was the first question to be solved. Thus, early in 1946, a united front was formed of different parties and groupings, democratic forces of various social strata.[9]
Democratic and economic reforms in north[edit | edit source]
On the basis of the people's committees, the Provisional People's Committee of North Korea (Korean: 북조선림시인민위원회; Hanja: 北朝鮮臨時人民委員會) was formed on February 8 of 1946.[10][11] The leaders of the Korean resistance agreed to make Kim Il-sung the new leader of Korea, and he became president of the provisional government on 8 February 1946.[8]
In March of 1946, the 20-Point Platform (Korean: 20개조정강) for realizing Korea's anti-imperialist, anti-feudal democratic reforms was announced, including such items as thorough liquidation of all remnants of Japanese imperialist rule, waging an implacable struggle against reactionary and anti-democratic elements, carrying out land reform, nationalizing important industries, direct and equal suffrage, and the institution of free medical care for the poor, among other points.[12][13][14] On November 3, 1946, the first democratic election in the history of Korea was held in the north, and the People's Committee of North Korea (Korean: 북조선인민위원회; Hanja: 北朝鮮人民委員會), which was no longer provisional, was created in February of 1947, functioning as the organ of the dictatorship of the proletariat.[9]
The new government redistributed land from landlords and Japanese officials to peasants, nationalized large companies, shortened the work day to eight hours (seven for dangerous occupations), banned child labor, established social security and paid vacations, and enforced gender equality.[8]
As a result of land reform, feudal landownership, which was the social and economic base of the undemocratic reactionary forces, was done away with in the rural villages of the north. At the time, the matter of land reform was of great concern, due to a large percentage of Korea's population being peasant farmers, many engaged in sharecropping and being exploited in feudal relations as well as by Japanese colonialism.[14] In addition to land reform, the nationalization of key industries was undertaken, wiping out the political and economic bases of imperialists and domestic reactionaries and promoting the general rehabilitation and development of the national economy in the wake of the Japanese colonial period. The Provisional People's Committee implemented the Law on the Nationalization of Important Industries in August 1946. Under it, all large factories, mines, power stations, railway transport, telecommunication facilities, banks and commercial and cultural establishments were made the property of the Korean people. Factories and other enterprises which had been owned by pro-Japanese elements were confiscated without compensation and became the property of the people, to be used for their own benefit rather than for the extraction of Korea's wealth for imperial Japan's benefit. Democratic reforms, beginning with the Labor Law and the Law on the Equality of the Sexes, were enforced, putting an end to unlimited exploitation of the working class and liberating women from feudal subordination.[9]
Author Kim Byong Sik describes the changes in social, economic, and class relations in the north during this time, noting that as a result of the reforms following liberation, capitalist economic relations were reduced to a small scale in limited areas of the economy, while socialist economic relations became dominant in all areas of the economy:
Radical changes were effected in social, economic and class relations in the northern half of the Republic, a people’s democratic system was established and a powerful revolutionary base for an all-Korea victory was founded. In other words, all colonial and semi-feudal components were removed, and socialist economic relations, based on state and cooperative economy, came to occupy a leading position in all areas of the people’s economy, with capitalist relations confined to only small commodity production by private farms and handicraft enterprises in urban areas and to some commerce and small-scale industry. Concerning class relations, landlords, comprador capitalists, pro-Japanese elements and traitors were eliminated and working people became the masters of the country, the leading role of the working class increased and the worker-peasant alliance was consolidated. In this way, the balance of forces developed decisively in favor of the revolution.[9]
As the above author later notes, by 1947 state-controlled industry accounted for 80.2% of industrial output, and private industry for only 19.8% of industrial output. In addition, mining was completely state-controlled. Industrial production jumped 70 per cent, and labor productivity 51 per cent, in fiscal 1947 in comparison with the previous year. 1947 was the first year in which an economic plan was implemented. 1948 also saw a successfully implemented economic plan.
Founding of Korean People's Army[edit | edit source]
The Provisional People's Committee trained national cadres and prepared a revolutionary armed force to defend the people's democratic system, establishing the Korean People's Army on February 8, 1948.
Reactionary regime forms in south[edit | edit source]
Throughout this time, reactionary and imperialist forces in the U.S.-occupied portion of Korea had been seeking ways to prolong Korea's division in order to form a state which was subordinate to U.S. interests and in which anti-communist forces would remain in power. As democratic reforms were taking place in the north and the base of power was being removed from feudal landlords, Japanese collaborators, and other reactionary forces in the north, the reactionaries were moving south, some of them forming right-wing anti-communist paramilitary groups such as the Northwest Youth League (Korean: 서북청년회), who later committed atrocities against ordinary citizens in the name of the southern regime, and many of whom went on to become police and members of the local government.[15] Among the imperialists' plans was the plan to hold a separate election in the south, which was opposed by many of the Korean masses.
In this context, Kim Il Sung submitted the draft Provisional Constitution of Korea for discussion by all the people north and south and he proposed the election of an all-Korea supreme legislative assembly through a general, direct, equal and secret ballot. At the same time he called on the political parties and social organizations of south Korea to hold a south-north joint conference to oppose the separate election and to discuss ways and means of saving the nation. In response to this call, a joint conference was held in Pyongyang on April 20, 1948, with attendants representing a range of political orientations. A resolution was adopted to boycott the separate elections. At the time of the controversial separate election held in May 1948, more than 140 polling stations and a number of police stations were destroyed and burned. The U.S.-backed southern regime resorted to fascist terror to suppress the opposition. After proceeding with the elections, the regime formed as a puppet regime consisting of collaborators, landlords, and subservient capitalists.[9]
Founding of the DPRK[edit | edit source]
The Democratic People's Republic of Korea was founded on 9 September 1948. The illegitimate government of the occupied portion of Korea (often referred to as South Korea, or Republic of Korea) had been established earlier the same year, when dictator Syngman Rhee, who was referred to as an "imported expatriate" and "extreme rightist" in a CIA document of the time,[16] came to power due to U.S. influence despite many Koreans opposing the holding of separate elections in the south. In DPRK, Kim Il-Sung became the first Premier of the DPRK, a position he would hold until 1972. DPRK soon requested for U.S. and Soviet troops to leave Korea. The Soviets left on 25 September, but the U.S. occupiers refused to leave.[17]
The Occupied Korean government was hostile to socialism and to the DPRK. Even though Western media accuses the DPRK of initiating the Fatherland Liberation War (often referred to as the Korean War), numerous acts of violence were perpetrated by the illegitimate southern government that were tantamount to war—namely the massacre on Jeju Island that targeted communists. The people of Jeju had been protesting the formation of a separate southern regime and the holding of separate elections in the south, but were eventually violently suppressed by the US-backed southern regime. The death toll was composed of thousands of civilians, many of whom were not affiliated with the Workers' Party of South Korea or communism at all. In addition, the Yeosu-Suncheon rebellion of 1948 was a rebellion among soldiers in the south who began guerrilla-style fights against the military, as the rebelling soldiers refused to participate in the brutal suppression of the Jeju uprising. Suppression of this rebellion by the southern regime led to hundreds of civilian deaths.[18] Furthermore, paramilitary groups from the Republic of Korea illegally crossed the border into the DPRK on multiple occasions.
In DPRK, a two-year economic plan for 1949-1950 was adopted on the basis of the previous plans of 1947 and 1948, with plans for furthering the socialist transformation of the economy as well as the continued correction of distortions in the economy which were the result of the colonial period. However, this plan had to be suspended due to the escalation of the war in 1950.[9]
Fatherland Liberation War[edit | edit source]

See main article: Fatherland Liberation War
During the Fatherland Liberation War, DPRK forces almost repelled the illegal occupation army; however, the United Nations and the United States sent extra forces to fight DPRK troops. Western forces pushed DPRK forces all the way to the border of the newly formed People's Republic of China, which had itself repelled reactionary Kuomintang forces from the mainland. PRC forces intervened to protect Korean sovereignty, repelling Western troops once more as part of the War to Resist the U.S. Aggression and Aid Korea campaign. The majority of the fighting during the rest of the Fatherland Liberation War took place near the 38th Parallel North, with only minor border changes occurring after a ceasefire was signed. The DPRK technically remains at war with its illegitimate southern neighbour as no truce has been signed between the two.
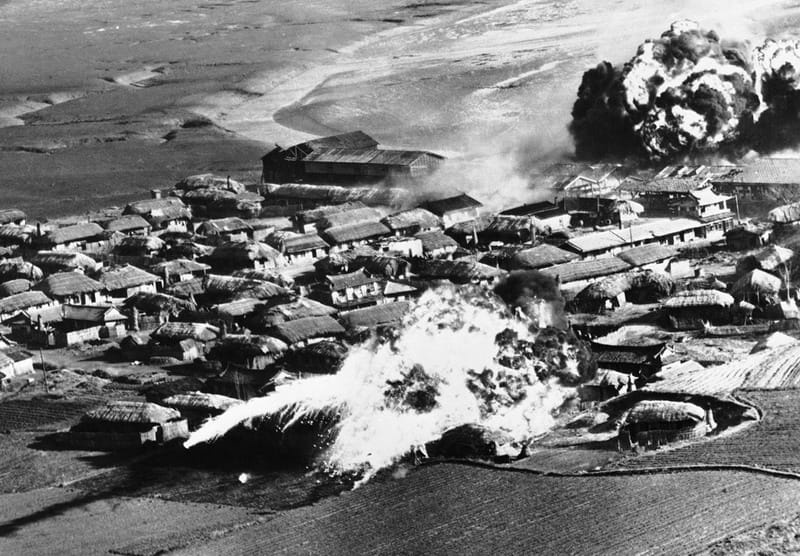

Virtually all of the major cities in DPRK were severely damaged and hundreds of thousands of civilians killed by U.S. saturation bombing during the war. The tonnage of bombs dropped on the north was about the same as the total dropped by the U.S. against Japan during the Second World War. By 1952, the bombing was so complete that the U.S. Air Force had run out of targets. According to an AP News article, the U.S. dropped 635,000 tons of bombs on Korea during the war, most of it in the north, including 32,500 tons of napalm. In the present day, DPRK citizens continue to find unexploded ordinance and be injured by old bombs that were dropped by the US and UN forces, and have to evacuate areas and send in bomb squads where such bombs are found, as well as educate citizens, especially children, about the explosives.[19]
US sanctions on DPRK began in conjunction with the 1950 escalation of the war, with the US imposing an export ban on DPRK and forbidding financial transactions by or on behalf of DPRK. This began with U.S. President Harry S. Truman ordering naval blockade of Korean coast and imposing a total trade embargo against the DPRK in June of 1950. This was followed by the Trading with the Enemy Act in December 1950, to terminate all US economic contacts with the DPRK and freezing its assets. Truman also imposed an embargo against China, freezing Chinese assets in US at this time. In 1952, an embargo was imposed on all exports of industrial equipment and raw materials.[20]
Post-Fatherland Liberation War[edit | edit source]
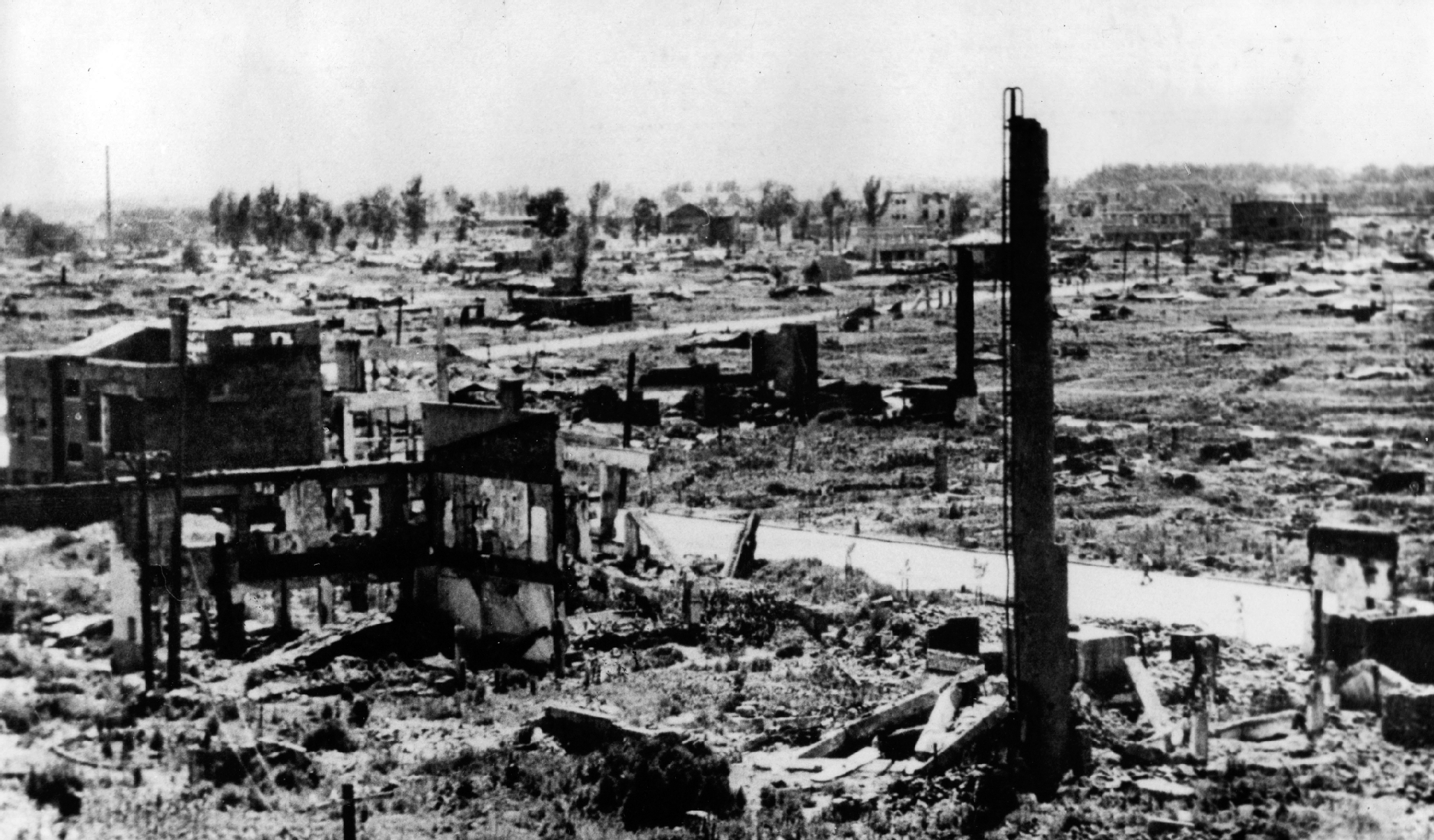


Following the war, the people of DPRK were faced with the task of converting the armistice into a lasting peace, rebuilding the destroyed economy as soon as possible, improving the people's living conditions, and strengthening the country politically, economically, and militarily as the base of the Korean revolution and converting it into a powerful material force for the reunification of Korea.
The sixth plenum of the Central Committee of the Korean Workers' Party was called on August 5, 1953 to consider these pressing tasks. A decision was made to promote postwar rehabilitation and development of the people's economy in three basic stages, according to a proposal by Kim II Sung. The first stage would be a period of six months to a year in which preparations and adjustments would be made for general rehabilitation. In the second stage, a Three Year Plan would be carried out to recover the economy to pre-war levels. In the third stage, a Five Year Plan would be worked out to complete the first stage of industrialization, to lay the foundation for socialist industrialization.[9] Author Kim Han Gil writes that the general task of laying the foundations of socialism was largely defined in two aspects: production relations and productive forces. In the first aspect, the task was to transform all the relations of production along socialist lines. In the second aspect the task was to establish the solid foundation of an independent national economy while laying the foundation for industrialization.[21]
A focus was placed on developing heavy industry as a priority, while simultaneously developing light industry and agriculture. Heavy industry was needed in order to maintain an independent national economy and to make the development of light industry and agriculture possible, while light industry and agriculture were necessary for improving the living conditions of the people, impoverished by the wartime destruction.[9]
After nine months, the first stage of the three-stage recovery and development plan was successfully carried out. During this stage, several thousands of temporary houses were built in the towns and countryside and rehabilitation and construction in the countryside were started. Prices were lowered, cities began being rebuilt, factories were restored and repaired, and various industrial and agricultural enterprises went into operation, beginning with the Kangson Steel Works, Songjin Steel Works, Sunghori Cement Factory and Komusan Cement Factory, with various enterprises in light industry such as Nampo Glass Factory and Pyongyang Spinning Mill being prepared for full-scale operation.[9]
Following this preparatory stage, the Party proposed a Three Year Plan for 1954-1956, the second stage of the recovery and development plan adopted after the war's end. The Three Year Plan aimed to restore the economy to pre-war levels, further raise the peoples' living standards, as well as correct the distortions of the economy resulting from the Japanese colonial period, and to continue developing heavy industry to lay a basis for socialist industrialization. The plan aimed to increase industrial production beyond 1949 levels, to produce grain at 1949 levels (the highest recorded previous grain production), further mechanization of agriculture, and to double the output of foodstuff and daily necessities compared to 1949 levels, as well as a five-fold increase in the production of cotton fabrics and a three-fold increase in production of rubber shoes. According to Modern Korea, these aims were met in two years and four months, and by the end of January 1955, industrial production of state-run and cooperative enterprises exceeded the level set for 1956 in the Three Year Plan. Additionally, on the basis of results accomplished during an experimental period in 1953-1954, the trend toward agricultural cooperatives was phased into a mass movement in 1956, and by the end of February 1956, 14,651 agricultural cooperatives were organized, comprising 65.2% of total farm households and accounting for 62.1% of the total land under cultivation.[9]
After the armistice agreement, the US continued to prohibit all US economic contacts with DPRK in line with its general strategic controls against socialist countries.[20]
In 1988, South Korean and the US eased isolation of People's Korea by opening bilateral dialogue and allowing limited export of goods to the North for humanitarian purposes. Some travel restrictions were also lifted on a case-by-case basis. However, in that same year, DPRK was added to the U.S. State Department State Sponsors of Terrorism list.[22][23]
A unified team under the name Korea (KOR) competed in 1991 World Table Tennis Championships and FIFA World Youth Championship with athletes from both North and South Korea. In 1991, the team used the Unification Flag and the anthem "Arirang".
In 1992, the ROK announced suspension of the "Team Spirit" military training exercise normally conducted each year in conjunction with US forces stationed in South Korea. On January 22, US Undersecretary of State Arnold Kanter and Korean Workers' Party Secretary Kim Yong Sun held the first of a series of bilateral talks, focusing on the future of US–People's Korean relations and unification issues on the peninsula. However, following difficulties regarding the Joint Nuclear Control Committee, the US and ROK decided to conduct the Team Spirit exercise after all, and DPRK refused to negotiate bilateral nuclear inspections unless the Team Spirit exercise would be cancelled. By 1993, the US and South Korea confirmed that Team Spirit would proceed as planned, and DPRK ended negotiations.[20]
In July 1993, President Bill Clinton, during a visit to the South Korean side of the DMZ, warned that the United States would respond to DPRK use of nuclear weapons with massive conventional or nuclear retaliation. In later January/early February of 1994, US officials in Washington let it be known they were considering transferring Patriot missiles to South Korea as a defensive move. In Seoul, a Defense Ministry official called for the resumption of Team Spirit unless the North agreed to full nuclear inspections. The US warned DPRK that unless it would allow inspections, it would bring a sanctions resolution before the UN Security Council.[20]
In July 1994, Kim Il-sung passed away.
Arduous March[edit | edit source]
The period of economic crisis, floods, and famine in DPRK known as the Arduous March (Korean: 고난의 행군) lasted from approximately 1994 to 1998. Factors such as the overthrow of the Soviet Union and worldwide economic shifts in its wake, unprecedented natural disasters, and economic sanctions imposed on DPRK compounded at this time, contributing to the severity of the crisis. The thriving north Korean economy, which had exceeded south Korea's in production of electricity, coal, fertilizer, machine tools and steel even into the 1980s, was thrown into turmoil as it faced these factors in the 1990s.[24][25]
The imperialist United States and its allies took advantage of this period, attempting to make the situation more deadly and more economically devastating via economic sanctions, to push DPRK into total collapse. It was at this time that the "military-first" policy of Songun (Korean: 선군; Hanja: 先軍) was initiated under the leadership of Kim Jong Il, in response to the constant threat of military aggression from the United States aimed at DPRK's destruction. The policy came of the determination that maintaining a strong military was essential for the defense of the country and the protection of its socialist system, and that the military was the backbone of the revolution and that it was necessary to give military affairs priority in order to proceed with socialist construction.[26][27][28]
During this time, DPRK deployed the People's Army to major construction sites as well as rural areas for flood recovery and food production, in order to overcome the Arduous March in each region and sector. Notably, DPRK was able to construct important infrastructure such as the Anbyon Youth Power Station at this time, erected by the service personnel of the People's Army, battling against harsh environmental conditions in order to construct the power station. Rather than yielding to the economic pressures imposed by the U.S. in combination with the environmental disasters and the worldwide economic upheavals, DPRK endured the hardships, defended the socialist system, and built structures of lasting value.[29][30][27] The end of the Arduous March was declared in October 2000.[31]
6.15 Declaration and ROK's "Sunshine Policy"[edit | edit source]

The South Korean policy towards DPRK from the late 1990s to mid 2000s is known as the "Sunshine Policy" and is primarily associated with the Kim Dae-jung administration (1998–2003) and the Roh Moo-hyun administration (2003–2008). During this time, a notable attitude of reconciliation between north and south Korea was expressed by south Korean leadership.
On June 13-15, 2000 leaders of the ROK and DPRK meet for the first time since the war. South Korean president Kim Dae-jung and DPRK leader Kim Jong-il signed an agreement calling for family reunions, economic cooperation, social and cultural exchanges and follow-up governmental contacts between the North and South to ease tensions.[20] This is known as the June 15th North–South Joint Declaration or the 6.15 Inter-Korean Joint Declaration.
The date "6.15" would subsequently become a popular reference among the Korean reunification movement. Additionally, the phrase uri minjok kkiri (Hangeul: 우리 민족끼리), which can be translated as "among our nation" or "between our people" can be found in the joint document signed by Kim Dae Jung and Kim Jong Il at the 6.15 talks. The phrase implies the idea of solving the questions of unification and peace on the Korean peninsula without the influence or meddling of outside powers. The numbers "6.15" and the phrase "uri minjok kkiri" can frequently be seen and heard in Korean unification-oriented media, publications, and activism.
2000s–present[edit | edit source]

In 2002, President Bush's State of the Union address singled out Iran, Iraq and DPRK as the so-called "Axis of Evil" for their supposed pursuit of weapons of mass destruction.[20]
According to Nodutdol, in 2018, 3,968 people in the DPRK, who were mostly children under the age of 5, died as a result of shortages and delays to UN aid programs caused by sanctions.[22]
Talks between General secretary Kim Jong-un and former U.S. President Donald Trump began on June of 2019 to discuss disarmament and potential reunification with the Republic of Korea.
In January 2020, South Korean President Moon Jae-in expressed interest in developing tourism to People's Korea, but the US ambassador Harry Harris blocked this effort. Harris claimed that "independent" tourism plans would have to undergo US consultation. He emphasized that the items inside South Korean tourists' luggage could violate sanctions, demonstrating the extent of US interference in inter-Korean affairs.[22]
Yoon Suk Yeol's presidency in the Republic of Korea (2022-present) marks a turn away from rapprochement with the North. Yoon has abandoned Sunshine Policy and strengthened ties with the US, shown most overtly in his April visit to the Pentagon.[32] Since 2022, the Republic of Korea has stepped up joint military exercises with the United States,[33] covertly sent artillery shells to Ukraine (via the United States to avoid official state policy against sending weapons to an active warzone),[34] and suspended a military agreement with the North designed to deescalate tensions.[35] In response to the ROK's apparent inseparability from US occupation, the DPRK announced in January that it was ending its long-standing policy of peaceful reunification with the ROK.[36] This demonstrates a recognition that a "one country two systems" style reunification with the South is no longer possible, as the North would never accept such a reunification if the US military was still allowed to occupy the peninsula. Reunification is only possible with the end of US military occupation and dismantling of the ROK state.
Nuclear weapons program[edit | edit source]
The DPRK joined the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1985. It withdrew in 1993 according to the terms of the treaty in order to preserve its sovereignty against U.S. aggression.[37]
Since the beginning of the DPRK nuclear tests in 2003, the Bush and Obama regimes respectively lifted some sanctions to facilitate negotiations around DPRK denuclearization, and then reinstated them when the negotiations failed to produce the results desired by the US.[22]
The DPRK detonated its first nuclear bomb on 2006 October 9. The invasions of Iraq and Libya proved this decision correct when those countries fell to NATO occupation after giving up their nuclear programs.[37]
Economy[edit | edit source]
The DPRK has maintained one of the most centralized economies in the world since the 1940s. For several decades, it has followed the Soviet pattern of five-year plans with the ultimate goal of achieving self-sufficiency. DPRK is also one of the most sanctioned countries in the world, and has been subject to sanctions since just after its foundation. The economy is heavily nationalized. Food and housing are extensively subsidized by the state, education and healthcare are free, and the payment of taxes was officially abolished in 1974.[38] The DPRK follows policy of Byungjin, meaning it simultaneously develops its nuclear weapons program and the economy.[39]
A 2020 book published in DPRK summarizes the DPRK's economic line of development as follows: "The DPRK has consistently adhered to the line of building an independent national economy in economic construction. In Juche 42 (1953) it put put forward the basic line of socialist economic construction, developing heavy industry preferentially and ensuring the simultaneous development of light industry and agriculture. True to this line, it laid solid material and technological foundations for an independent national economy. In the 1960s when the hostile forces’ moves of aggression became undisguised, the WPK advanced the line of simultaneously carrying on economic construction and building up defences, thus establishing a socialist industrial state while increasing its defence capabilities."[40]
According to DPRK's constitution, the DPRK regards the steady improvement of the material and cultural standards of the people as "the supreme principle of its activities", and holds that the state "shall provide all the working people with every condition for obtaining food, clothing and housing." Furthermore, the constitution states that DPRK's economy relies on socialist relations of production and on the foundation of an independent national economy, with the means of production owned in some cases by the state and in other cases owned collectively by social cooperative organizations. The eventual goal of the DPRK is to "combine the two forms of property in an organic way", and to gradually transform the means of production owned by cooperative organizations into the property of the people as a whole (i.e., into state property), based on the voluntary will of the social cooperative organizations' members. While the means of production are under the ownership of the working class in the form of state property and social cooperative organizations, property that is owned and consumed by individual citizens is also legally protected, including products of individual sideline activities such as products from kitchen gardens and income from other legal economic activities. This type of personal property is protected by the state and guaranteed by law the right for people to inherit it.[41]
Socialist economic management[edit | edit source]
Throughout DPRK's development, systems of socialist economic management and methods of work have been developed, adapted to the country's particular needs. Notable among them is the Taean (or Daean) work system, an industrial management system which grew out of the Chongsanri agricultural management system. Each system has been described by north Korean author and politician Kim Byong Sik as implementations of the mass line in production, which were developed in response to DPRK's changing needs as it transitioned away from individualistic, bureaucratic capitalist-style management toward collective socialist-style management in production. As Kim Byong Sik explains, "the Daean work system means, in a word, to embody the mass line in economic control; to get rid of survivals of capitalism in economic management such as bureaucracy, over-centralization and individualism, and to implement the Chongsanri spirit and method, enabling workers to contribute to the maximum in accelerating socialist construction."[9]
Each method is named after a location in which it saw early implementation: Chongsanri refers to Chongsanri Cooperative Farm in Kangso county, South Pyongan province, while the Taean work system is named after Taean Electric Machine Factory.[9]
Kim Il Sung noted that in the DPRK's early development, the factory management system "still retained many capitalist elements" despite being socialist. These lingering capitalist elements in management led to bureaucracy, departmentalism, and individualism hampering the activity and initiative of the workers, as well as led to a lack of cooperative spirit between workshops and to insufficient worker participation in management. Quoted in Kim Byong Sik's Modern Korea, Kim Il Sung described the problem as follows:
It must be admitted that the old system of factory management, though socialist, still retained many capitalist elements. Bureaucracy, departmentalism, and individualism were found in large measure. Superiors shouted commands at their subordinates in a bureaucratic manner instead of going to help them; a spirit of cooperation between workshops was lacking; and among some people there was a tendency toward individualism of the “You attend to your business, I’ll stick to mine!” variety. Therefore, under the old system of work, it was not possible to give full play to the activity and initiative of workers, people busied themselves for nothing, and no sizable achievements were made in production.[9]
Kim Byong Sik adds that in factories administered exclusively by managers, the lingering capitalist elements were the most concentrated. In such factories, workers lacked interest in whether production was going well or not because they did not have sufficient participation in management. The managers who held sole decision-making powers engaged in arbitrary control, subjective discretion, and other bureaucratic methods, and so the workers felt their job was to "work for eight hours, as assigned, and then go home" which gave little room for stimulating their "political, moral and material interest" in their work or giving full play to their creativity and talent. Therefore it was necessary to bring factory management in line with a socialist management system. In contrast with the lingering capitalist style of management, in the Daean work system, the people cooperate with each other and work units help one another in economic management, with the essential purpose of the Daean work system being to enable people to give maximum play to their revolutionary enthusiasm and creative talent, to increase production, and to control and to manage the economy through promoting comradely accommodation and close cooperation among producers and producing units. Kim Byong Sik also notes that the Daean work system, as a socialist management system, is a prototype of communist economic management, stating "it is clear that economic management in a communist society will take the form of collective management by millions of conscious, communist working people."[9]
Special Economic Zones[edit | edit source]
Foreign trade surpassed pre-crisis levels in 2005 and continues to expand. The DPRK has a number of special economic zones (SEZs) and Special Administrative Regions where foreign companies can operate with tax and tariff incentives while DPRK establishments gain access to improved technology.[42][43]
Economic sanctions[edit | edit source]
See also: Economic sanctions#Democratic People's Republic of Korea
The US first imposed sanctions on DPRK during the 1950s.[20] The United States has repeatedly targeted the DPRK with sanctions, citing its nuclear weapons program as their reason.[44] Following the country’s 2006 nuclear test, the US, EU, and others added more stringent sanctions, which have periodically intensified since then. In 2017, sanctions imposed by the UN caused thousands of DPRK workers who had been working abroad to be forced to return to DPRK as well as led to the closure of numerous DPRK companies and joint ventures.[45] Sanctions now target oil imports, and cover most finance and trade, and the country’s key minerals sector.[46] However, 49 countries, including Cuba, Iran, and Syria have violated these sanctions and traded with the DPRK anyways.[47]
According to Foreign Policy in Focus, sanctions on DPRK have "demonstrably failed." FPIF notes that sanctions didn’t deter DPRK from pursuing a nuclear weapons program, nor have they been subsequently responsible for pushing it toward denuclearization, and adds that DPRK has been under sanctions for nearly its entire existence and it doesn’t have a strong international economic presence that can be penalized, and "has been willing to suffer the effects of isolation in order to build what it considers to be a credible deterrence against foreign attack."[48]
Government[edit | edit source]
Central government[edit | edit source]
The highest organ of state power is the Supreme People's Assembly, which is elected for a term of five years. It elects a Speaker and Deputy Speaker to preside over its sessions. While the Supreme People's Assembly is not in session, the Presidium is the highest organ of state power. It consists of a President, Vice-Presidents, and other members.
The Supreme People's Assembly also elects a State Affairs Commission consisting of a Chairman, multiple Vice-Chairmen, and other members and a Cabinet consisting of a Premier, Vice-Premiers, Chairmen, Ministers, and other members. The Premier organizes the work of the cabinet and is the head of government of the DPRK.[49]
Local government[edit | edit source]
Provinces, cities, and counties elect local people's assemblies for a term of four years. The local people's assembly elects a speaker to preside over its sessions and a local people's committee. Local people's assemblies and committees are subordinate to the Supreme People's Assembly and Cabinet.[49]
Administrative divisions[edit | edit source]
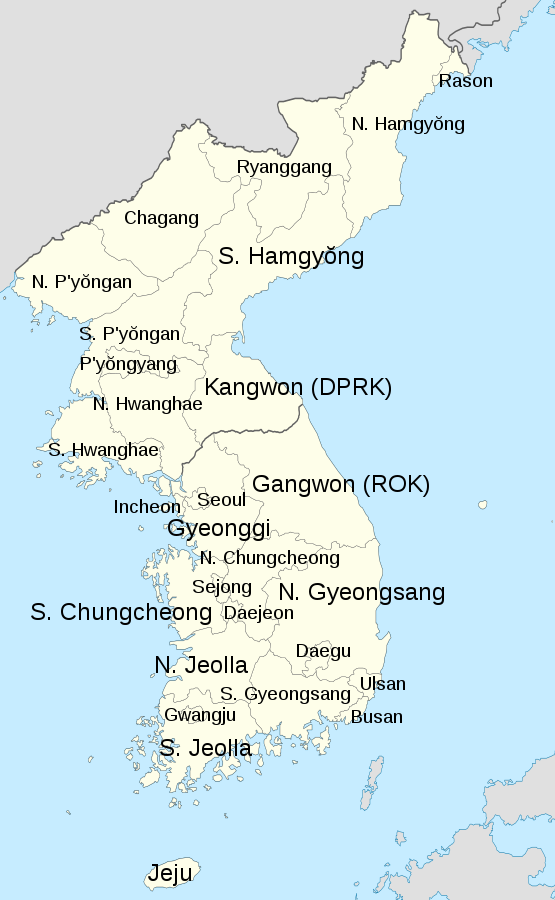
DPRK is divided into nine provinces, the direct-administered capital city, and three special cities.
The nine provinces (Korean: 도; Hanja: 道) of DPRK are Chagang, North Hamgyong, South Hamgyong, North Hwanghae, South Hwanghae, Kangwon, North Pyongan, South Pyongan, and Ryanggang.
Pyongyang is designated as the capital city, or the direct-administered city (Korean: 직할시; Hanja: 直轄市) while three other cities, namely Rason, Nampo, Kaesong, are special cities (Korean: 특별시; Hanja: 特別市).
A 2014 demographic survey of DPRK, conducted as a joint project between DPRK's Central Bureau of Statistics and the United Nations Population Fund, found that the majority of the country's population resides in four contiguous provinces: South Pyongan (17% of population), Pyongyang (14%), South Hamgyong (13%), and North Pyongan (12%). Together, these four contiguous provinces account for over 55% of the country's population. The highest population density area was in the capital city of Pyongyang, while the lowest population density was in Ryanggang. It was also found that more than six out of ten persons reside in urban areas in the country, at 61.2% of the population, while 38.8% of the population lives in rural areas.[50]
DPRK's method of administrative division is similar to that in south Korea, as both are based on the common system in Korea as a whole, having its roots in the mid-Goryo dynasty in the 11th century.[51]
As a result of the division of Korea, three provinces, namely Hwanghae, Gyeonggi, and Kangwon, were split due to being on the line of division. The smaller portions of post-division Hwanghae and Gyeonggi provinces were mostly incorporated into nearby provinces, with the larger part of Hwanghae ending up in DPRK and the larger part of Gyeonggi in south Korea. However, Kangwon was divided roughly in half, and as a result, both DPRK and south Korea have a Kangwon province, romanized as Kangwon in DPRK and Gangwon in the south.
Foreign relations[edit | edit source]
Article 17 of the DPRK's constitution states that independence, peace, and friendship are the basic ideals of the foreign relations of the DPRK. Additionally, the constitution holds that the state "shall establish diplomatic as well as political, economic and cultural relations with all friendly countries, on the principles of complete equality, independence, mutual respect, non-interference in each other’s affairs and mutual benefit" and "promote unity with people all over the world who defend their independence, and resolutely support and encourage the struggles of all people who oppose all forms of aggression and interference and fight for their countries’ independence and national and class emancipation."[41]
DPRK does not reject foreign exchange, nor reject foreign knowledge, nor adhere to an isolationist policy, nor does it aim to promote national chauvinism.[52] Rather, DPRK upholds proletarian internationalism, national liberation, and anti-imperialism, and aims for international exchanges based in mutual respect. Speaking on DPRK's attitude toward international exchange and the study and adoption of foreign knowledge, Kim Il Sung clarifies that it is not DPRK's position to reject foreign things, but rather to adopt them critically and non-dogmatically, with Korea's sovereignty and particular conditions in mind: "What we are opposing is the nihilistic attitude of looking down upon our nation, while looking up to foreign countries, as well as the dogmatist attitude of uncritically swallowing up foreign things in disregard of the actual conditions of our country."[53]
Kim Il-sung has said that completing the Korean revolution is the internationalist duty of the Korean people, and explained that, in the modern conditions where imperialism and borders still exist (as opposed to a stateless, communist future), and in conditions where Korea currently remains divided and antagonized by imperialism, DPRK's socialist patriotism is "indispensable for us who have to drive out the US imperialist aggressors and accomplish the national-liberation revolution", and that "the Korean revolution is the internationalist duty devolving on the Korean people. For this reason, only when the Korean people satisfactorily carry out the Korean revolution as their first priority, will they be performing their internationalist duty faithfully."[54]
Opposing chauvinism and promoting proletarian internationalism, Kim Il-sung has emphasized that care should be taken to prevent the growth of national chauvinism when promoting socialist patriotism, explaining that DPRK should not pursue a chauvinist policy or national isolation, and that Koreans should be educated in the spirit of internationalism "to fight in close unity with many other peoples of the world" against imperialism as well as against both right and left opportunism.[55] While in the present day, defense of national sovereignty and socialist patriotism holds importance in DPRK, Kim Il-sung notes: "Needless to say, it will be another matter after imperialism is completely overthrown and socialism and communism emerge victorious throughout the world in the future, and the boundaries of nations vanish and states cease to exist."[54]
Support for anti-imperialist liberation[edit | edit source]

The DPRK's revolutionary government has supported other liberation struggles around the world. The support has at times included material support such as providing weapons and military training to various movements, hosting delegations representing various liberation struggles, as well as gestures and expressions of solidarity such as in speeches at the UN General Assembly and support for liberation movements written about in official DPRK publications.
The DPRK trained two thousand guerrilla fighters from twenty-five countries from the mid-1960s to the late 1980s, including members of the Japanese Red Army, Palestinian Liberation Organization, and the Official Irish Republican Army. The training in these camps lasted from six to eighteen months, and during that time, the DPRK military taught foreign revolutionaries Korean martial arts. The foreign revolutionaries were also put through training such as running through the mountains at night while carrying one hundred pound sandbags.[56]
DPRK has supported liberation struggles in Africa both materially and through expressions of solidarity.[57] President Kim Il Sung was a staunch opponent of both South African and Zionist apartheid.[58]
When Kwame Nkrumah's government in Ghana was overthrown in a CIA-backed coup in 1966, Kim Il-sung sent a letter to Nkrumah shortly afterword, stating, "We are especially enraged at the reactionary coup d’état which took place in Ghana at the instigation of the imperialists [...] The imperialists engineer similar plots and perpetrate subversive activities against progressive countries everywhere. We resolutely condemn the machinations of the imperialists against the just cause of the peoples for national liberation, independence and progress. We express our unreserved support to your Excellency’s determination to fight for the freedom of Ghana on your return to Africa."[59]
On March 31, 1970, nine members of the Japanese Red Army (JRA) hijacked a Japan Air Lines plane and landed it in Pyongyang. These nine members eventually settled in a housing complex on the outskirts of Pyongyang and the DPRK government used the JRA connection to send money and arms to various Third World-oriented organizations, such as the PLO, the Red Army Faction, and the Italian Red Brigades.[56]
During the 1980s, the DPRK sent free weapons to Cuba.[60]
DPRK Minister of Foreign Affairs Ri Yong Ho's 2017 UN General Assembly statements of solidarity with Cuba, Venezuela, and Syria and condemning Israel:
My delegation takes this opportunity to extend strong support to and solidarity with the Cuban government and people who are fighting to defend national sovereignty and realize international justice against the high-handedness, arbitrariness and unilateral embargo of the U.S.
We also express strong support to and solidarity with the government and people of Venezuela who are fighting to defend the national sovereignty and the cause of socialism.
The unjust and contemptible acts such as turning a blind eye to the heinous acts of Israel while condemning in every manner only the Syrian government fighting to protect its national sovereignty and security should not be tolerated any longer.
The DPRK government will certainly defend peace and security of the country with its powerful nuclear deterrence and also contribute to safeguarding world peace and security.[4]
The DPRK representative Kim Song at the 2021 UN General Assembly spoke on the DPRK delegation extending "its full support and encouragement to the Cuban government and people who continue to move forward holding aloft the banner of socialism in the face of the U.S. moves to impose illegal sanctions and blockade and to undermine Cuba from within" and expressed "constant support to and solidarity with the independent countries including Syria and Palestine and their peoples in their unyielding struggle to defend the national dignity, sovereignty and territorial integrity."[5]
Support for Black liberation in the United States[edit | edit source]

Kim Il-sung praised the Black Panther Party (BPP) for their "just struggle to abolish the cursed system of racial discrimination of the US imperialists". The Black Panther Party sent a delegation to the DPRK to meet with President Kim Il Sung and other officials to exchange ideas.[58] Numerous examples of writings in support of the DPRK and against U.S. imperialism can be found in BPP publications, while many articles in support of the BPP and denouncing U.S. imperialism and systemic racism can be found in DPRK publications.
In addition to specific support of the BPP, it is common to find DPRK publications calling out and denouncing the United States as racist, and voicing support for Black people and other racial minorities of the U.S. in their struggle against it. For example, DPRK state media commented on the shooting of Trayvon Martin, stating: "The U.S. true colors as a kingdom of racial discrimination was fully revealed by last year’s case that the Florida Court gave a verdict of not guilty to a white policeman who shot to death an innocent Black boy." DPRK has also made commentary on the case of George Floyd, emphasizing the hypocrisy for the US to preach about human rights while perpetrating racial oppression against its own citizens. An official from Central Committee stated via the state newspaper Rodong Sinmun: "Demonstrators enraged by the extreme racists throng even to the White House. This is the reality in the U.S. today" and further stated "American liberalism and democracy put the cap of leftist on the demonstrators and threaten to unleash even dogs for suppression."[61]
DPRK-US relations[edit | edit source]
The core of US policy toward DPRK has been summarized in a 2008 book from DPRK as follows: "The US attempt to crush the DPRK and realize domination over the whole Korean peninsula constitutes the core of its policy towards the DPRK and the key to its building of a foundation on which to achieve world hegemony."[62]
In a 2021 speech to the United Nations General Assembly, the DPRK's representative Kim Song stated, "In the course of the DPRK-U.S. showdown spanning over half a century, we have been very much accustomed to the U.S. military threats, and we know well how to deal with the U.S., the most hostile country. We have learned the mode of existence to cope with the U.S. hostile policy and accumulated rich experience."[5] The representative further characterized the DPRK-US relationship in the following way:
From the first day of the foundation of the DPRK, the U.S. has not recognized our sovereignty, treating us as an enemy state, and openly showed its hostility towards the socialist system chosen by our people. The U.S. designated the DPRK as a "communist state" and a "state of non-market economy", and it completely blocked, both institutionally and legislatively, the establishment of relations between the DPRK and the U.S. in the fields of politics, economy and trade, under the unreasonable pretexts of "human rights issue", "proliferation of the WMD", "sponsoring of terrorism", "oppression of religion", "money laundering" and etc.
If it is not a hostile policy, should it be called a "friendly policy"?
The U.S. hostile policy against the DPRK finds its clearest expression in its military threats against us. Not a single foreign troop, not a single foreign military base exists in the territory of the DPRK. But in south Korea, almost 30,000 U.S. troops are stationing at numerous military bases, maintaining a war posture to take military action against the DPRK at any moment. The DPRK has no record of having conducted a military exercise even a single time around the U.S., but the U.S. has annually staged all sorts of war drills on and around the Korean peninsula and in the Korean waters for the last several decades, by mobilizing army, naval and air forces across the world including the U.S. troops in south Korea, and it has threatened us through military demonstrations of intimidating nature while deploying numerous armaments to south Korea from time to time.[5]
The representative also noted that the possible outbreak of a new war on the Korean peninsula is contained "not because of the U.S.’s mercy on the DPRK" but because the DPRK "is growing reliable deterrent that can control the hostile forces in their attempts for military invasion".[5]
Kim Yo Jong, First Vice Department Director of Central Committee of Workers’ Party of Korea, in response to being called a “rogue state” by the US Defense Secretary, has been quoted by Nodutdol as saying, "the sufferings imposed upon us by the U.S. have now turned into the hatred for the U.S., and this hatred would drive us to break through the blockade of persistent sanctions led by the U.S. and to live our own way by our own efforts."[22]
The 2018 book Origin of the Korean Question published in DPRK analyzes the USA's long history of imperialist aggression toward Korea, even prior to the division of the Korean nation into north and south. The book explains: "From the first days of its emergence from the sea of blood of American Indians, the US waged ceaseless wars of conquest with the ambition of territorial expansion. [...] Having accomplished transition from capitalism to imperialism by achieving forced initial accumulation of capital through aggression and plunder, in the 19th century the US and European powers made their colony of extensive regions in Africa, America, Southeast Asia and on the shores of the Pacific. Not satisfied with it, they plunged into a competition for seizing before anyone else Korea, Qing China and Japan that had been still outside of any other country's influence. [...] The US, a latecomer in this competition, tried to contain the intervention of other powers in the Far East; its primary efforts in the Far East were directed to Korea." The authors further explain that towards the end of the Second World War, the US began to advocate a "new order of the US-led world," backpedaling on its commitments to the anti-fascist Allied Powers, and that since then, it has openly pursued policy of stamping out socialism on the globe and seeking to achieve world supremacy. The authors note that the Asia-Pacific area has since become the center of global trade and that the US has a "huge economic dependence" on it. Due to the growing influence of Asian economies, the US is "hell bent on winning control over Asia", and has determined that it must dominate the Korean peninsula, a regional strategic point politically, militarily and economically, in order to complete its goal of hegemonic power. For this reason, the US regards it as a major goal to stamp out the DPRK and dominate the Korean peninsula as a whole, setting the DPRK as a major target in the "axis of evil", and "resorting to every means to internationalize the Korean question", treating the issue arbitrarily in international arenas such as the UN, in collaboration with its satellite countries.[63]
Describing the history of the USA's imperialist designs on Korea, which continues to this day in modern Korea-US relations, the book's authors note that the USA has had its eyes on Korea since the 1800s, due to the importance of Korea's strategic position, the Korean peninsula being good springboard for advance into Asia. Additionally, the authors explain that the USA was compelled toward imperialist expansion by the fact that its industry demanded overseas markets for selling its products, and that the USA saw Korea as a suitable market for its commodities. Finally, Korea was seen as a key location where ships from the USA could refuel on their way to China. Several incidents, such as the criminal intrusion of the USA's ship General Sherman into the Taedong river in 1866, which, demanding "trade" and refusing to leave, perpetrated theft, violence, and kidnapping and killing of Koreans until Pyongyang citizens finally were able to set the boat on fire and sink it, was followed by other incidents with USA's naval vessels continuing to intrude into Korean territory as well as conducting illegal gold prospecting in Korea.[63]
Eventually, after a Korea-US treaty was made in 1882, the US won many privileges including the extraterritorial right and "most favoured nation" treatment. Thus the US moved to reduce Korea to its commodity market, a source of precious metals and other raw materials, and an object of capital investment. The US capitalists brought surplus goods like old firearms, petroleum, tobacco and drops to sell them at exorbitant prices, meanwhile purchasing Korea's precious metals including gold and silver at low prices. Over time, Christian missionaries promoted pro-US sentiment and sent "bourgeois sycophants" and "traitors to the nation" such as future dictator Syngman Rhee to the US to study, "at the expense of part of the colossal wealth obtained by bleeding the Korean people white."[63]
By 1905, in a meeting referred to as the Taft-Katsura agreement, the USA's secretary of war and soon-to-be president, William Howard Taft, and Japan's prime minister Katsura Taro had a confidential discussion in which they expressed their respective views on control over nations in the Pacific, with Japan emphasizing that it had no designs on the Philippines, and the USA expressing that it would be "logical" for Japan to assert control over Korea. The USA's secretary of war and future president expressed his view that "the establishment by Japan of a suzerainty over Corea to the extent of requiring that Corea enter into no foreign treaties without the consent of Japan" would directly contribute to "permanent peace" in East Asia.[64][65] The authors of Origin of the Korean Question point out that in the Taft-Katsura Agreement, the US recognized Japan's protection of Korea and, in return, Japan promised not to interfere with the US supremacy over the Philippines. Placing this agreement in the context of the USA's series of aggressions and intrusions into Korea, its imperialistic trade relations, its promotion of pro-US bourgeois ideology through Christian missionaries, and its disregard for agreements made in the 1882 Korea-US treaty, it demonstrates the USA's longstanding record of aggressive, imperialist self-interest in its dealings with Korea as a key country for the US to subjugate on its path to imperialist world hegemony. In line with this history, the authors evaluate that the US of the present day spreads misinformation about the DPRK and misuses the UN and other international apparatuses to "isolate and suffocate the recalcitrant country that aspires after independence [...] to bring the Korean people to their knees by internationalizing the Korean question at all costs in pursuit of its world strategy."[63]
DPRK-ROK relations[edit | edit source]
Among the political leadership, bourgeoisie, and working people of South Korea, there is variation in attitudes toward DPRK. For the majority of South Korea's history, its leaders have been far-right anti-communist military dictators as well as corrupt oligarchs. A handful of ROK presidents are notable for their "Sunshine Policy" stance toward DPRK, a stance of reconciliation. Most notably associated with this attitude are Kim Dae-jung and Roh Moo-hyun. The more recent president, Moon Jae-in, has been described as having revived certain elements of the Sunshine Policy era. However, his presidency was followed by the right-wing Yoon Suk-yeol who took office in 2022, and has a much more aggressive pro-US stance.
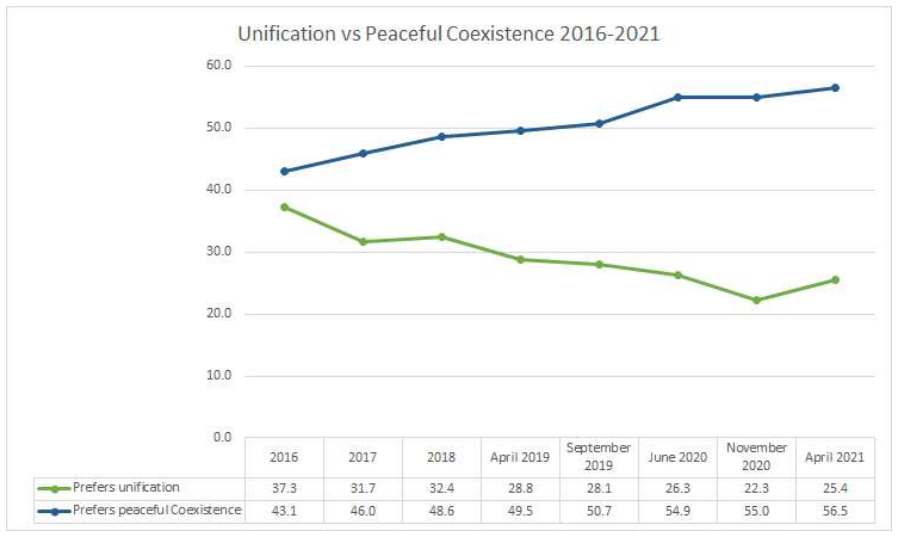
In regard to public opinion in South Korea, the 2021 KINU Unification Survey[66] reported that positive responses to the question “If North Korea open the borders to each other and cooperate on political and economic matters, such a state can be considered unification even if the two Koreas are not one country” have reached 63.2%. In addition, the survey found there is a growing tendency to be indifferent to DPRK and to "give up expectations" rather than a negative view for the future of inter-Korean relations. The IMF generation and millennial generations clearly show a high level of indifference toward the DPRK compared to the older generations. (IMF generation 68.3%, Millennial generation 74.1%).
According to the survey, the gap between ‘Prefers unification’ and ‘Prefers peaceful coexistence’ is very huge in the millennial generation. In the 2021 survey, the percentage of ‘Prefers peaceful coexistence’ was 71.4% and the percentage of ‘Prefers unification’ was 12.4%, showing a difference of 59%P. The summary of the results suggests that "the trend that younger generations view North Korea as the subject of coexistence and not unification will become stronger in the future." The younger generation tends to loosely favor confederations. The Millennial generation most actively preferred confederations and has the lowest percentage of preference for unitary state system at only 6.5%. The preference for unification in the unitary state system, which is the traditional unification view, was relatively high among the war generation (17.8%). However, more` than half of the War generation (52.1%) preferred confederations.
67.7% of survey respondents agreed to the statement “The agreements between the two Koreas should be continued regardless of the government's change” and 90.3% of the respondents said ‘necessary’ to the question “Do you think that U.S. Armed Forces in Korea is needed now?” 69% of respondents showed a positive attitude toward the question “Do you think U.S. President Biden should hold a summit with North Korean leader Kim Jong-un?” The survey also found that people under 30 are apparently more vulnerable to fake news about DPRK than those over 40. Income level, residence area, political ideology, and party identification also seem to influence the reception of fake news on DPRK and unification issues.[66]
The US consistently interferes in inter-Korean affairs and polices Korean reunification efforts by citing sanctions. According to Nodutdol, only a few months after the Korean leaders signed the Panmunjeom Declaration, the US-led UN Command which oversees the DMZ, blocked development of the inter-Korean railway. In January 2020, South Korean President Moon Jae-In expressed interest in developing tourism to People's Korea, but the US ambassador Harry Harris blocked this effort. Harris claimed that "independent" tourism plans would have to undergo US consultation. He emphasized that the items inside South Korean tourists' luggage could violate sanctions, demonstrating the extent of US interference.[22]
During Moon Jae-in's presidency, a number of inter-Korean activities took place, such as the 2018 inter-Korean summit. In the 2018 Winter Olympics, the teams representing DPRK and south Korea entered the Opening Ceremony marching under the Korean Unification Flag, while in women's ice hockey there was a single united Korean team. A music concert titled "Spring is Coming" was also held in 2018, in which a number of south Korean artists performed alongside People's Korean artists in Pyongyang, DPRK.
Pro-DPRK voices in South Korea are stifled by the existence of the National Security Law. The National Security Law is a south Korean law enforced since 1948 following events such as the Jeju Uprising where Koreans opposed the division of the country into north and south. The National Security Law has the avowed purpose "to secure the security of the State and the subsistence and freedom of nationals, by regulating any anticipated activities compromising the safety of the State." Behaviors or speeches in favor of the DPRK or communism can be punished by the National Security Law. In an article from The Diplomat, it was referred to as a "Cold War holdover" that "allows the government to selectively prosecute anyone who 'praises, incites or propagates the activities of an anti-government organization'" which the article describes as "a deliberately vague clause that broadly implies the North Korean state and its sympathizers." The article continues, explaining "Under Article 7, individuals have been prosecuted and imprisoned for merely possessing North Korean publications or satirically tweeting North Korean propaganda. In recent years this clause has been harshly criticized by Amnesty International and Human Rights Watch, who claim the government abuses the law to repress dissenting voices."[67]
According to the People's Democracy Party (PDP), a revolutionary workers' party in south Korea, the continued U.S. military occupation of south Korea is the primary barrier to peaceful reunification of the Korean peninsula.[68]
On August 13, 2022, thousands of south Korean unionists and their progressive supporters rallied in downtown Seoul to protest against joint US-south Korea war game exercises. In a video uploaded by Press TV, Oh Eun-Jung of the National Teachers Union was quoted as saying "The threat of nuclear war is growing on the Korean peninsula, conservative forces of Yoon Suk-yeol in south Korea and those in the U.S. are frantically conducting aggressive war drills in the sky, the land, and the sea, and are about to start large-scale military exercises, aimed at the invasion of North Korea. We must stamp out this behavior of anti-reunification forces." In the same video, construction worker Lee Seung-Woo stated, "We not only oppose the war exercises, but we want the U.S. Forces Korea, which is actually controlling and interfering with the Korean peninsula to leave this land. We believe that only then will the eighty million Koreans from both north and south be able to live peacefully."[69]

Unconverted long-term prisoners[edit | edit source]
See main article: Unconverted long-term prisoners
Unconverted long-term prisoners is a term which refers to political prisoners who have been imprisoned in south Korea, generally on charges of "anti-state" activities or views in support of communism or DPRK. The term commonly refers to people who were mostly arrested from the 1950s to 1980s and imprisoned and tortured for decades and who refused to sign a "conversion" statement renouncing communist or left-wing ideology, which had been a condition for their release. It can also refer to those who ultimately did sign the so-called "conversion" statement but do not consider it a true conversion as it was extracted under torture.[70][71]
In the 1990s, some of the elderly prisoners began being released, and began living in the south under difficult economic, legal, and social conditions. Many sought to be repatriated to DPRK, and 63 of them were allowed to do so in the year 2000. Many who participated in the repatriation in 2000 and many of those who remained in south Korea made their decisions based on their impression at the time that there was going to be more freedom of movement between ROK and DPRK thereafter. However, further repatriations have not taken place, despite a continued movement calling for it. Meanwhile, those who remained in the south have had to live under strict surveillance by the south Korean state.[70][71]
Further reading[edit | edit source]
External links[edit | edit source]
References[edit | edit source]
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 UNData (2021). DPRK – UNData
- ↑ Articles 1 and 3 of the Constitution of the DPRK
- ↑ Thomas Stock (2019). North Korea’s Marxism-Leninism: fraternal criticisms and the development of North Korean ideology in the 1960s. doi:10.1215/21581665-7258081 [HUB] [LG]
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 4.2 Ri Yong Ho, DPRK Minister for Foreign Affairs. "Statement by H.E. Mr. RI YONG HO, Minister for Foreign Affairs of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea at the General Debate of the 72 Session of the United Nations General Assembly." New York, 23rd September 2017. gadebate.un.org. Archived 2022-08-28.
- ↑ Jump up to: 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Kim Song. "Statement by Head of the DPRK Delegation H.E. Mr. KIM SONG, Permanent Representative of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea to the United Nations At the General Debate of the 76th session of the United Nations General Assembly." New York, 27 September 2021. UNmeetings.org. Archived 2022-08-28.
- ↑ https://gowans.blog/2007/03/03/understanding-north-korea/
- ↑ Bruce Cumings (2005). Korea’s place in the sun: a modern history. W.W. Norton & Company; p. 404.
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.0 8.1 8.2 Stephen Gowans (2018). Patriots, Traitors and Empires: The Story of Korea’s Struggle for Freedom: 'The Patriot State' (pp. 88–93). [PDF] Montreal: Baraka Books. ISBN 9781771861427 [LG]
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.00 9.01 9.02 9.03 9.04 9.05 9.06 9.07 9.08 9.09 9.10 9.11 9.12 9.13 9.14 Kim Byong Sik. "Modern Korea: The Socialist North, Revolutionary Perspectives in the South, and Unification." International Publishers, 1970.
- ↑ "북조선림시인민위원회." ("North Korea Provisional People's Committee.") 조선의 오늘, 주체109(2020)년 2월 8일. DPRK Today, February 8, Juche 109 (2020). Archived 2023-10-05.
- ↑ “북조선임시인민위원회(北朝鮮臨時人民委員會).” Encyclopedia of Korean Culture. Archived 2023-10-05.
- ↑ Kim Han Gil. "Modern History of Korea." Foreign Languages Publishing House. Pyongyang, Korea, 1979.
- ↑ “[헌법으로 보는 북한-서문] 사회 전 분야의 방향이 제시된 20개조 정강.” ("[North Korea as seen through the Constitution - Preface] A 20-point platform that sets out the direction for all areas of society.") 자주시보, 2022-02-25. Archived 2022-07-07.
- ↑ Jump up to: 14.0 14.1 “[북 현대사] 북조선림시인민위원회와 토지개혁 (4).” ("[North Korea Modern History] North Korea Provisional People’s Committee and Land Reform (4)") 통일시대. April 6, 2022. Archived 2023-10-04.
- ↑ Flenniken, Lauren. “The Northwest Youth League.” Jejuweekly.com. 2011-04-10. Archived 2023-10-05.
- ↑ "March 18, 1948 Central Intelligence Agency, ORE 15/48, 'The Current Situation in Korea'". Wilson Center Digital Archive. Archived from the original.
- ↑ Stephen Gowans (2018). Patriots, Traitors and Empires: The Story of Korea’s Struggle for Freedom: 'The Political Partition of Korea' (p. 114). [PDF] Montreal: Baraka Books. ISBN 9781771861427 [LG]
- ↑ “439 Civilians Confirmed Dead in Yeosu-Suncheon Uprising of 1948.” Jan. 8, 2009. Hankyoreh. Archived 2023-06-14.
- ↑ Talmadge, Eric. “64 Years after Korean War, North Still Digging up Bombs.” AP NEWS. Associated Press. April 22, 2021. Archived 2023-03-13.
- ↑ Jump up to: 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 Gary Clyde Hufbauer (PIIE), Jeffrey J. Schott (PIIE), Kimberly Ann Elliott (PIIE) and Barbara Oegg (PIIE). “US and UN v. North Korea: Case 50-1 and 93-1.” 2016. Peterson Institute for International Economics. May 1, 2008. Archived 2022-09-09.
- ↑ Kim Han Gil. "Modern History of Korea." Foreign Languages Publishing House, Pyongyang, Korea, 1979.
- ↑ Jump up to: 22.0 22.1 22.2 22.3 22.4 22.5 "제국의 제재 - Sanctions of Empire." Nodutdol. October 20, 2020. PDF. Archive.
- ↑ “Democratic People’s Republic of Korea.” United States Department of State.
- ↑ Kim, Crystal. “North Koreans Mourn Death of Leader Kim Jong Il.” Liberation News, 22 Dec. 2011, Accessed 10 Apr. 2023. Archived 2023-04-10.
- ↑ “North Korean History 1980s & 1990s | KTG® Tours.” North-Korea-Travel.com.
- ↑ "The Evolution of DPRK’s Socialist Lifestyle." Explore DPRK. Archived 1012-09-28.
- ↑ Jump up to: 27.0 27.1 Ri Jong Chol. "Songun Politics in Korea." Foreign Languages Publishing House. Pyongyang, Korea, Juche 101 (2012). [PDF]
- ↑ "[북현대사] 선군정치의 시작." ("[North Modern History] The beginning of Songun politics.") 한반도정론: 북 바로알기. 통일시대. 2023-02-27. Archived 2023-09-27.
- ↑ "[북현대사] 고난의 행군과 강계정신" ("[North Modern History] Arduous March and Ganggye Spirit"), 한반도정론: 북 바로알기. 통일시대. 2023-02-18. Archived 2023-09-27.
- ↑ "Man's Destiny and Juche Idea." Foreign Languages Publishing House. Pyongyang, Korea, Juche 101 (2012).
- ↑ "[북현대사] 36년 만에 열린 조선로동당 제7차 대회" ("[North Modern History] The 7th Congress of the Workers' Party of Korea held after 36 years"). 한반도정론: 북 바로알기. 통일시대. 2023-05-06. Archived 2023-09-28.
- ↑ Jim Garamone (2023-04-27). "South Korean President Yoon Visits Pentagon, Discusses Deterrence" U.S. Department of Defense. Retrieved 2024-3-3.
- ↑ Hyonhee Shin (2023-01-31). "Defence chiefs of U.S., S.Korea vow to step up drills to counter North" Reuters. Retrieved 2024-3-3.
- ↑ Lee Bon-young, Kwon Hyuk-chul (2023-12-06). "WaPo: Seoul supplied more shells to Ukraine than all of Europe" Hankyoreh. Retrieved 2024-3-3.
- ↑ Jean Mackenzie (2023-11-22). "North Korea spy satellite: South partially suspends military deal after launch" BBC. Retrieved 2024-3-3.
- ↑ Justin McCurry (2024-01-15). "Unification with South Korea no longer possible, says Kim Jong-un" The Guardian. Retrieved 2024-3-3.
- ↑ Jump up to: 37.0 37.1 Stephen Gowans (2018). Patriots, Traitors and Empires: The Story of Korea’s Struggle for Freedom: 'Byungjin' (pp. 208–214). [PDF] Montreal: Baraka Books. ISBN 9781771861427 [LG]
- ↑ Zak Brown (2023-11-18). "Towards a concrete analysis of the DPRK" Anti-Imperialism.org. Archived from the original on 2020-01-18. Retrieved 2023-03-12.
- ↑ Ankit Panda. "Is North Korea’s ‘Byungjin Line’ on the US-China Strategic Agenda?" The Diplomat. Archived from the original on 2022-03-21. Retrieved 2022-04-24.
- ↑ "DPRK Photobook." Foreign Languages Publishing House, Printing Plant of Foreign Languages Publishing House, October Juche 109 (2020).
- ↑ Jump up to: 41.0 41.1 "Socialist Constitution of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (2019)." Wikisource. [PDF] on manoa.hawaii.edu.
- ↑ "Special Economic Zones in the DPRK".
- ↑ "North Korea’s Special Economic Zones: Plans vs. Progress".
- ↑ "US Reps Pass "Harshest Sanctions Ever" Against North Korea" (2017-10-25). TeleSur. Retrieved 2022-04-24.
- ↑ “North Korean Workers Leave China because of UN Sanctions.” Asianews.it. 2017. Archived 2022-09-09.
- ↑ Galant, Michael. “CEPR Sanctions Watch, May-June 2022” Center for Economic and Policy Research. July 8, 2022. Archived 2022-09-07
- ↑ Rishi Iyengar (2017-12-06). "Report: 49 countries have been busting sanctions on North Korea" CNN. Archived from the original on 2021-05-08. Retrieved 2022-04-24.
- ↑ Feffer, John. 2021. “The Problem of Sanctions against North Korea.” Foreign Policy in Focus. November 22, 2021. Archived 2022-09-09.
- ↑ Jump up to: 49.0 49.1 12th Supreme People's Assembly (2016). Socialist Constitution of the Democratic People's Republic of Korea: 'State Organs'.
- ↑ Central Bureau of Statistics, Pyongyang and United Nations Population Fund. "Democratic People's Republic of Korea Socio-Economic, Demographic and Health Survey, 2014." December, Juche 104 (2015).
- ↑ DPRK Explained. “DPRK Provinces EXPLAINED - Part One | North Korea’s Provinces.” YouTube Video.
- ↑ “In educating the working people in socialist patriotism, care should be taken to prevent the growth of tendencies to national chauvinism and restorationism. One may be apt to head for chauvinism on the plea of building an independent national economy by one’s own efforts and promoting national pride. If we steer in the direction of chauvinism as Regent Taewongun pursued a policy of national isolation, we will come to reject international exchange and advanced science and technology from other countries and, accordingly, hinder the development of our country.”
Kim Il Sung. Collected Works Volume 17: 'On Further Developing the Chollima Workteam Movement' (p. 276). [PDF] - ↑ Kim Il Sung. "On Improving Education in Universities." April 18, 1963. Collected Works, Volume 17.
- ↑ Jump up to: 54.0 54.1 Kim Il Sung. "Our People's Army Is an Army of the Working Class, An Army of the Revolution; Class and Political Education Should Be Continuously Strengthened." February 8, 1963. Kim Il Sung Collected Works, Volume 17. Archived 2023-04-03.
- ↑ Kim Il Sung. "On Strengthening the Work of Factory Party Committees And Further Developing the Chollima Workteam Movement." Collected Works Volume 17. May 15, 1963. Archived 2023-04-03.
- ↑ Jump up to: 56.0 56.1 “Juche in the United States: The Black Panther Party’s Relations with North Korea, 1969-1971.” 2015. The Asia-Pacific Journal: Japan Focus. Archived 2023-03-25.
- ↑ President Kim Il Sung’s Immortal Contributions to African Liberation APRIL 17, 2017 by Internationalist 360º on libya360.wordpress.com
- ↑ Jump up to: 58.0 58.1 “Thread by @Uhusofree: ‘a Quick Thread on the DPRK and African and Diaspora Liberation Movements. I Hope It Reaches Someone Who Didn’t Know Before. President Kim Il […].’” Threadreaderapp.com. Thread Reader. Archived 2023-03-25.
- ↑ Nkrumah, Kwame. Dark Days in Ghana. "Appendix." 1968.
- ↑ David Iocanangelo (2013-08-14). Fidel Castro Says North Korea Sent Cuba Free Weapons During Cold War Latin Times. Archived from the original on 2020-01-18.
- ↑ “North Korea and the Black Civil Rights Movement.” Young Pioneer Tours. December 23, 2020. Archived 2022-11-29.
- ↑ "The United States: 'War Against Terrorism'." Foreign Languages Publishing House, Pyongyang, Korea. Juche 97 (2008).
- ↑ Jump up to: 63.0 63.1 63.2 63.3 "Origin of the Korean Question." Foreign Languages Publishing House, Pyongyang, Juche 107 (2018).
- ↑ "The Taft-Katsura Agreed Memorandum, July 29, 1905." ICAS Historical Document, Institute for Corean-American Studies. PDF of document. Archived 2023-08-29.
- ↑ "Korea: A Legal History: Taft-Katsura Agreed Memorandum." Korean Legal Studies. Columbia.edu. Archived 2023-08-29.
- ↑ Jump up to: 66.0 66.1 66.2 Dr. Sang Sin Lee, et. al. "KINU Unification Survey 2021: Executive Summary." July, 2021. Korea Institute for National Unification.
- ↑ Meredith Shaw and Joseph Yi. (2022-03-15). "Will Yoon Suk-yeol Finally Reform South Korea’s National Security Law?" The Diplomat.
- ↑ People's Democracy Party and Liberation School. “70 Years Too Long: The Struggle to End the Korean War – Liberation School.” Liberation School – Revolutionary Marxism for a New Generation of Fighters, 25 June 2020. Archived.
- ↑ Frank Smith. “‘South Korean Unionists Protest US-South Korea War Games.’” PressTV News. August 13, 2022. Archived 2022-08-28.
- ↑ Jump up to: 70.0 70.1 "Still fighting for Korea’s liberation: An interview with Ahn Hak-sop" Liberation School, June 27, 2023. Archived 2024-02-27.
- ↑ Jump up to: 71.0 71.1 Kim Dong-won. Repatriation (2003). Documentary.


